inl#
MCS@-51 ARCHITECTURAL OVERVIEW
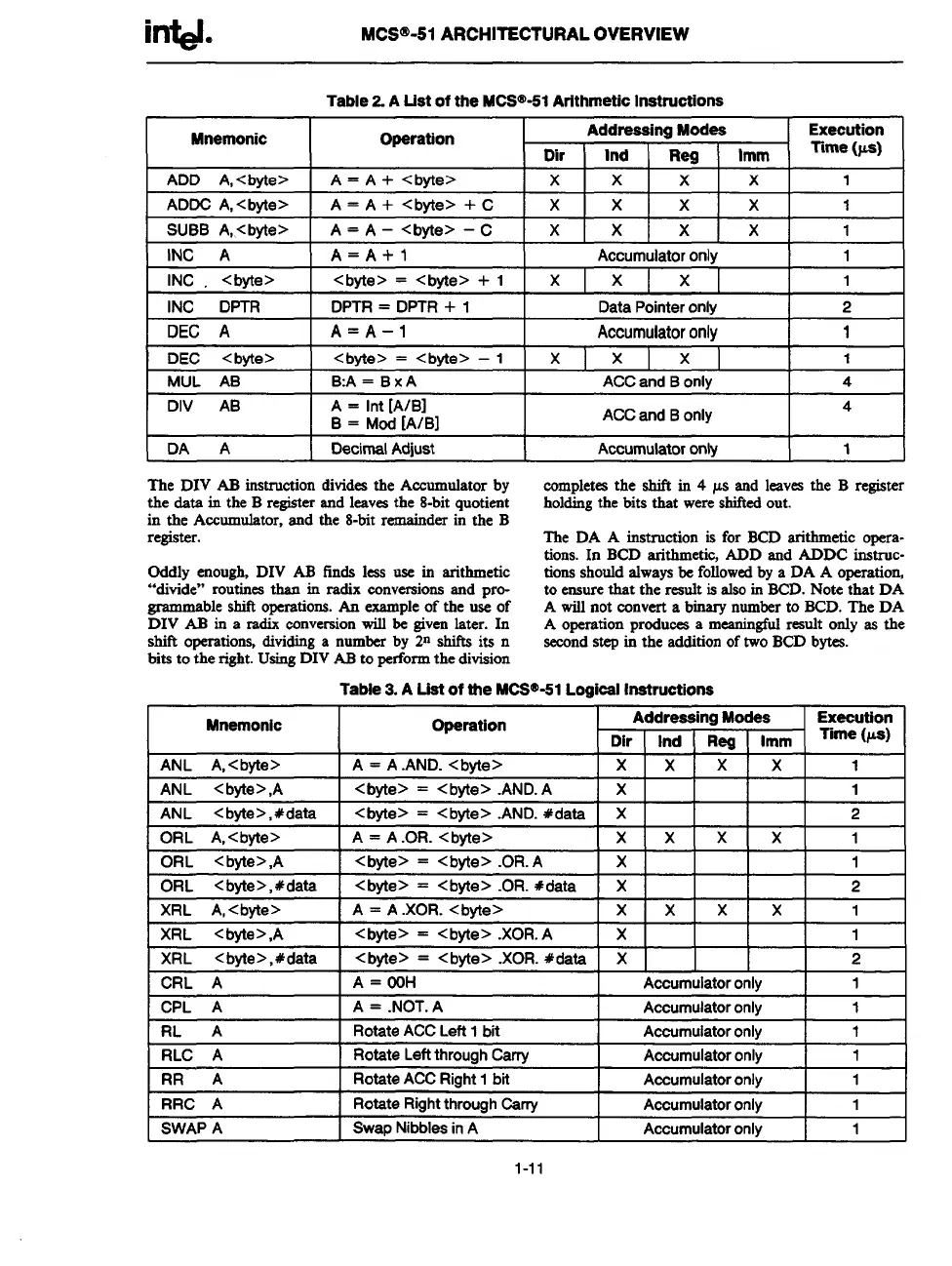
Table 2 A Ust of the MCS@I-51 Arithmetic Instructions
Mnemonic Operation
Addressing Modes
Execution
Dk I Ind Rq lmm
Time (@
ADD A, <byte> A = A + <byte>
x
x
x x
1
I ADDOA, <byte> I A= A+< byte>+C I X I X I X I X ] 1 I
SUBB A, <byte> A= A–<byte>-C
x x
x
x 1
INC A
I A=A+l I Accumulator onlv I 1
I INC . <byte>
I
<byte> =<byte>+l I X I X I X I
11-1
I lhJC DPTR I DPTR = DpTR + 1 I
Data Pointer only
121
I DEC A
I A= A-l
I
Accumulator only
Ill
DEC <byte>
<byte> = <byte> – 1
x
I
x x
I
1
MUL
AB B.A=Bx A ACC and B only 4
I
DIV AB
I
A = Int [A/B]
B = MOd[A/Bl
ACC and
B only
I
4
I
IDAA I Decimal Adjust
I
Accumulatoronly
Ill
The DIV AB instruction divides the Accumulator by
the data in the B register and leevea the 8-bit quotient
in the Accumulator, and the 8-bit remainder in the B
register.
Oddly enough, DIV AB finds lees use in arithmetic
“divide” routines than in radix eonversions and pro-
~ble shift operstioILs.k example of the use of
DIV AB in a radix conversion will be given later. In
s~ operations, dividing a number by 2n shifts its n
bits to the right. Using DIV AS to perform the division
eompletcs the shift in 4 p.s and leaves the B register
holding the bits that were shifted out.
The DA A instruction is for BCD arithmetic opera-
tions. In BCD arithmetic, ADD and ADDC instruc-
tions should always be followed by a DA A operation,
to ensure that the
red is also in BCD. Note that DA
A will not convert a binary number to BCD. The DA
A operation produces a meaningfid
result only as the
second step in the addition of two BCD bytes.
Table 3. A Uet of the MCS@J-51Logical Instructions
I
Mnemonic
I
Operation
Addressing Modes
Execution
Dir
Ind I Reg I
Imm
Time (ps)
I
ANL A,< byte> A = A .AND. <byte> x x x x
1
ANL <byte>,A
<byte> = <byte> .AND. A
x 1
ANL <bvte>, #data
<byte> = <byte>
.AND. #data
x 2
ORL A,< byte>
I
A = A.OR. <byte>
I
X1X1X1X
1
ORL <bvte>,A
<byte> = <byte> .OR.A
x 1
ORL <byte>, #data
I
<byte> = <byte> .OR. #data
x
2
XRL A,< byte> A = A .XOR. <byte> X1X1X
x
1
XRL <byte>,A
I
<byte> = <byte> .XOR. A
x
I
I
1
XRL <byte>, #data
<byte> = <byte> .XOR. #data I X
I
2
CRL A
A=OOH
Accumulator only 1
CPL A
A =
.NOT. A
Accumulator
only
I
1
IRL A I Rotate ACC Left 1 bit I
Accumulator onlv
Ill
RLC A
I
Rotate Left through Csrry
I
Accumulator only
I
1
RR A
Rotate ACC Right
1 bit
Accumulator only 1
RRC A
Rotate Right through Carry
Accumulator only 1
SWAP A
Swap Nibbles in A
Accumulator
onlv 1
1-11
 Loading...
Loading...