Motor control
SIMOCODE pro
4-56 GWA 4NEB 631 6050-22 DS 03
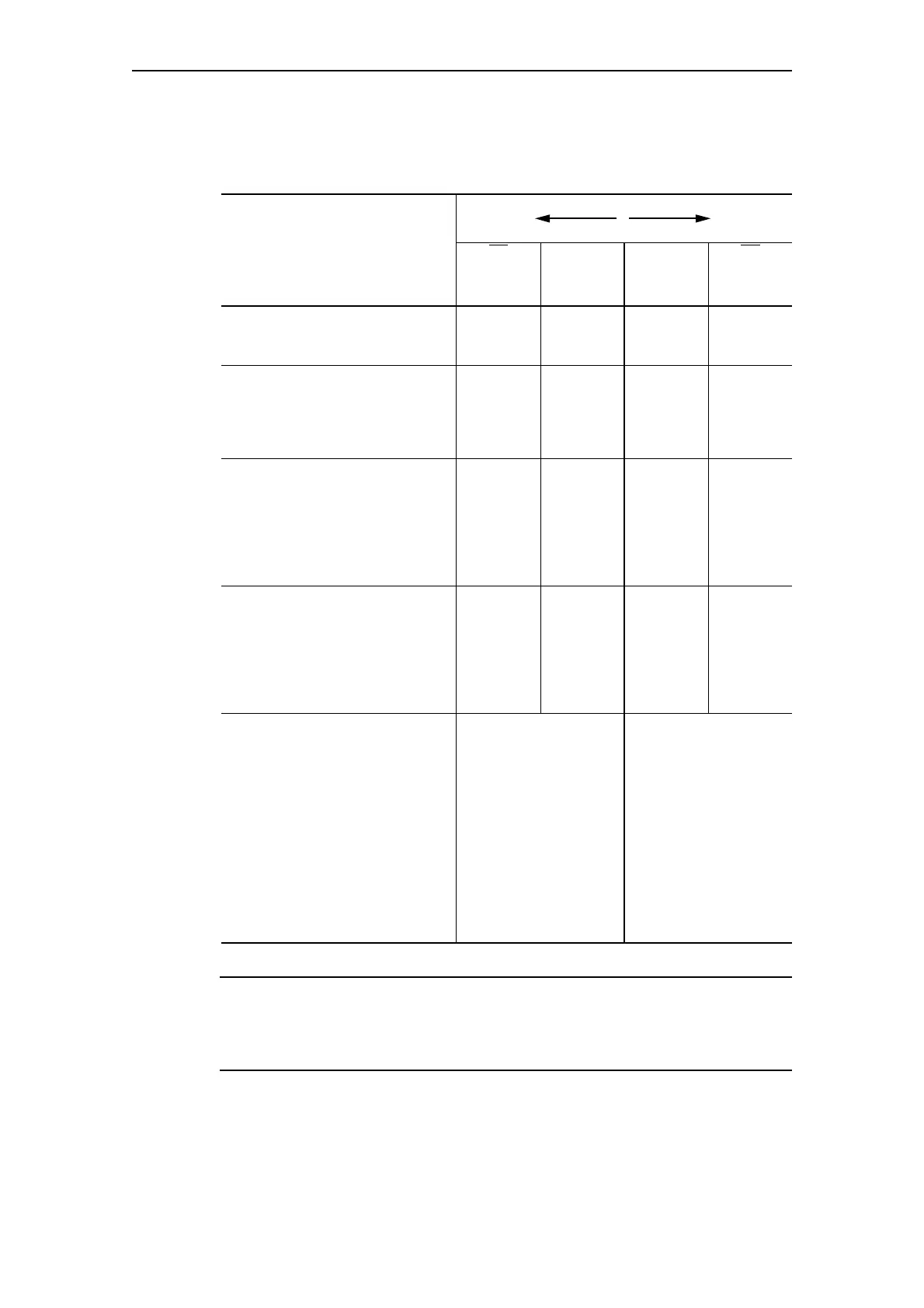
Types of positioner control
The following table shows the five types of positioner control:
Table 4-17: Types of positioner control
Notice
The signals of the torque switches and the limit switches must be wired to
the inputs of the basic unit. Torque switches must be 0-active, whereas the
limit switches must be 1-active.
Ty p e
Tripping
TC
Torque
CLOSED
FC
Limit
CLOSED
FO
Limit
OPEN
TO
Torque OPEN
Positioner 1
After reaching the end position FO
(OPEN) or FC (CLOSED).
—X X—
Positioner 2
After reaching the end position FO
(OPEN) or FC (CLOSED) AND
response of the associated torque
switch TO (OPEN) or TC (CLOSED)
XXXX
Positioner 3
After reaching the end position FO
(OPEN). After reaching the end
position 'CLOSED', the respective
torque switch TC must also respond
after the limit switch FC has
responded.
XXX—
Positioner 4
After reaching the end position FC
(CLOSED). After reaching the end
position FO (OPEN), the respective
torque switch TO must also
respond after the limit switch FO
has responded.
—X X X
Positioner 5
After reaching the end position or the
torque. The actuator is monitored by
either the limit switches or by the
torque switches. The switches are
implemented as change-over
contacts and are checked for
antivalence. In the case of non-
antivalent feedback (e.g. FC=0 and
TC=0), SIMOCODE pro recognizes a
wire break and deactivates the
positioner with the fault message
"Trip - Antivalence"
Antivalent active Antivalent active
 Loading...
Loading...

















