Newtec Proprietary
Confidentiality: Unrestricted
R3.2_v1.0
247/387
Feature Descriptions
MDM9000 Satellite Modem
16.11.3 TS Encapsulation
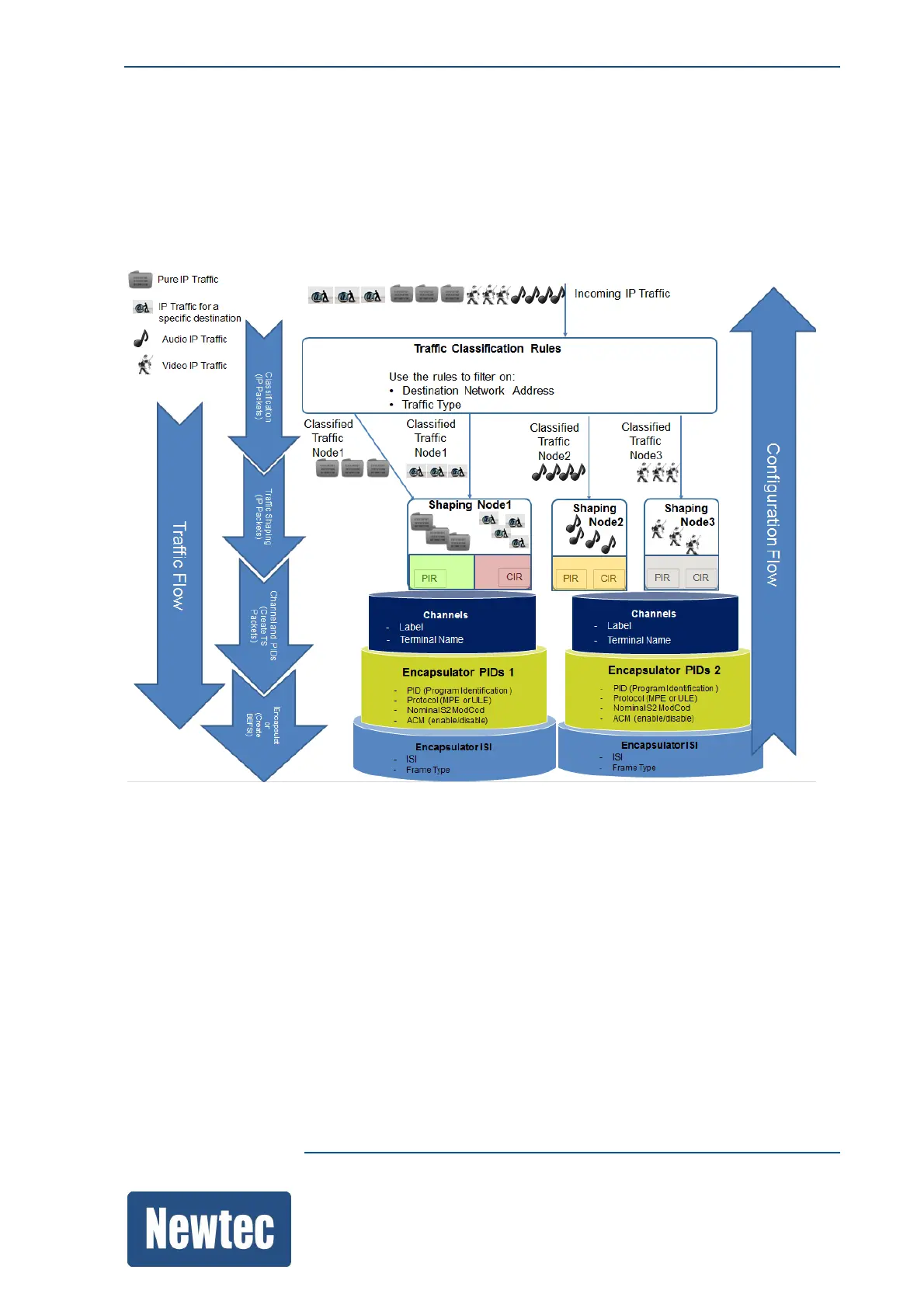
This encapsulator inserts IP packets first into TS packets and then into BBFs.
The following picture shows the complete traffic flow through the encapsulation block in case of TS
Encapsulation.
As is visualized in the figure, the incoming IP traffic is first classified by the classification rules. Once
the rules are applied traffic shaping is performed.
Traffic shaping is a mechanism to perform congestion control. Configure the shaping nodes in such
a way that the traffic capacity and the quality of service is respected according to the needs or
contracts of the customer. Shaped traffic is still in IP format and not ready yet to be modulated.
The channel, encapsulator PIDs and encapsulator ISI configuration parameters are used to create
baseband frames. An intermediate step in this procedure is to create TS packets. This is done in the
encapsulator PIDs block.
Creating baseband frames is done by configuring the BBF header parameters.
By configuring the channels you define a logical pipe that carries traffic coming from shaping nodes.
These shaping nodes are linked to this particular channel. Next to linking the shaping nodes to a
channel, a label and a terminal name are defined.
Creating TS packets is done by configuring the Encapsulator PIDs. In this block define the Program
Identification and what protocol (MPE or ULE) is used to encapsulate the payload.
In the encapsulator ISI define the Input Stream Identifier and the frame type (normal/short).
Once the BBF header is completed the traffic can be forwarded towards the modulator block.
 Loading...
Loading...