ZXR10 GER (V2.6.03) General Excellent Router User Manual Volume-I
156 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
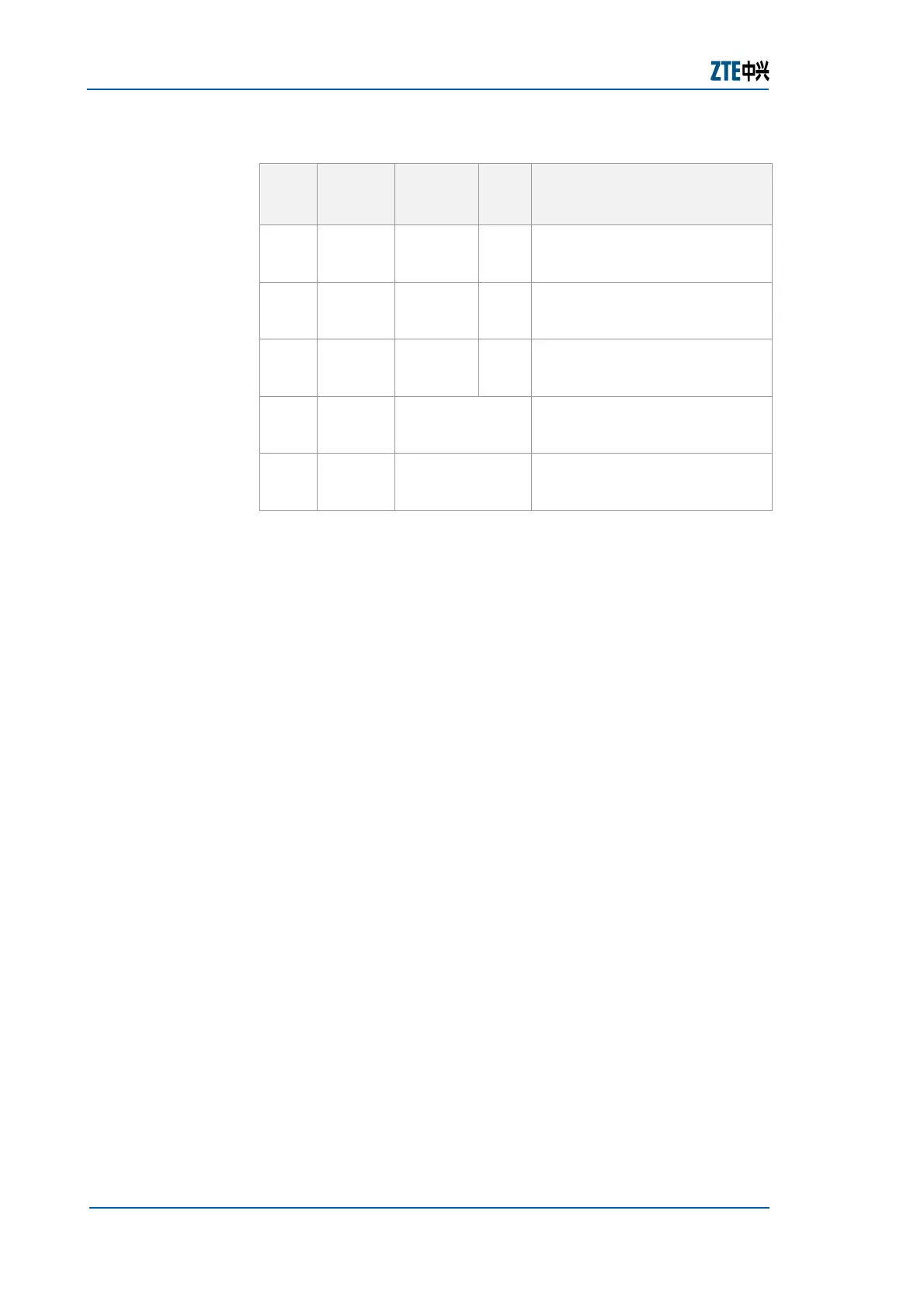
TABLE 195 IP ADDRESSES RANGE
Class
Feature
Bit of
Header
Network
Bit
Host
Bit
Range
Class
A
0 8 24 0.0.0.0~127.255.255.255
Class
B
10 16 16 128.0.0.0~191.255.255.255
Class
C
110 24 8 192.0.0.0~223.255.255.255
Class
D
1110 Multicast
address
224.0.0.0~239.255.255.255
Class
E
1111 Reserved 240.0.0.0~255.255.255.255
Among three classes (A, B and C) of IP addresses, some
addresses are reserved for private networks. This is
recommended that private network addresses must be used for
establishing internal networks. These addresses refer to:
Class A: 10.0.0.0~10.255.255.255
Class B: 172.16.0.0~172.31.255.255
Class C: 192.168.0.0~192.168.255.255
Address division is originally intended to facilitate design of
routing protocols, so that header feature bit of an IP address is
enough for judging type of a network. However, classification
method restricts utilization of address space to greatest extent.
With rapid expansion of Internet, problem of insufficient
addresses becomes more and more serious.
To utilize IP addresses to greater extent, a network can be
divided into multiple subnets. The "bit borrowing" mode can be
used: highest bits of host bits are borrowed to serve as subnet
bits and left host bits still serve as host bits. Thus structure of an
IP address consists of three parts: Network bits, subnet bits and
host bits.
Network bits and subnet bits are used to uniquely identify a
network. Use subnet mask to find which part in IP address
indicates network bits and subnet bits, which part stands for
host bits. The part with subnet mask of "1" corresponds to
network bits and subnet bits of IP address, while the part with
subnet mask of "0" corresponds to host bits.
Division of subnets greatly improves utilization of IP addresses,
which relieves the problem of insufficient IP addresses to some
extent.
(0.0.0.0) is used when a host without an IP address is
started. RARP, BOOTP and DHCP are used to obtain IP
Subnets
Regulations on
IP addresses:

 Loading...
Loading...