ROBOT MOVEMENT IN PROGRAMMING STATUS
REFERENCE TERNS
A Cartesian reference system, or reference tern, is a geometrical concept which makes it possible to repre
-
sent an object in space. For example, the corner of a table can be chosen as reference system to represent
the table itself. The same may be done with a book rested on the table, just as for a welding gun fitted on the
robot flange.
A transformation of co-ordinates describes the position of one reference system in relation to another. It is
described by a POSITION type variable. For example if a table is in a room, its position in relation to the
room is expressed by POSITION p_table, which describes the transformation of co-ordinates between the
two reference systems. Transformation of co-ordinates may also be used to calculate the position of an ob
-
ject in relation to different reference systems. For example, a book whose position in relation to the table cor
-
ner is p_book will have the position (p_table:p_book) in relation to the corner of the room. The (:) sign
represents the relative position operation, and makes it possible to compose the effect of different co-ordi
-
nate transformations. For further information, refer to the PDL2 Programming Language Manual.
SYSTEM REFERENCE TERNS
The controller has three system variables ($BASE, $TOOL and $UFRAME) which make it possible to de
-
scribe the main co-ordinate transformations. Before proceeding with the explanation of these transforma
-
tions, definition of some reference terns is necessary.
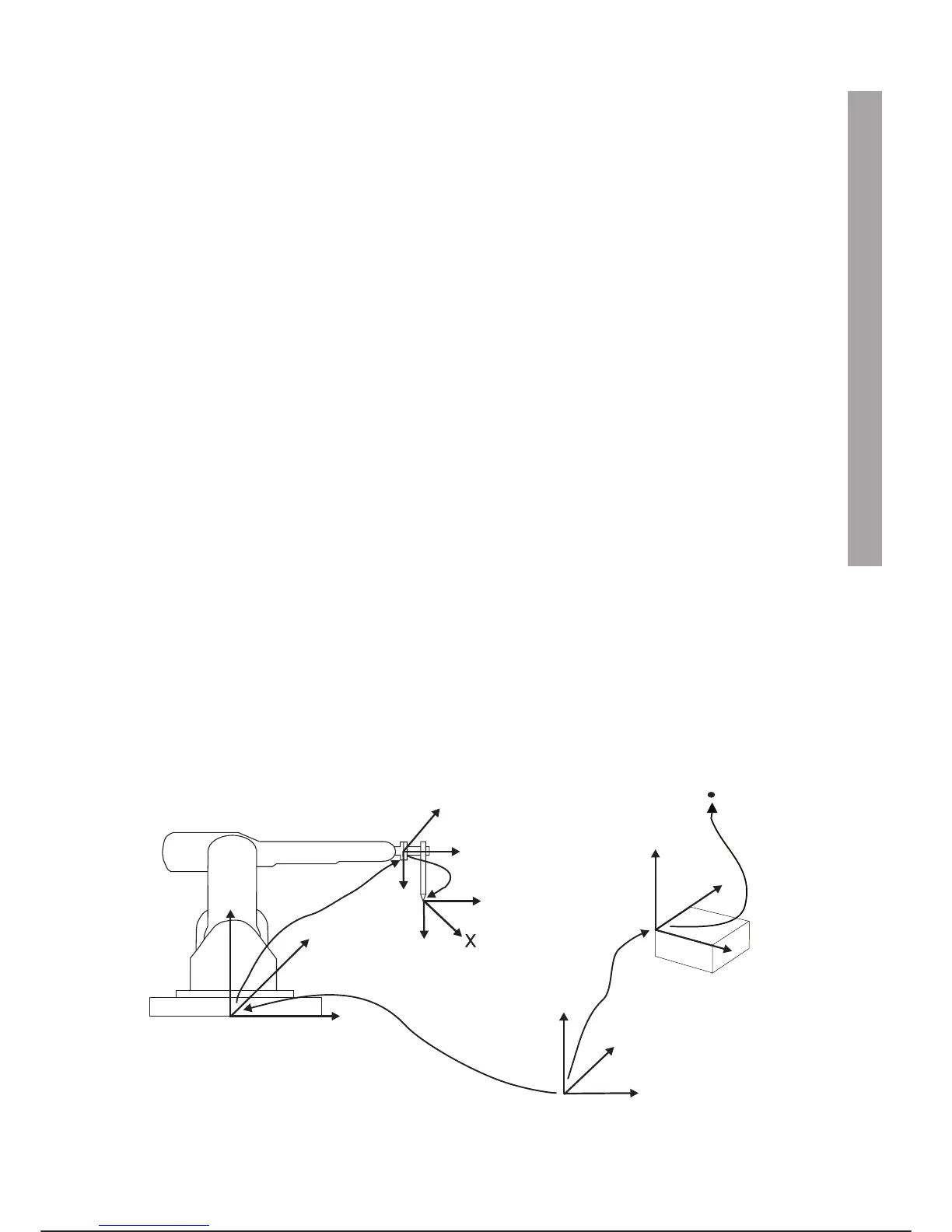
World tern – Reference tern of the workshop with respect to which the
machines are positioned.
Base tern – Tern that indicates the robot base
User tern – Tern that indicates the piece to be machined
Flange tern – Tern that indicates the robot flange
TCP tern – Tern that indicates tool bit
The $TOOL variable describes the position of the TCP tern with respect to that of the flange tern; the $BASE
variable describes the position of the base tern with respect to the world tern; lastly the $UFRAME variable
describes the position of the piece to be machined with respect to the world tern. POS transformation indi-
cates the taught point P on which the TCP will position itself during programme execution. Remember that all
the taught POSITIONS are defined in relation to the user reference tern (defined by $UFRAME).
For better understanding, imagine the corner of the room indicated by the world tern and a robot positioned
near a table, as shown below.
Reference terns for system and movement of co-ordinates
C3G Plus MAIN OPERATIONS FOR SYSTEM USE
00/1097 5-5
ROBOT MOVEMENT IN PROGRAMMING STATUS
User Fram
 Loading...
Loading...