149
2-12.2 MLD Snooping
Curiously enough, a network node that acts as a source of IPv6 multicast traffic is only
an indirect participant in MLD snooping—it just provides multicast traffic, and MLD
doesn’t interact with it. (Note, however, that in an application like desktop
conferencing a network node may act as both a source and an MLD host; but MLD
interacts with that node only in its role as an MLD host.)
A source node creates multicast traffic by sending packets to a multicast address. In
IPv6, addresses with the first eight bits set (that is, “FF” as the first two characters of the
address) are multicast addresses, and any node that listens to such an address will
receive the traffic sent to that address. Application software running on the source and
destination systems cooperates to determine what multicast address to use. (Note that
this is a function of the application software, not of MLD.)
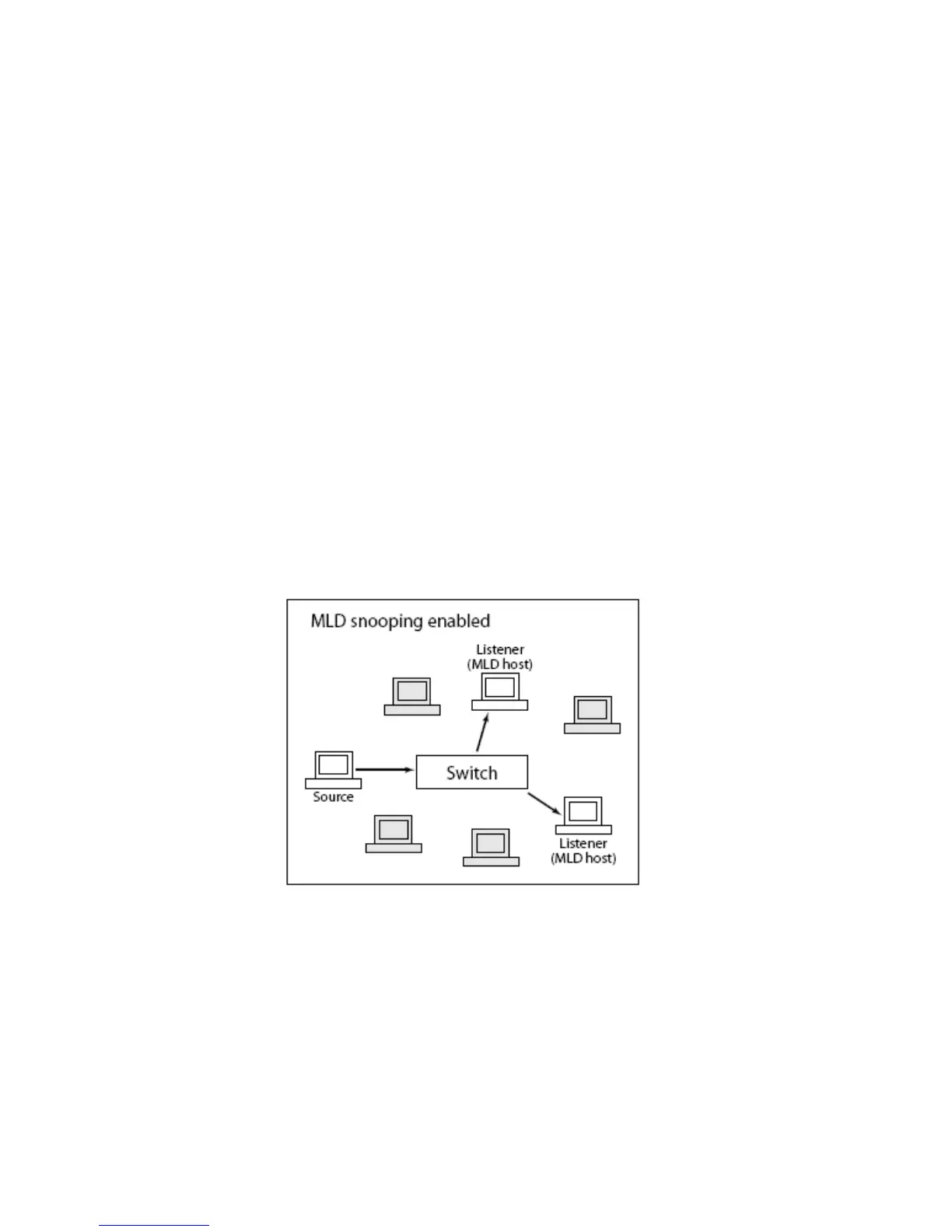
When MLD snooping is enabled on a VLAN, the switch acts to minimize unnecessary
multicast traffic. If the switch receives multicast traffic destined for a given multicast
address, it forwards that traffic only to ports on the VLAN that have MLD hosts for that
address. It drops that traffic for ports on the VLAN that have no MLD hosts
2-12.2.1 Basic Configuration
The section will let you understand how to configure the MLD Snooping basic
configuration and the parameters.
Web Interface
 Loading...
Loading...