CD600 Plus - User's Manual
4.26
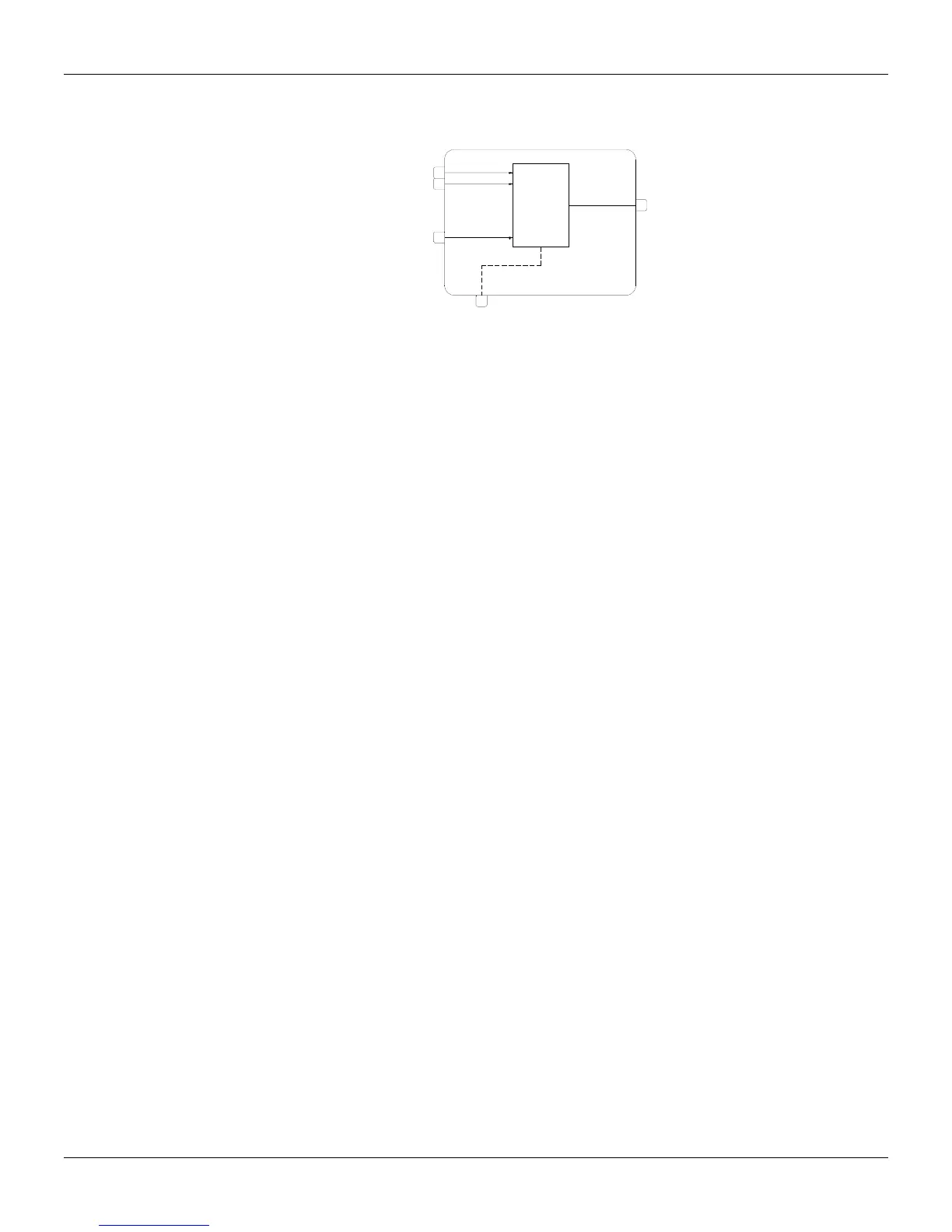
Function 10 - Simple PID (PID)
BLK 043/044/045/046
B
C
D
55/56
57/58
TRACK FB
PI.D
PID
I.PD
SP
PV
FB
Operation
This block offers a wide range of control algorithms, using the traditional Proportional (P), Integral (I)
and Derivative (D) modes in various arrangements.
There are two choices of PID algorithm: one is the parallel, ideal and the other is noninteractive, ISA
algorithm. Calculation of the PID prevents the saturation of the output by the integral mode (anti-
reset-windup). Saturation limits are adjustable by the user, a unique feature of the SMAR CD600
Digital Controller, that brings more flexibility to the control strategy.
Manual to Automatic transfer may be bumpless or hard. Bumpless transfer makes the automatic
mode start from the last manual value prior to the switching. Hard transfer will add to this value the
proportional action: (K
P
.e). In both cases, it is necessary to connect the output signal of the
Auto/Manual block to input C (Feedback) and the status signal of the Auto/Manual block to input D
(track FB).
TYPE OF PID (CTYP)
PI.D - The P and I act on the deviation, and D on the Process Variable. In this way, the output signal
follows the changes of the Setpoint according to the Proportional and Integral actions, but does not
give an undesirable impulse due to the Derivative action. This combination is the most
recommended for the majority of applications with Setpoint adjustable by the operator.
PID - The P, I and D actions act on the deviation. In this way, the output signal changes when there
are changes in the Process Variable or on the Setpoint. This option is recommended for ratio control
or for the slave control of a cascade.
I.PD - In this type only the Integral mode acts on the deviation. Changes on the Setpoint cause
variation of the output according to the Integral mode, which is a very smooth effect. This
combination is recommended for processes that can be upset by abrupt changes of the Setpoint.
This is the case of heating processes with high proportional gain.
ACTION (CACT)
There are processes that require the output signal to increase when the Process Variable increases,
while others require the other way around.
Parameter CACT selects the type of action:
TYPE 0, 2,4 or 6 - output signal decreases when PV increases.
eS
P
=−
()
TYPE 1, 3, 5 or 7 - output signal increases when PV increases.
eP
S
=−
()
In order to standardize operation, it is recommended to consider that an output signal equal to 100%
means valve open and that an output signal equal to 0% means valve closed. Operation of the front
anel keys follows the same principle: p
 Loading...
Loading...