2-22 Theory of Operation
Magnetic Stripe Primary Data Standards
The magnetic stripe on a card can store binary data in any form you wish;
however, to maintain consistency, national and international standards are
followed. A primary data standard is one that specifies how information is
stored on a card. A secondary standard is one that specifies the content of the
information stored on a card.
ISO/IEC 7811 (Parts 2 and 6)
This is the primary standard for recording that most other formats and standards
are based on. This standard dictates how information is written to a card, but
does not describe the content of the information. It covers 2-track and 3-track
magnetic stripe cards, where 1, 2, or 3 tracks may be used.
In the past, this 3-track recording standard was referred to as IAT, which is an
acronym for IATA, ABA, and TTS. This acronym should not be used to describe
a 3-track card, because it describes the “content” not the “technique.” It is more
accurate to describe these tracks as ISO-1, 2, or 3.
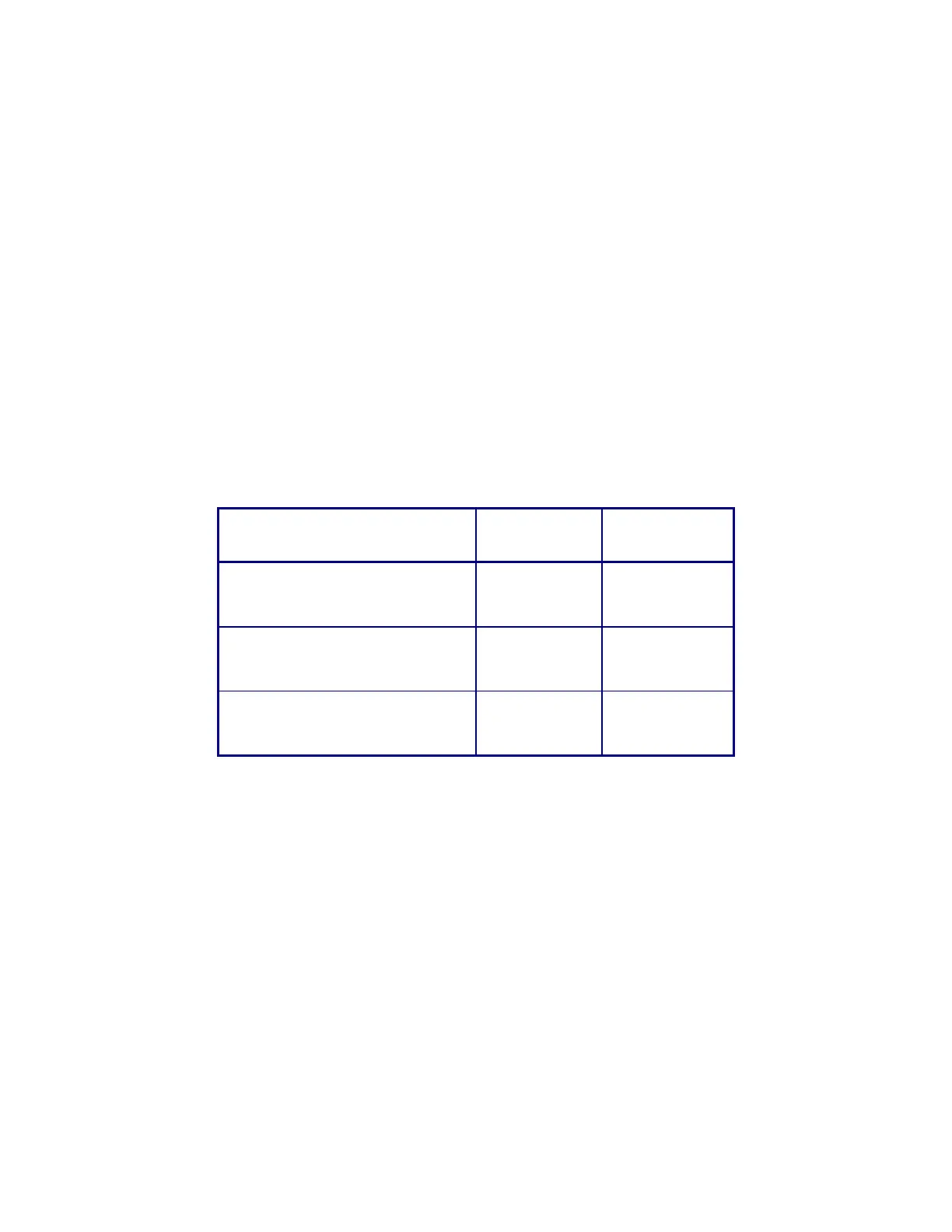
Full Name Abbreviated
Name
Former
Designation
ISO/IEC 7811 part 2 or 6
Track 1
ISO-1 IATA
ISO/IEC 7811 part 2 or 6
Track 2
ISO-2 ABA
ISO/IEC 7811 part 2 or 6
Track 3
ISO-3 TTS
Note that this standard permits the use of a single-track recording, but doing
so does not make the recording a JIS Type-II card. That is a completely
different standard, and is discussed below.
AAMVA DL/ID-2000
This is the standard used for U.S. driver’s licenses. It follows the ISO standard
except for some changes in data type and record length. Technically, this is not a
primary standard, but since it modifies some aspects of the primary ISO/IEC
standard, it is treated as though it were a primary standard.
Saflok and Ving
These are proprietary formats that the printer is capable of encoding, however
the specifics of these formats cannot be published.

 Loading...
Loading...