Cleverscope CS300 Reference Manual v2.11
Page 130 www.cleverscope.com ©Cleverscope 2004-2015
19.5 Example - Deriving the Differential Voltage [Maths]
The differential voltage is calculated from the voltages at test points A and B connected to the Cleverscope via
probes on Channels A and B (x1 range).
On Cleverscope Control Panel window click the View menu option, click Maths Equation Builder in the
dropdown list to display the equation builder.
Type the formula directly in the input field or click the required formula input buttons to build the expression.
Click Used? Process and Destination buttons to complete setup.
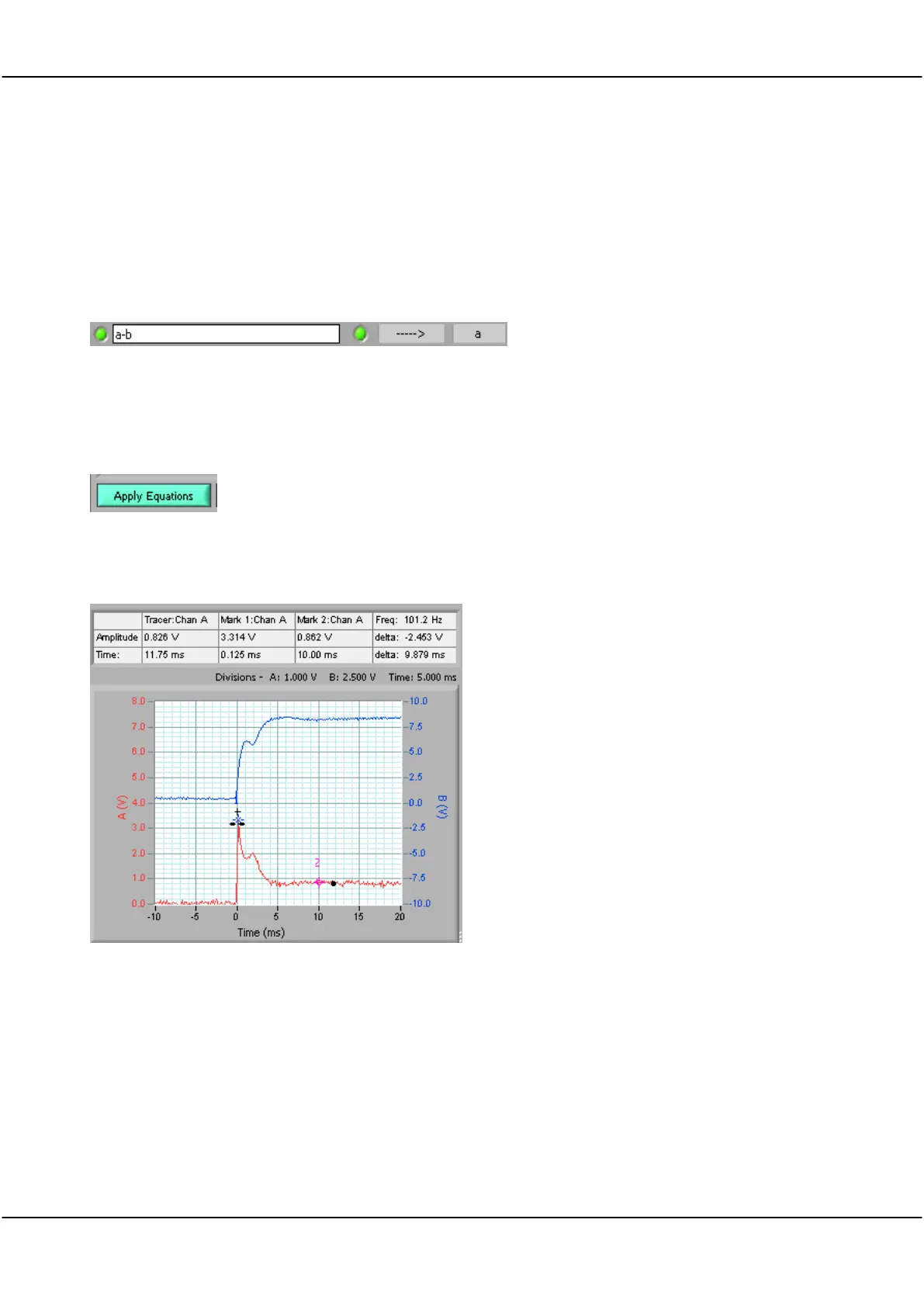
The a-b equation subtracts each sample value in channel B at a particular time, from the sample value in channel
A at the same time and then transfers it into channel A.
Channel B displays the actual voltage going into the unit being tested.
Click on Apply Equations to save the formula.
In the Cleverscope Control Panel window click the View menu option then click Maths Display.
The result of Maths with A-B A is the following graph:
19.6 Example - Deriving Current [Maths]
In the result graph we can see the current demand was initially high, and then fell back following start-up. It
would be more useful to have this result expressed in mA.
From V = IR, using a 1.4 ohm resistor,
I = V/R
= V x 1000 x 1/1.4 mA
= V x 714 mA
 Loading...
Loading...