i~.
83C152 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
4.3.5 Internal Logic of the Requester
The internal logicof the requester is shownin Figure
4.10.INtially, the requester’sinternal signalDMXRQ
~mto
XRAMRequest)is at O,so Q2 is set andthe
HLD output is high. As long as Q2 stays set, the re-
questeris inhibitedfromstartinganyDMAto XFL4M.
Whenthe requeater
wants to DMA the XRAM,it first
aetivateaDMXRQ.ThissignalenablesQ2to becleared
(but doesn’tclear it), and, if= is high,rdsoacti-
vatesthe ~ output.
A l-to-Otransition from HLDA can now clear Q2,
whichwillenablethe requesterto commenceits DMA
to XRAM. Q2being
low also maintains an output low
at HLD. Whenthe DMAis completed,DMXRQgoes
to O,whichsets Q2and de-activates~.
OnlyDMXRQgoingto Ocan set Q2.That meansonce
Q2gets cleared,enablingthe requester’sDMA to pro-
ceed, the arbiter has no way to stop the requester’s
DMA in progress.At this poinLde-activatingHLDA
will have no effect on the requeater’suse of the bus.
Onlythe requesteritselfcan stopthe DMAin progress,
and when it does, it de-activatesboth DMXRQ and
m.
the requestand receiveanotheracknowledgebeforean-
other DMAcycleto XRAMcartpti. Obviouslyin
this ~ the “alternate cycles”mode may consist of
singleDMAcyclesseparatedbyanynumberof instruc-
tioncycles,dependingon howlongit takesthe request-
er to regainthe bus.
A channel 1 DMA in progresswillalwaysbe overri-
ddenbya DMA requestofanykindfromchannelO.If a
channel 1DMA to XRAMis in progressand is over-
riddenbya channelODMAwhichdoeanot require the
bus,DMXRQwifl~o Oduringthe channelODMA,
thus de-activatingHLD. Again,the requestermust re-
newits requeatfor the b~ andmustreceivea new 1-
to-otransitionin HLDAbeforechannel1can continue
its DMA to XRAM.
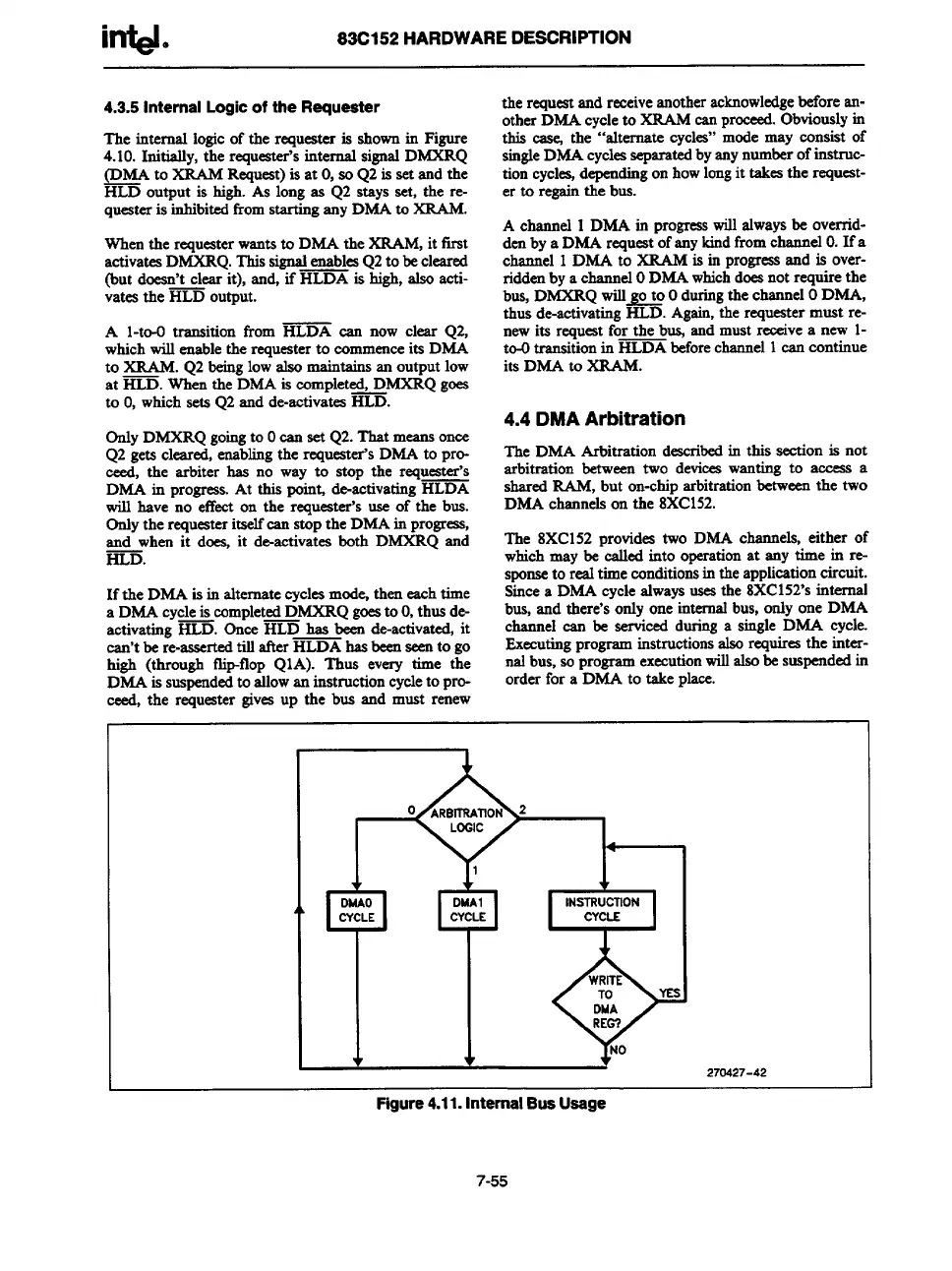
4.4 DMAArbitration
The DMA Arbitration dsscribedin this section is not
arbitration betweentwo devieeawanting to access a
sharedRAM, but on-chiparbitrationbetweenthe two
DMA channelson the 8XC152.
The 8XC152 providestwo DMA channels, either of
whichmay be called
into operationat any time in re-
sDOnaeto realtimeconditionsinthearmlicationcircuit.
If the DMA is in alternatecyclesmode,then eachtime
&we a DMA cyclealwaysusesthe ~XC152’sinternal
a DMAcycleiscompletedDMXRQgoestoO,thus de-
bus, and there’sonly one internalbus, ordyone DMA
activating~. once ~ has been de-activated,it
channel earsbe serviced duringa singleDMA cycle.
can’tbe re-asaertedtill tier HLDA hasbeenseento go
Executingprograminstructionsalsorequiresthe inter-
high (through flip-flopQIA). Thus every time the
rsalbus,soprogramexecutionwillalsobe suspendedin
DMA issuspendedto allowan instructioncycleto pre-
orderfor a DMA to take place.
ceed, the requeatergivesup the bus and must renew
I
1
4 L
270427-42
Figure4.11.InternalBus Usage
7-55
 Loading...
Loading...