Because RFL™ and Hubbell® have a policy of continuous product improvement, we reserve the right to change designs and specifications without notice.
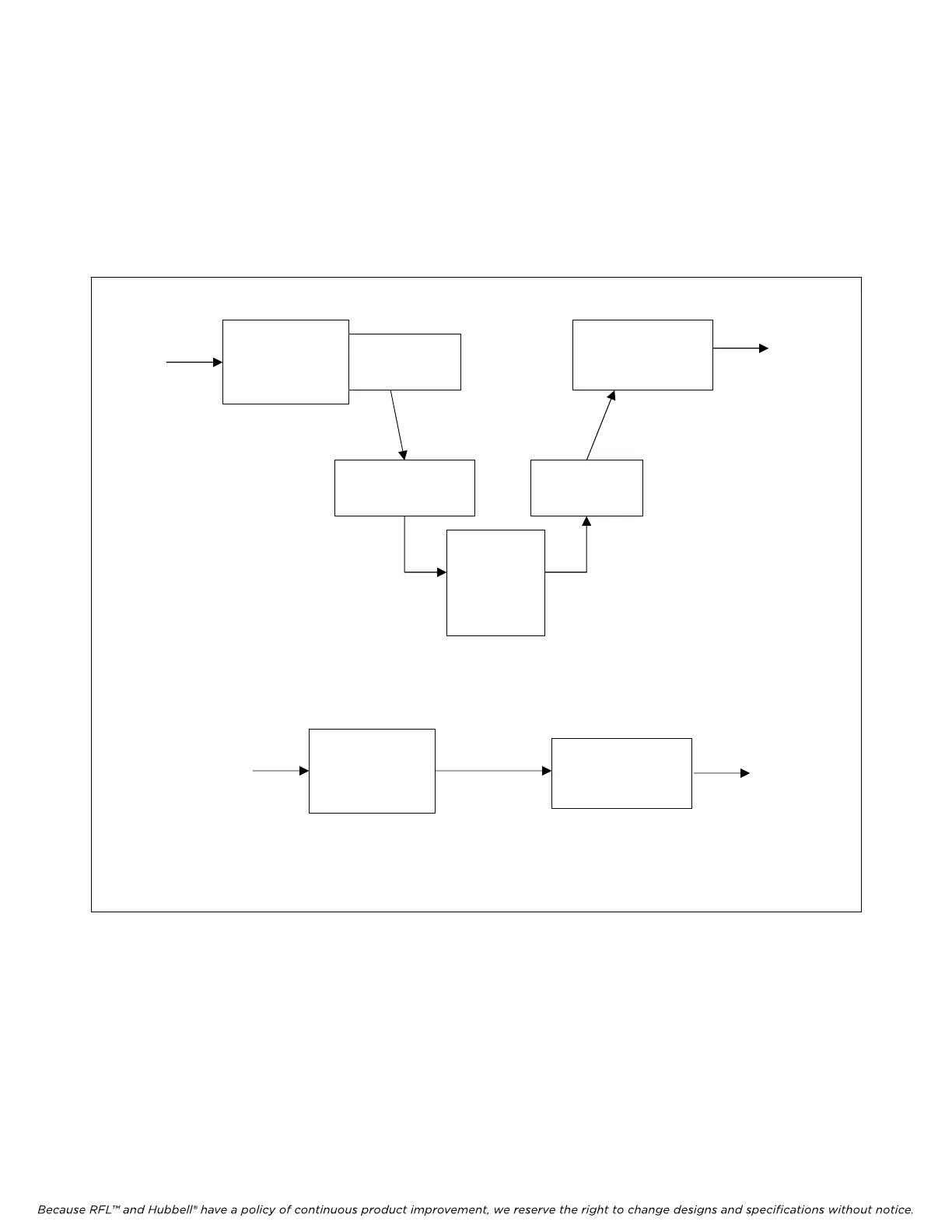
2.2.8 COMPARISON OF CROSS-CONNECT AND LINE-SWITCH MODES.
The DACS module can operate in one of two basic modes, Cross-Connect mode or Line-Switch mode.
The basic difference between the two is that Cross-Connect mode utilizes elastic stores and buffers for
interim storage of data, while Line Switch mode feeds the received DS1 stream directly to a
transmitter.
a. DACS Module Cross-Connect Mode
b. DACS Module Line-Switch Mode
DS0
disassembly
Timing,
framing
and DSO
grooming
engine
DS0
reassembly
DS1
receiver
Elastic data
store
DS1
transmitter
DS1
receiver
DS1
transmitter
Figure 2-7. DACS module Cross-Connect and Line-Switch mode data paths.
Cross-Connect mode provides great flexibility in handling payload data, and is inherently more stable
and immune to DS1-level disturbances.
On the other hand, Line Switch mode offers an order of magnitude shorter through-delay, which is
particularly important in sensitive teleprotection applications. In a typical network, a DS1 path may
cross each M-DACS twice and the delays add quickly. The need to remain within delay limits of the
equipment can easily trade off against other performance parameters. A comparison of the
characteristics of each of the two modes is shown in Table 2-1.
M-DACS-T1 RFL Electronics Inc.
October 16, 2012 2-8 (973) 334-3100
 Loading...
Loading...