7 Series FPGAs SelectIO Resources User Guide www.xilinx.com 127
UG471 (v1.10) May 8, 2018
OLOGIC Resources
This section of the documentation discusses the various features available using the
OLOGIC resources.
Combinatorial Output Data and 3-State Control Path
The combinatorial output paths create a direct connection from the FPGA logic to the
output driver or output driver control. These paths are used automatically by software
when:
1. There is direct (unregistered) connection from logic resources in the FPGA logic to the
output data or 3-state control.
2. The
pack I/O register/latches into IOBs software map directive is set to OFF.
Output DDR Overview (ODDR)
7 series devices have dedicated registers in the OLOGIC to implement output DDR
registers. This feature is accessed when instantiating the ODDR primitive. DDR
multiplexing is automatic when using OLOGIC. No manual control of the mux-select is
needed. This control is generated from the clock.
There is only one clock input to the ODDR primitive. Falling edge data is clocked by a
locally inverted version of the input clock. All clocks feeding into the I/O tile are fully
multiplexed, i.e., there is no clock sharing between the ILOGIC or the OLOGIC blocks. The
ODDR primitive supports the following modes of operation:
• OPPOSITE_EDGE mode
• SAME_EDGE mode
The SAME_EDGE mode is the same as for the Virtex-6 architecture. This mode allows
designers to present both data inputs to the ODDR primitive on the rising-edge of the
ODDR clock, saving CLB and clock resources, and increasing performance. This mode is
implemented using the DDR_CLK_EDGE attribute. It is supported for 3-state control as
well. The following sections describe each of the modes in detail.
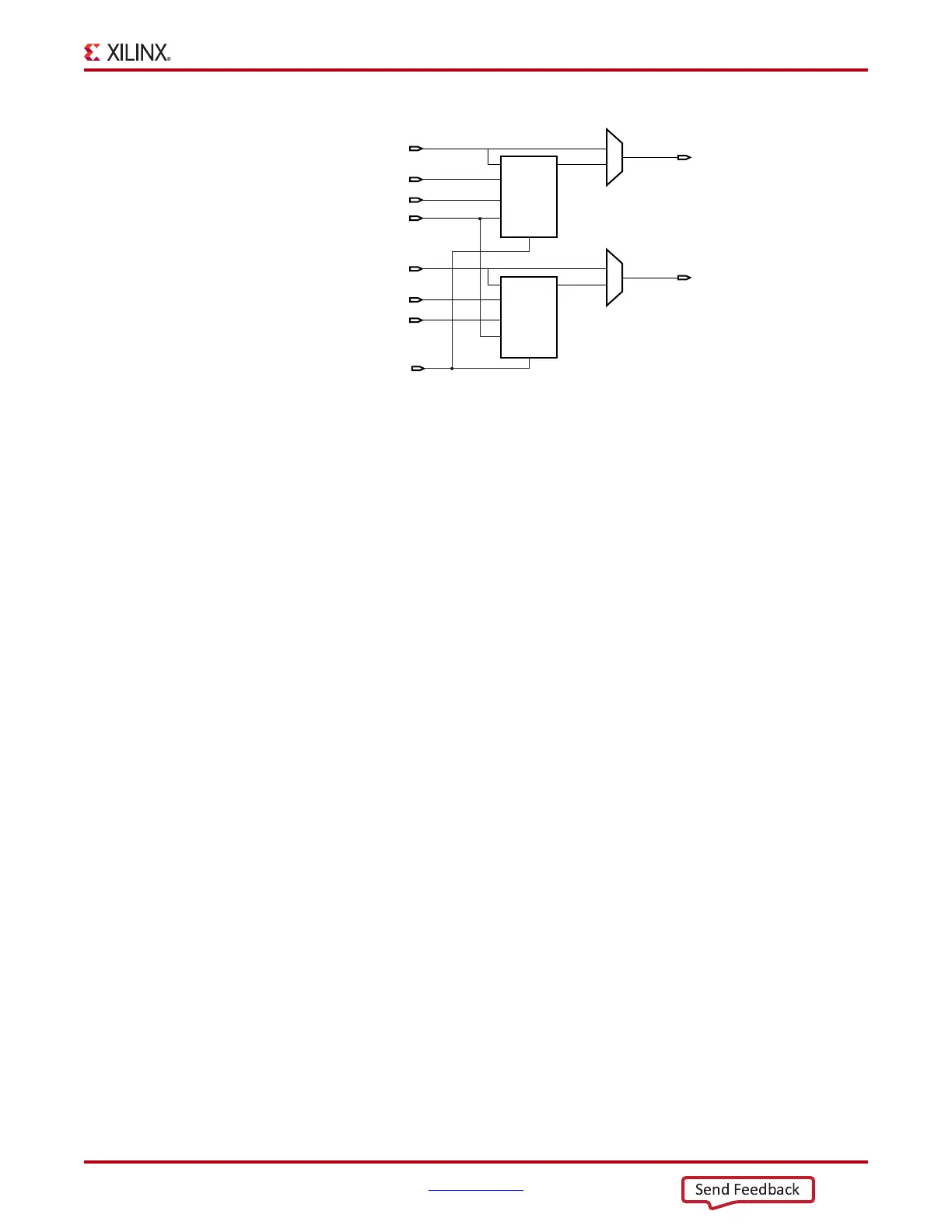
X-Ref Target - Figure 2-1 7
Figure 2-17: OLOGIC Block Diagram
D1
D2
T1
T2
TCE
CLK
S/R
Q
TQ
CE
CK
S/R
ug471_c2_15_022715
D1
D2
D1
D2
OCE
Q
OQ
CE
CK
S/R

 Loading...
Loading...