1 ENGINE SYSTEMS 23
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
The EGR system includes the following:
• EGR control valve
• EGR cooler
• Air intake manifold
• Inlet and EGR mixer duct
• Exhaust manifold
• Exhaust gas crossover
The Exhaust Gas R ecirculation (EGR) system
reduces Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) emissions.
NO
X
forms during a reaction between nitrogen and
oxygen at high temperature during combustion.
Combustion starts when fuel is injected into the
cylinder before or slightly after the piston reaches
top-dead-center.
EGR Flow
Some exhaust from the exhaust manifold flows into
the EGR cooler. Exhaust from the EGR cooler flows
through the exhaust gas crossover to the EGR valve.
When EGR is c ommanded, the EGR control valve
opens allowing cooled exhaust gases to enter the
EGR mixer duct to be mixed with filtered intake air.
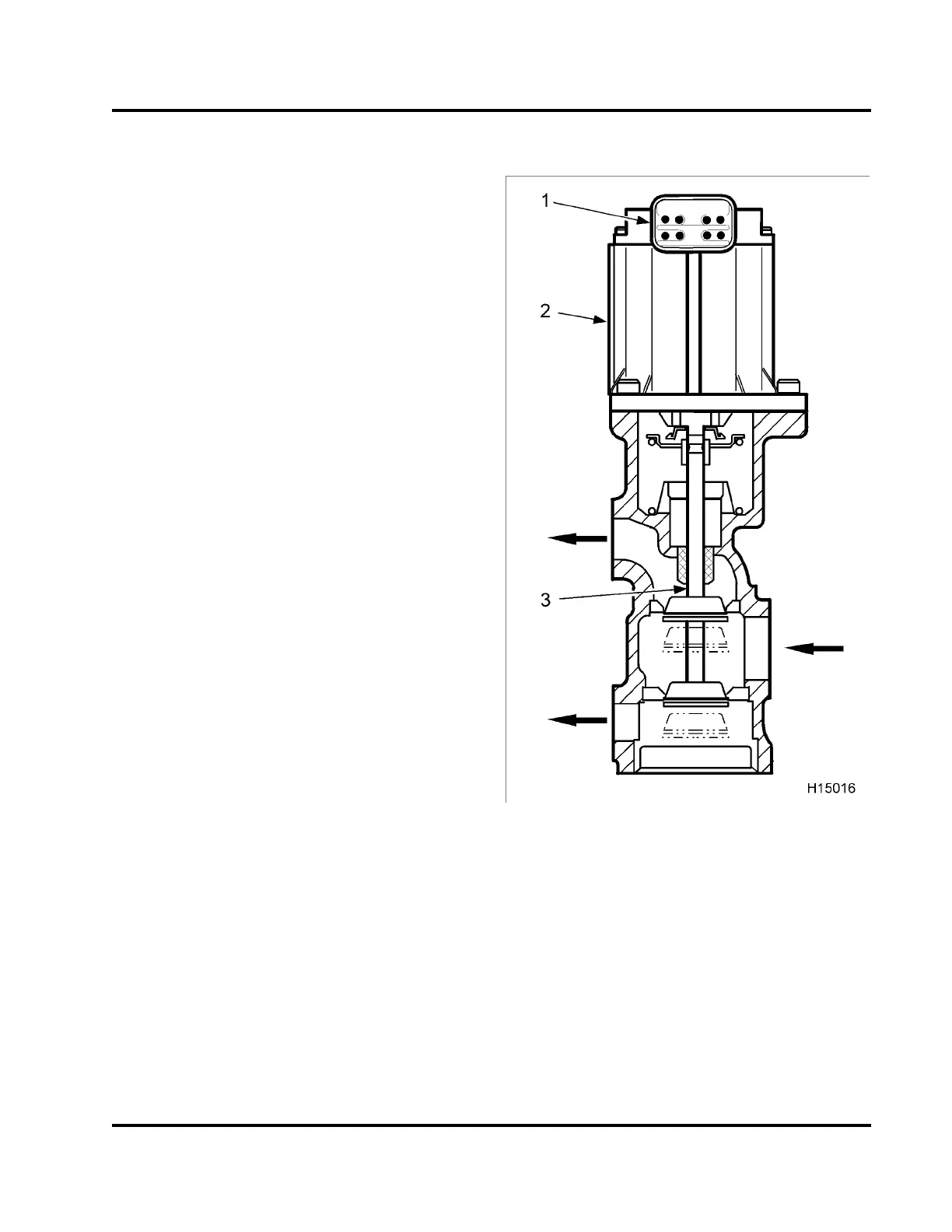
EGR Control Valve
Figure 15 EGR contr
ol valve
1. Connector
2. DC motor with positi
on sensor
3. Valve asse mbly
The EGR valve uses a
DC motor to control the position
of the valve assem
bly. The motor pushes directly
on the valve assem
bly. The valve assembly has two
valve heads on a c
ommon shaft.
The EGR actuator c
onsists of t hree majo r
components, a v
alve, an actuator motor, and
Integrate d Cir
cuit (IC). The IC has thre e Hall effect
position sens
ors to monitor valve movement. The
EGES-270-1
Read all safety instructions in the "Safety Information" section of this manual before doing any procedures.
Follow all warnings, cautions, and notes.
© August 2008 Navistar, Inc.

 Loading...
Loading...











