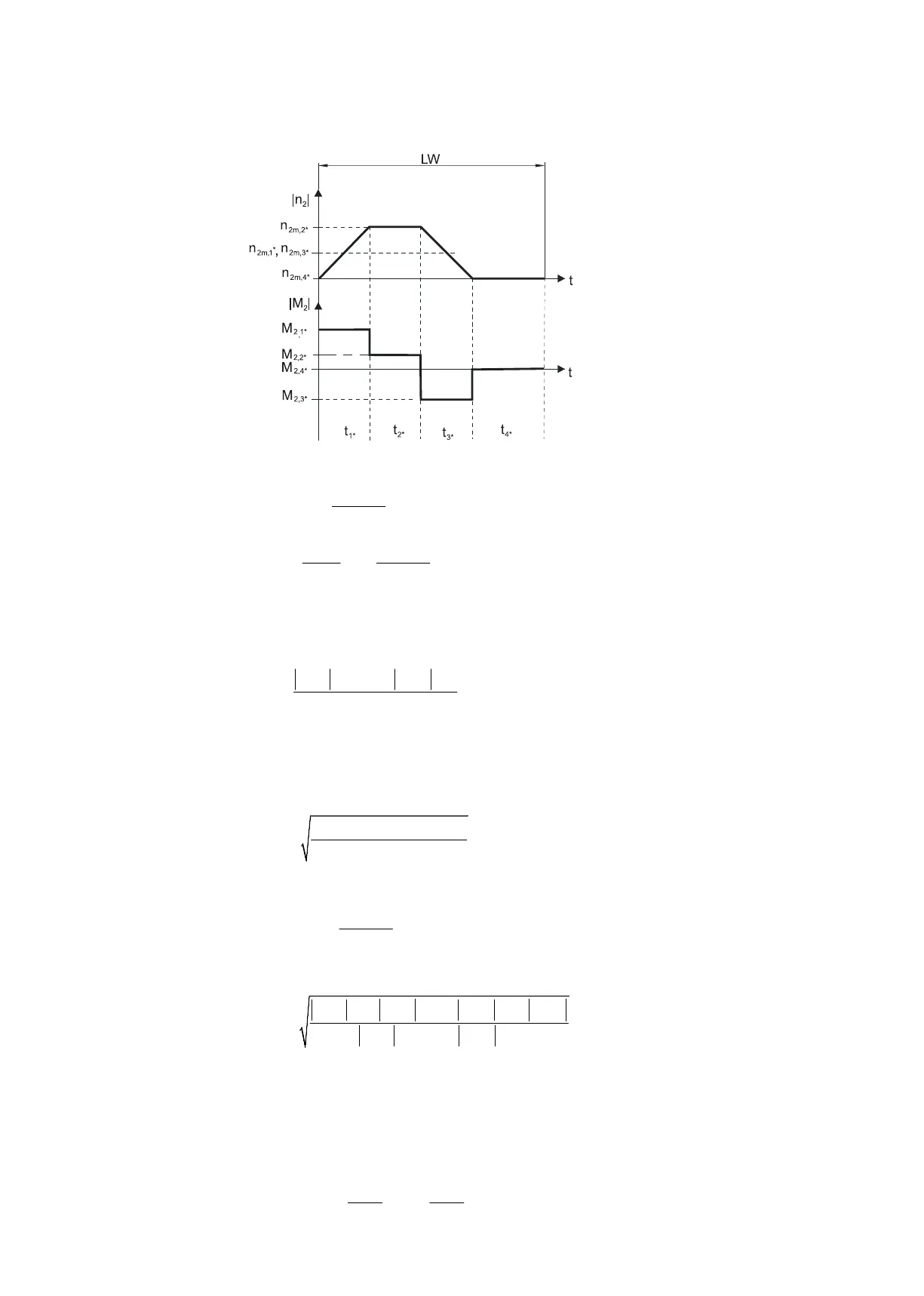
Example of cyclic operation
The following calculations are based on a representation of the power taken from the output based in ac-
cordance with the following example:
Calculation of the actual maximum acceleration torques
2
2acc * tot L*
n
M J M
9,55 t
D
= × +
× D
D
= + ×
× h × D
2acc *
1
1acc * 1
get
M
n
M J
i 9,55 t
Calculation of the actual average input speed
2m,1* 1* 2m,n* n*
2m*
1* n*
n t ... n t
n
t ... t
× + + ×
=
+ +
If t
1*
+ ... + t
3*
≥ 6min, calculate n
2m*
without the rest phase t
4*
.
The values for the ratio i can be found in the selection tables.
Calculation of the actual effective torque
2 2
1* 2,1* n* 2,n*
2eff *
1* n*
t M ... t M
M
t ... t
× + + ×
=
+ +
Calculation of the actual emergency-off torque
2
2NOT* tot L*
n
M J M
9,55 t
D
= × +
× D
Calculation of the actual equivalent torque
3 3
2m,1* 1* 2,1* 2m,n* n* 2,n*
3
2eq*
2m,1* 1* 2m,n* n*
n t M ... n t M
M
n t ... n t
× × + + × ×
=
× + + ×
Calculation of the thermal limit torque
Calculate the thermal limit torque M
2th
for a duty cycle ED
10
> 50% and the actual average input speed n
1m*
.
(At K
mot,th
≤ 0 you must reduce the average input speed n
1m*
accordingly or select another geared motor size.)
2th op mot,th
M M i K= × ×
3
th
1m*
mot,th T
a
n
K 0,93 fB
1000 1000
æ ö
= - × ×
ç ÷
è ø
Refer to the selection tables for the values of i and a
th
.
4 PHQplanetary geared motors 4.6 Project configuration
79
 Loading...
Loading...