Checking and Calibrating the Anesthetic Gas Module 9 Anesthetic Gas Module
193
Complete the following to perform a zero calibration in service mode:
1 In the Setup Gas Analyzer menu select Service Window.
2 Select Calibration to access the Gas Analyzer Calibration window.
3 In the Setup Gas Analyzer menu select Zero Cal and press Confirm when prompted to.
4 Wait until zero calibration is complete. In the Gas Analyzer Calibration window a OK /
Failed indication is displayed against each channel. If a Failed indication cannot be cleared by
another zero calibration refer to the appropriate section of this manual and correct the fault. Then
repeat this procedure.
Barometric Pressure Check and Calibration
For this calibration you need the absolute barometric pressure at your hospital location. Normally this
value can be provided by the hospital as it is needed in the laboratory.
If the hospital cannot provide an accurate value for the barometric pressure, call the local airport or
weatherstation. Since airports and weatherstations normally provide you with a pressure that has been
corrected to sea level, ensure that the value you are given is an uncorrected absolute barometric pressure
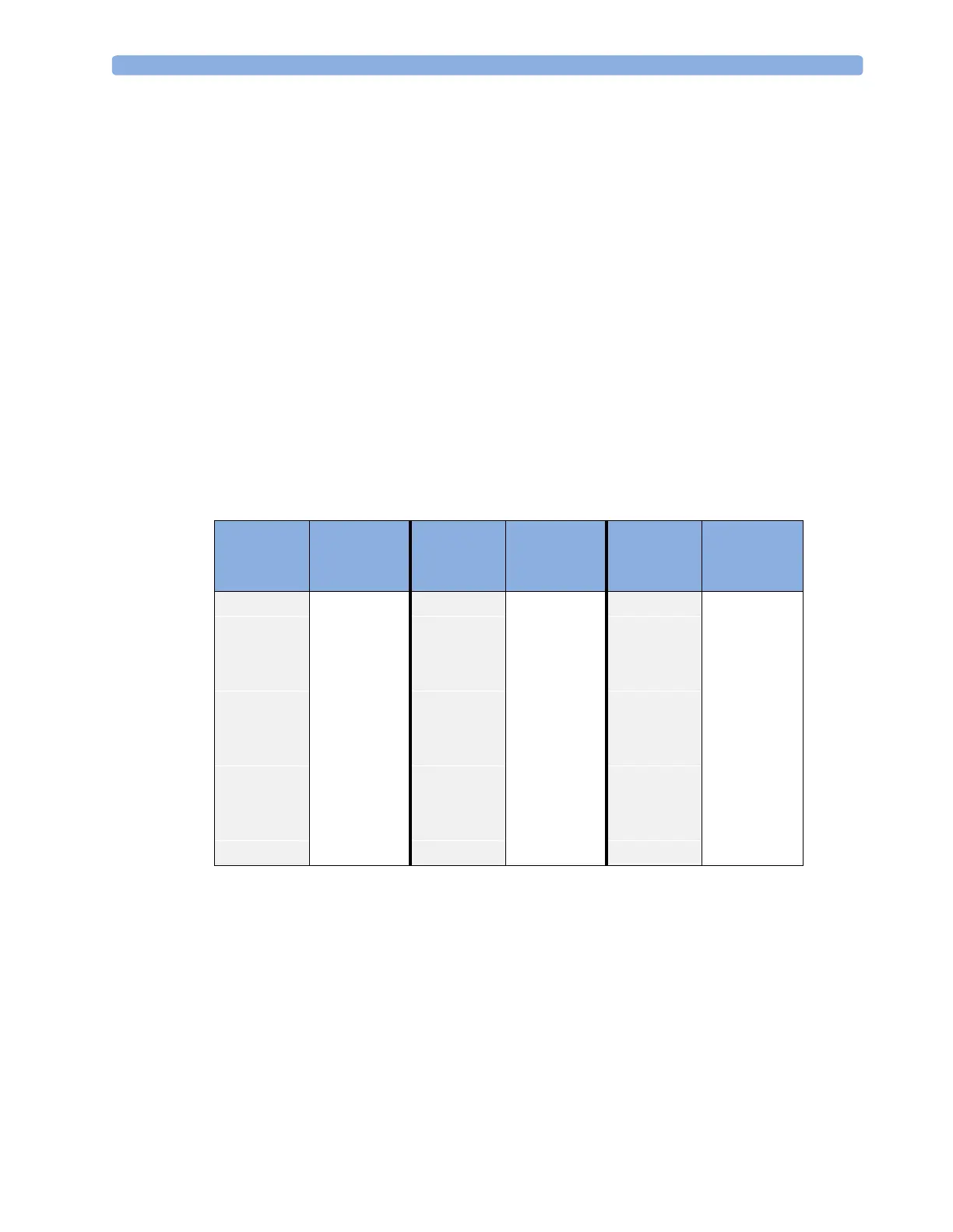
reading! The following table shows you typical barometric pressures at various altitudes.
If only a corrected (to sea-level or 0 meters) reading is available, uncorrect the reading for the altitude
you are on using the following equation:
Altitude Typical
Barometric
Pressure
Altitude Typical
Barometric
Pressure
Altitude Typical
Barometric
Pressure
0 m 760 mmHg 1100 m 664 mmHg 2200 m 577 mmHg
100 m 751 mmHg 1200 m 656 mmHg 2300 m 570 mmHg
200 m 742 mmHg 1300 m 648 mmHg 2400 m 562 mmHg
300 m 733 mmHg 1400 m 639 mmHg 2500 m 555 mmHg
400 m 724 mmHg 1500 m 631 mmHg 2600 m 548 mmHg
500 m 715 mmHg 1600 m 623 mmHg 2700 m 540 mmHg
600 m 707 mmHg 1700 m 616 mmHg 2800 m 533 mmHg
700 m 698 mmHg 1800 m 608 mmHg 2900 m 526 mmHg
800 m 689 mmHg 1900 m 600 mmHg 3000 m 519 mmHg
900 m 681 mmHg 2000 m 592 mmHg
1000 m 672 mmHg 2100 m 585 mmHg

 Loading...
Loading...











