Part B - System description cobas p 512
2-16 Operator's Manual - Version 1.6 - 10/2015
Detection principle
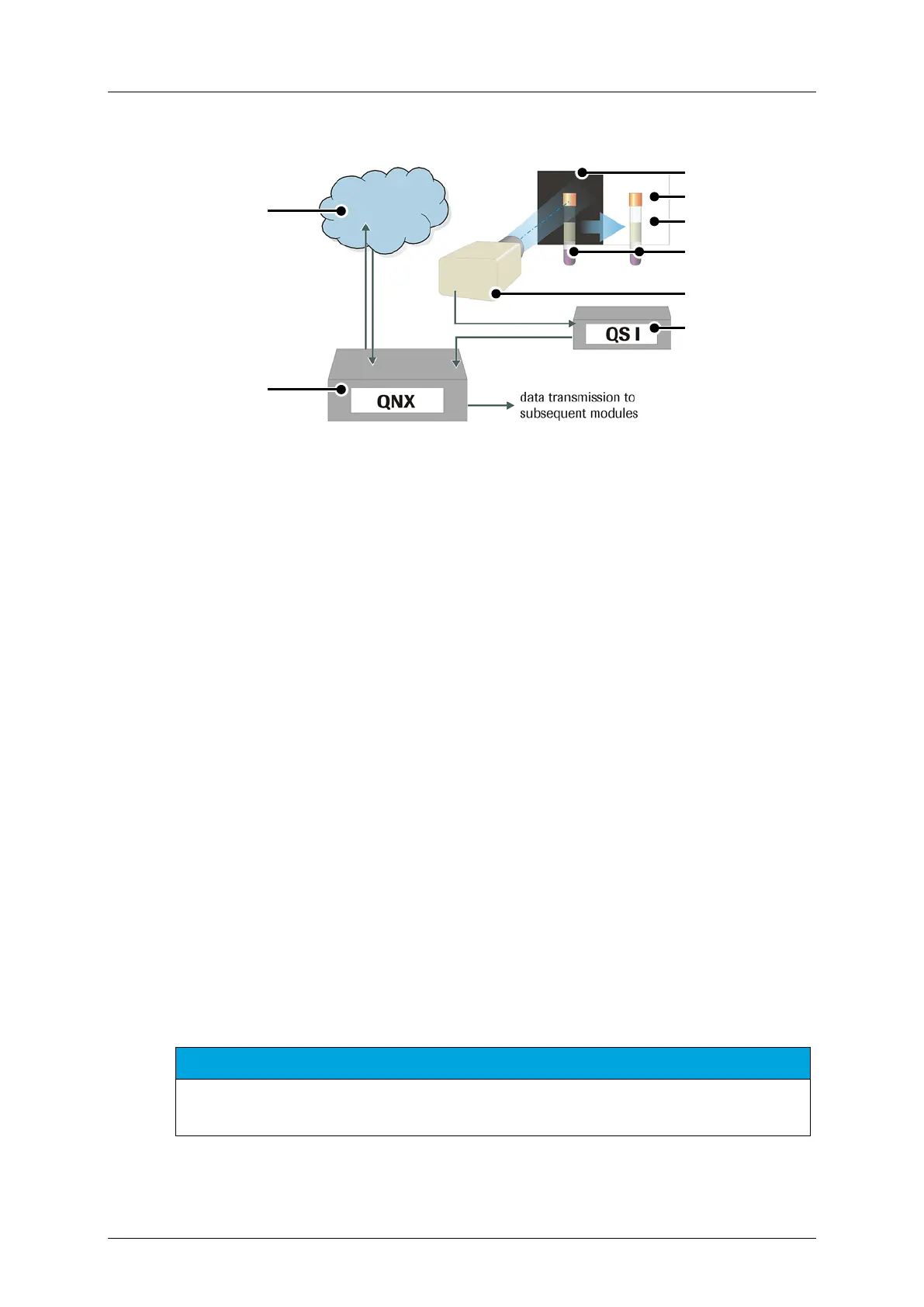
Figure 2-10: Measurement principles of the QS I system
Laboratory Information system (host)
3rd step: fill-level detection on white
background
cap identification on black
2nd step: serum analysis on white
background
QS I computer w/ frame grabber card
QS I full version
The QS I camera operates hand in hand with the QS I image processing computer, which
forwards the result to the QNX computer. The image processing computer (QS I PC) is
responsible for recognizing the cap color and for determining the quality of the processed
samples. Reference images for the individual quality levels (these are referred to also as
classes) are assigned to corresponding image areas. At the same time, the system crops out a
rectangular serum-window segment from the recorded camera image, which allows the user
to view as much of the available serum as possible. The size and quality of this window
depends on several parameters such as the type and manufacturer of the sample tube, the
material properties, overlap by barcode labels or the amount of serum present.
A serum window is determined and the serum quantity is calculated based on the tube type
with an accuracy of +/- 200 µl. After this, the color values of this window are compared with
the reference values. The quality of the serum is determined on the basis of this comparison.
The quality is expressed with three classes (hemolytic, icteric, lipaemic) based on the
comparison.
NOTICE
An additional lab analysis must be made for an exact analysis of the serum. The QS I system result
should not be interpreted as an exact measurement, but more as a rough assignment.

 Loading...
Loading...