Device Configuration 5 - 267
10. Select OK to save the changes and overrides made to the DNS configuration. Select Reset to revert to the last saved
configuration.
5.4.5.4.2 Overriding an ARP Configuration
Overriding the Network Configuration
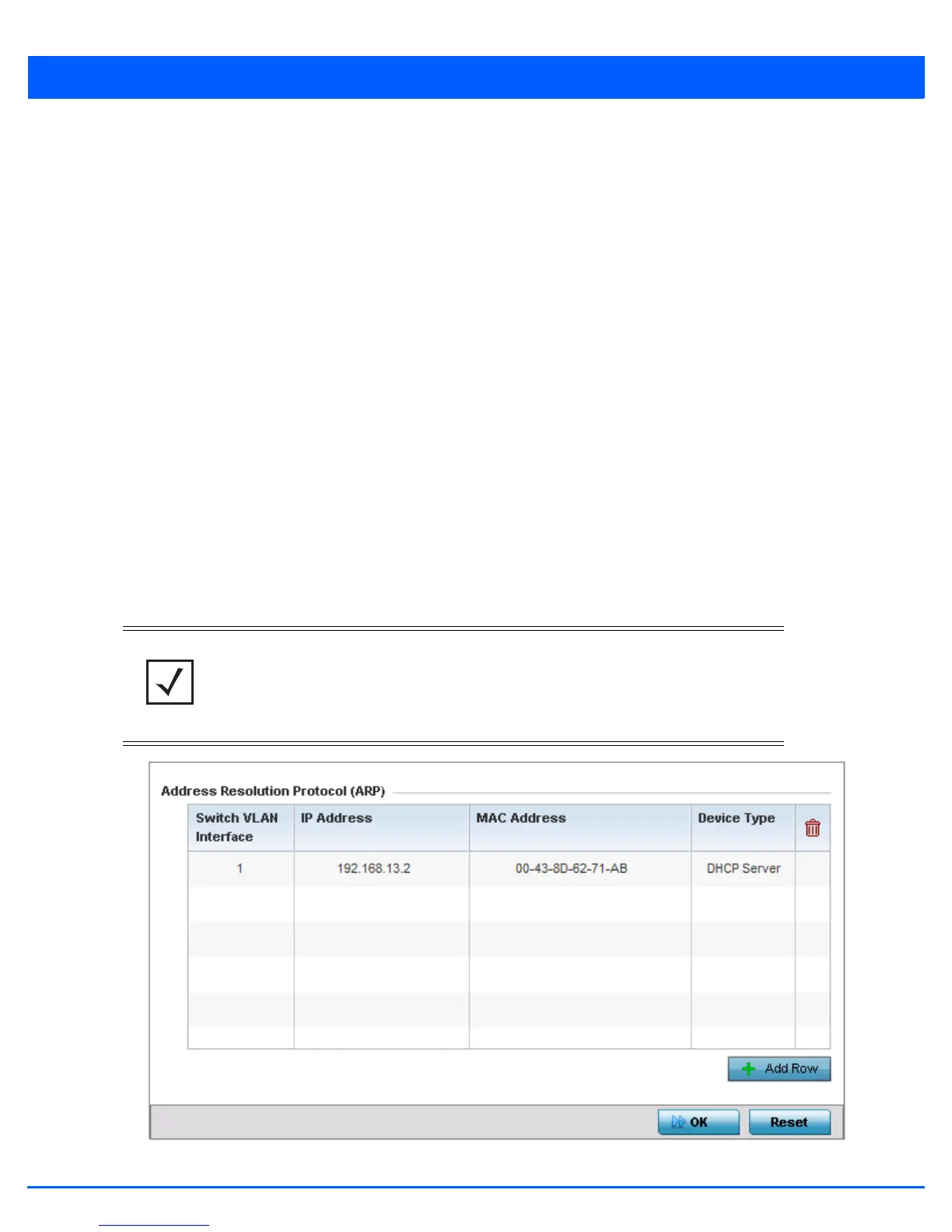
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol for mapping an IP address to a hardware MAC address. ARP provides protocol
rules for making this correlation and providing address conversion in both directions. This ARP assignment can be overridden
as needed, but removes the device configuration from the managed profile that may be shared with other similar device
models.
When an incoming packet destined for a host arrives at the access point, the access point’s gateway uses ARP to find a physical
host or MAC address that matches the IP address. ARP looks in its ARP cache and, if it finds the address, provides it so the
packet can be converted to the right packet length and format and sent to the destination. If no entry is found for the IP address,
ARP broadcasts a request packet in a special format to all the machines on the LAN to see if one machine knows it has that IP
address associated with it. A machine that recognizes the IP address as its own returns a reply indicating as such. ARP updates
the ARP cache for future reference and then sends the packet to the MAC address that replied.
To define an ARP supported configuration:
1. Select Devices from the Configuration tab.
2. Select Device Overrides from the Device menu to expand it into sub menu options.
3. Select a target device from the device browser in the lower, left-hand, side of the UI.
4. Select Network to expand its sub menu options.
5. Select ARP.
Figure 5-172 Device Overrides - Network ARP screen
NOTE: A blue override icon (to the left of a parameter) defines the parameter as having
an override applied. To remove an override, go to the Basic Configuration screen’s
Device Overrides field and select Clear Overrides. This will remove all overrides
from the device.

 Loading...
Loading...











