xStack® DES-3528/DES-3552 Series Layer 2 Stackable Fast Ethernet Managed Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Appendix A Mitigating ARP Spoofing Attacks
Using Packet Content ACL
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is the standard method for finding a host’s hardware address (MAC address) when
only its IP address is known. However, this protocol is vulnerable because crackers can spoof the IP and MAC
information in the ARP packets to attack a LAN (known as ARP spoofing). This document is intended to introduce the
ARP protocol, ARP spoofing attacks, and the countermeasures brought by D-Link’s switches to thwart ARP spoofing
attacks.
How Address Resolution Protocol Works
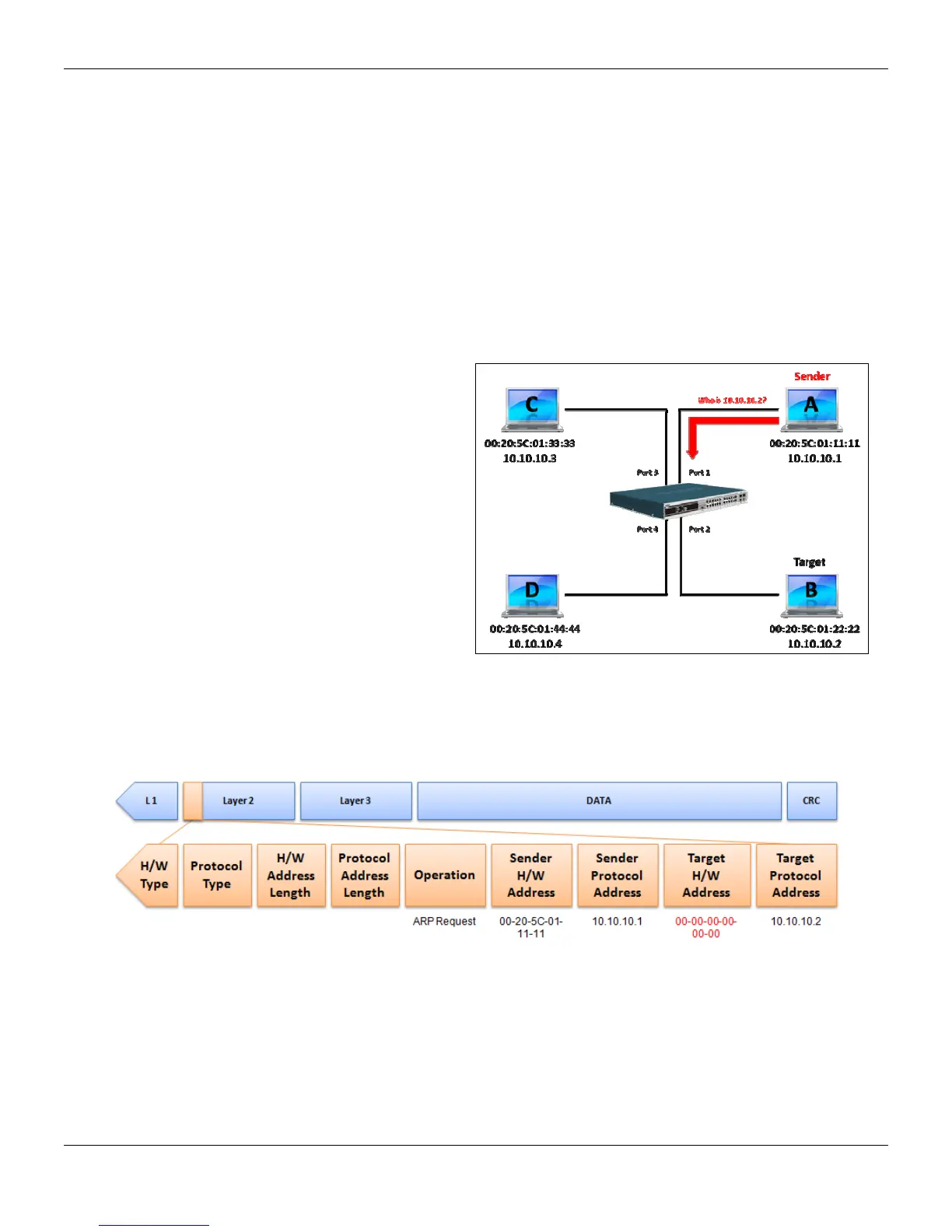
In the process of ARP, PC A will first issue an ARP
request to query PC B’s MAC address. The network
structure is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1
In the meantime, PC A’s MAC address will be written into the “Sender H/W Address” and its IP address will be
written into the “Sender Protocol Address” in the ARP payload. As PC B’s MAC address is unknown, the “Target
H/W Address” will be “00-00-00-00-00-00,” while PC B’s IP address will be written into the “Target Protocol
Address,” shown in Table1.
Table 1 ARP Payload
The ARP request will be encapsulated into an Ethernet frame and sent out. As can be seen in Table 2, the “Source
Address” in the Ethernet frame will be PC A’s MAC address. Since an ARP request is sent via broadcast, the
“Destination address” is in a format of Ethernet broadcast (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF).
339

 Loading...
Loading...











