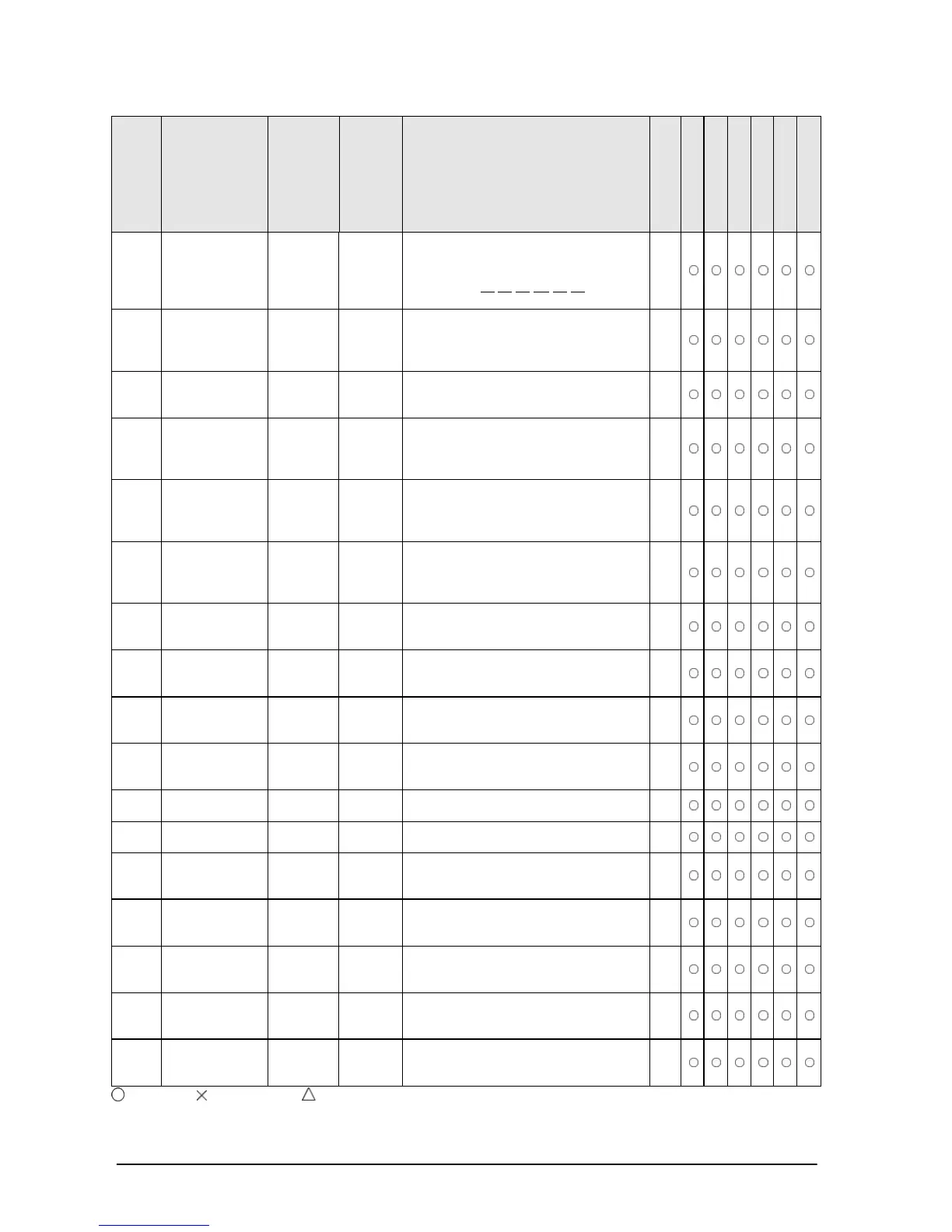
11-66
Num-
ber
Name Boolean
Ope-
rand
Description
Steps
FP0/FP-e
FP0R
FP
FP-X
FP2
FP2SH/FP10SH
F76
P76
ASCII code
16-bit binary
data
ABIN
PABIN
S1, S2,
D
Converts the ASCII code specified by
“S1” and “S2” to 16 bits of binary data
and stores it in “D”.
Example: H
30 30 31 2D 20 20
7
→ K-100
Converts the 32 bits of binary data
(S1+1,
S1) to ASCII code and stores it in D
(area of “S2” bytes).
11
F78
P78
DABI
PDABI
S1, S2,
D
Converts the ASCII code specified by
“S1” and “S2” to 32 bits of binary data
and stores it in (D+1, D).
Converts the 16 bits of binary data
specified by “S” to four digits of BCD
data and stores it in “D”.
Example: K100 → H100
5
F81
P81
4-digit BCD
data
16-bit
binary data
BIN
PBIN
S, D Converts the four digits of BCD data
specified by “S” to 16 bits of binary data
and stores it in “D”.
8-digit
BCD data
DBCD
PDBCD
S, D Converts the 32 bits of binary data
specified by (S+1, S) to eight digits of
BCD data and stores it in (D+1, D).
7
F83
P83
DBIN
PDBIN
S, D Converts the eight digits of BCD data
specified by (S+1, S) to 32 bits of binary
data and stores it in (D+1, D).
Inverts each bit of data of “D”.
NEG
PNEG
D Inverts each bit of data of “D” and adds
1 (inverts the sign).
3
Inverts each bit of data of (D+1, D) and
adds 1 (inverts the sign). 3
F87
D Gives the absolute value of the data of
Gives the absolute value of the data of
16-bit data
sign extension
EXT
PEXT
D Extends the 16 bits of data in “D” to 32
bits in (D+1, D).
3
Decodes part of the data of “S” and
stores
it in “D”. The part is specified by “n”.
7
F91
P91
7-segment
decode
SEGT
PSEGT
S, D Converts the data of “S” for use in a 7-
segment display and stores it in (D+1,
Encodes part of the data of “S” and
stores it in “D”. The part is specified by
16-bit data
combine
UNIT
PUNIT
S, n, D The least significant digit of each of the
“n” words of data beginning at “S” are
stored (united) in order in “D”.
7
: Available, : Not available, : Not available partially
 Loading...
Loading...











