XtraDrive User Manual Appendix C: Specifications for Peripheral Devices
C-17
! Regenerative Energy Calculation Method
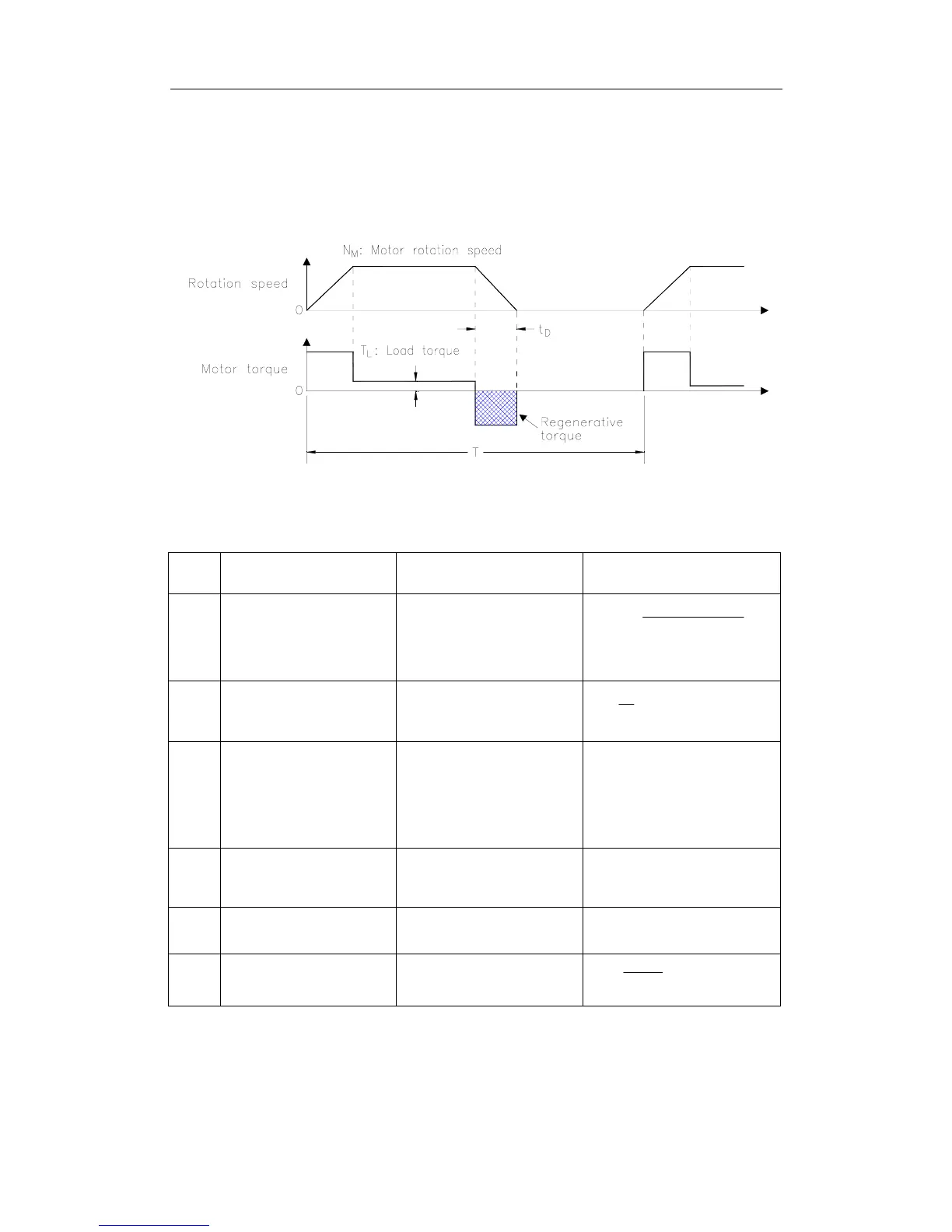
This section shows the procedure for calculating the regenerative
resistor capacity when acceleration and deceleration operation is as
shown in the following diagram.
Calculation Procedure
The procedure for calculating the capacity is as follows:
Step
Procedure
Units
[in. (mm)]
Equation
1
Find the rotational energy of
the servo system (E
S
).
E
S
= [Joules] = [J]=
[ oz·in·s
2
(kg·m
2
·s
2
)]
J
L
= J
M
= J
N
M
= rpm
E
S
=
()
182
Nx J J
2
MML
+
Where: N
M
= Motor speed
J
L
= Load Inertia
J
M
= Motor Inertia
2
Find the energy consumed
by
load system loss (E
L
) during
the deceleration period (t
D
).
τ
L
= oz·in (N·m)
E
L
= Joules = J
N
M
= rpm
t
D
= s
E
L
=
60
π
(N
M
x τ
L
x t
D
)
Where: τ
L
= Motor torque
3
Calculate the energy lost
(E
M
)
from servomotor winding
resistance.
t
D
= s = deceleration stopping
time
E
M
= Joules = J
E
M
= ( Value from the
“Servomotor Winding
Resistance Loss” graph below)
x t
D
4
Calculate the servo amplifier
energy (E
C
) that can be
absorbed.
E
C
= Joules = J
E
C
= Value from the
“Absorbable Servo Amplifier
Energy” graph below.
5
Find the energy consumed
by the regenerative resistor
(E
K
).
E
K
= E
S
=E
L
=E
M
= E
C
=
Joules = J
E
K
= E
S
— ( E
L
+E
M
+ E
C
)
6
Calculate the required
regenerative resistor
capacity (W
K
).
W
K
= W
E
K
= Joules = J
T = s
W
K
=
Tx 2.0
E
K
Where: T = Time
* 1. The “0.2” in the equation for calculating W
K
is the value for when the regenerative resistor’s
utilized load ratio is 20%.
If the previous calculation determines that the amount of regenerative power
(W
Wk
) that can be processed by the built-in resistor is not exceeded, then an
external regenerative resistor is not required.
 Loading...
Loading...











