UM10360 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2013. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 3 — 19 December 2013 420 of 841
NXP Semiconductors
UM10360
Chapter 18: LPC176x/5x SSP0/1
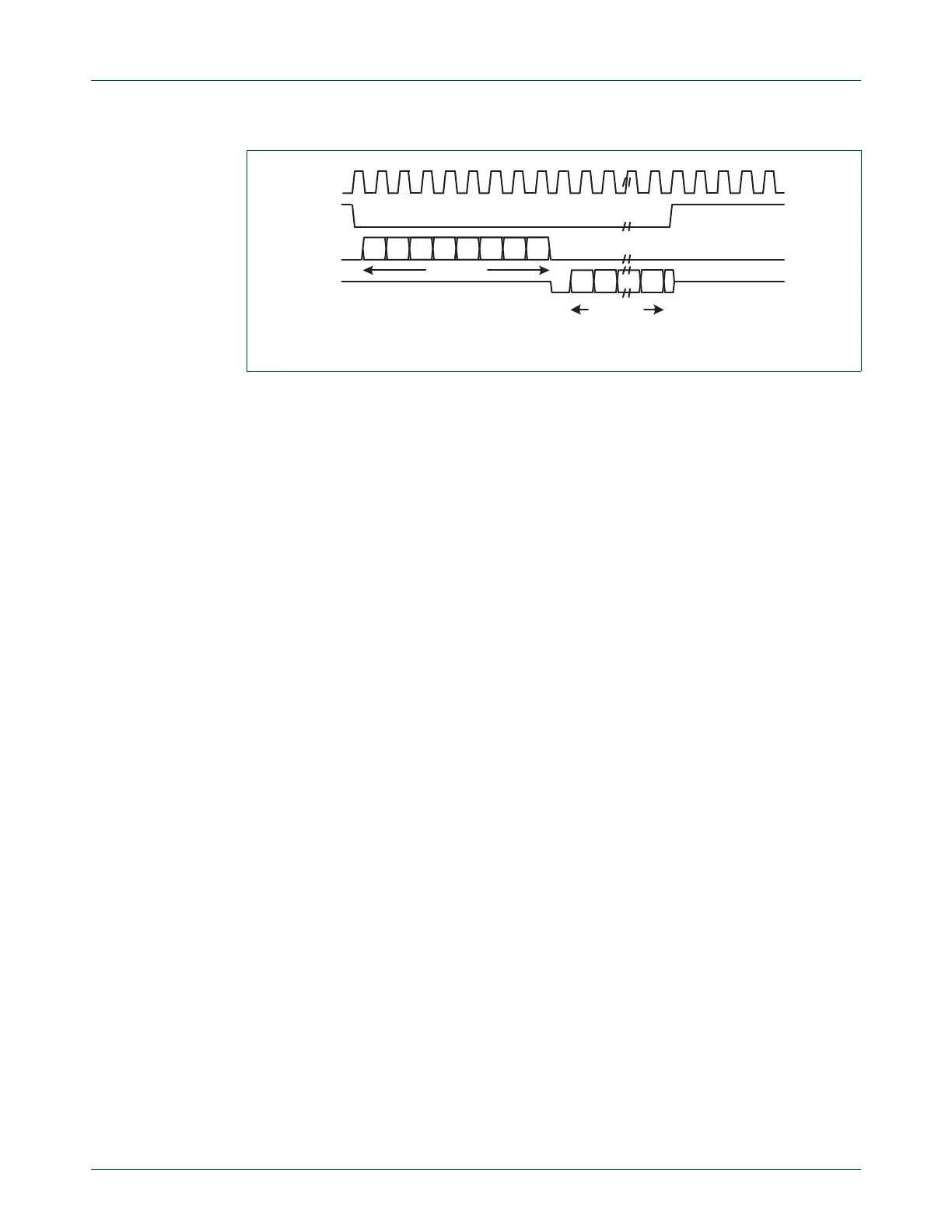
Microwire format is very similar to SPI format, except that transmission is half-duplex
instead of full-duplex, using a master-slave message passing technique. Each serial
transmission begins with an 8-bit control word that is transmitted from the SSP to the
off-chip slave device. During this transmission, no incoming data is received by the SSP.
After the message has been sent, the off-chip slave decodes it and, after waiting one
serial clock after the last bit of the 8-bit control message has been sent, responds with the
required data. The returned data is 4 to 16 bits in length, making the total frame length
anywhere from 13 to 25 bits.
In this configuration, during idle periods:
• The SK signal is forced LOW.
• CS is forced HIGH.
• The transmit data line SO is arbitrarily forced LOW.
A transmission is triggered by writing a control byte to the transmit FIFO.The falling edge
of CS causes the value contained in the bottom entry of the transmit FIFO to be
transferred to the serial shift register of the transmit logic, and the MSB of the 8-bit control
frame to be shifted out onto the SO pin. CS remains LOW for the duration of the frame
transmission. The SI pin remains tristated during this transmission.
The off-chip serial slave device latches each control bit into its serial shifter on the rising
edge of each SK. After the last bit is latched by the slave device, the control byte is
decoded during a one clock wait-state, and the slave responds by transmitting data back
to the SSP. Each bit is driven onto SI line on the falling edge of SK. The SSP in turn
latches each bit on the rising edge of SK. At the end of the frame, for single transfers, the
CS signal is pulled HIGH one clock period after the last bit has been latched in the receive
serial shifter, that causes the data to be transferred to the receive FIFO.
Note: The off-chip slave device can tristate the receive line either on the falling edge of
SK after the LSB has been latched by the receive shiftier, or when the CS pin goes HIGH.
For continuous transfers, data transmission begins and ends in the same manner as a
single transfer. However, the CS line is continuously asserted (held LOW) and
transmission of data occurs back to back. The control byte of the next frame follows
directly after the LSB of the received data from the current frame. Each of the received
values is transferred from the receive shifter on the falling edge SK, after the LSB of the
frame has been latched into the SSP.
Fig 81. Microwire frame format (single transfer)
SK
CS
SO
4 to 16 bits
output data
SI
8-bit control
MSB LSB
0
MSB LSB
 Loading...
Loading...