Device Configuration 5 - 67
8. Set the following DNS Servers IPv6 configuration data when using IPv6:
9. Select OK to save the changes made to the DNS configuration. Select Reset to revert to the last saved configuration.
5.2.6.2 ARP
Profile Network Configuration
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol for mapping an IP address to a hardware MAC address recognized on the
network. ARP provides protocol rules for making this correlation and providing address conversion in both directions.
When an incoming packet destined for a host arrives, the gateway uses ARP to find a physical host or MAC address that
matches the IP address. ARP looks in its ARP cache and, if it finds the address, provides it so the packet can be converted to
the right packet length and format and sent to the destination. If no entry is found for the IP address, ARP broadcasts a request
packet in a special format to all the machines on the LAN to see if one machine knows that it has that IP address associated
with it. A machine that recognizes the IP address as its own returns a reply. ARP updates the ARP cache for future reference,
and then sends the packet to the MAC address that replied.
To define an ARP supported configuration:
1. Select the Configuration tab from the Web UI.
2. Select Devices.
3. Select System Profile from the options on left-hand side of the UI.
4. Expand the Network menu and select ARP.
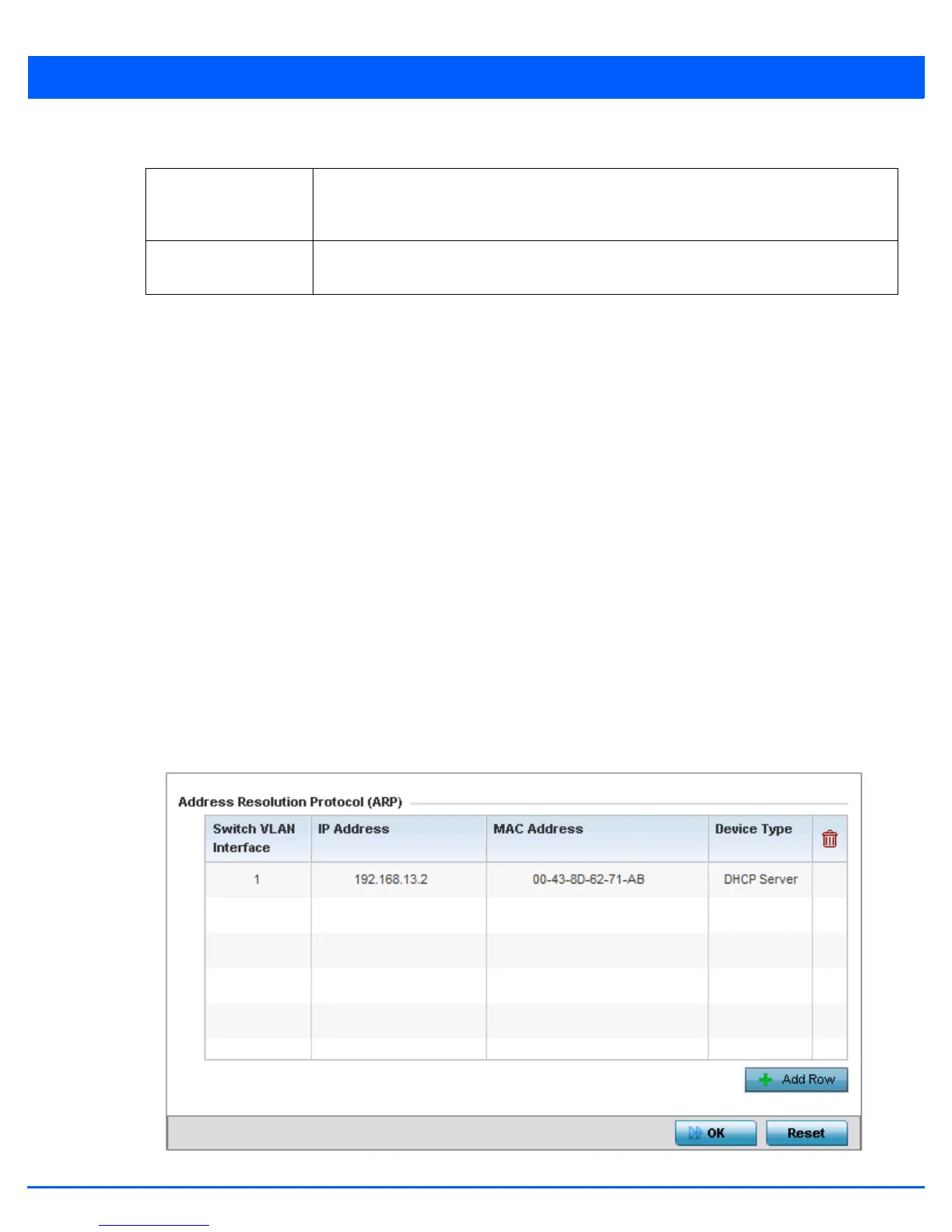
5. Select + Add Row from the lower right-hand side of the screen to populate the ARP table with rows used to define ARP
network address information.
Figure 5-39 Network - ARP screen
IPv6 DNS Name
Server
Provide the default domain name used to resolve IPv6 DNS names. When an IPv6 host is
configured with the address of a DNS server, the host sends DNS name queries to the server
for resolution. A maximum of three entries are permitted.
IPv6 DNS Server
Forward
Select the check box to enable IPv6 DNS domain names to be converted into numerical IP
destination addresses. The setting is disabled by default.

 Loading...
Loading...











