572 Chapter 16
W-CDMA Uplink Digital Modulation for Receiver Test
W-CDMA Uplink Concepts
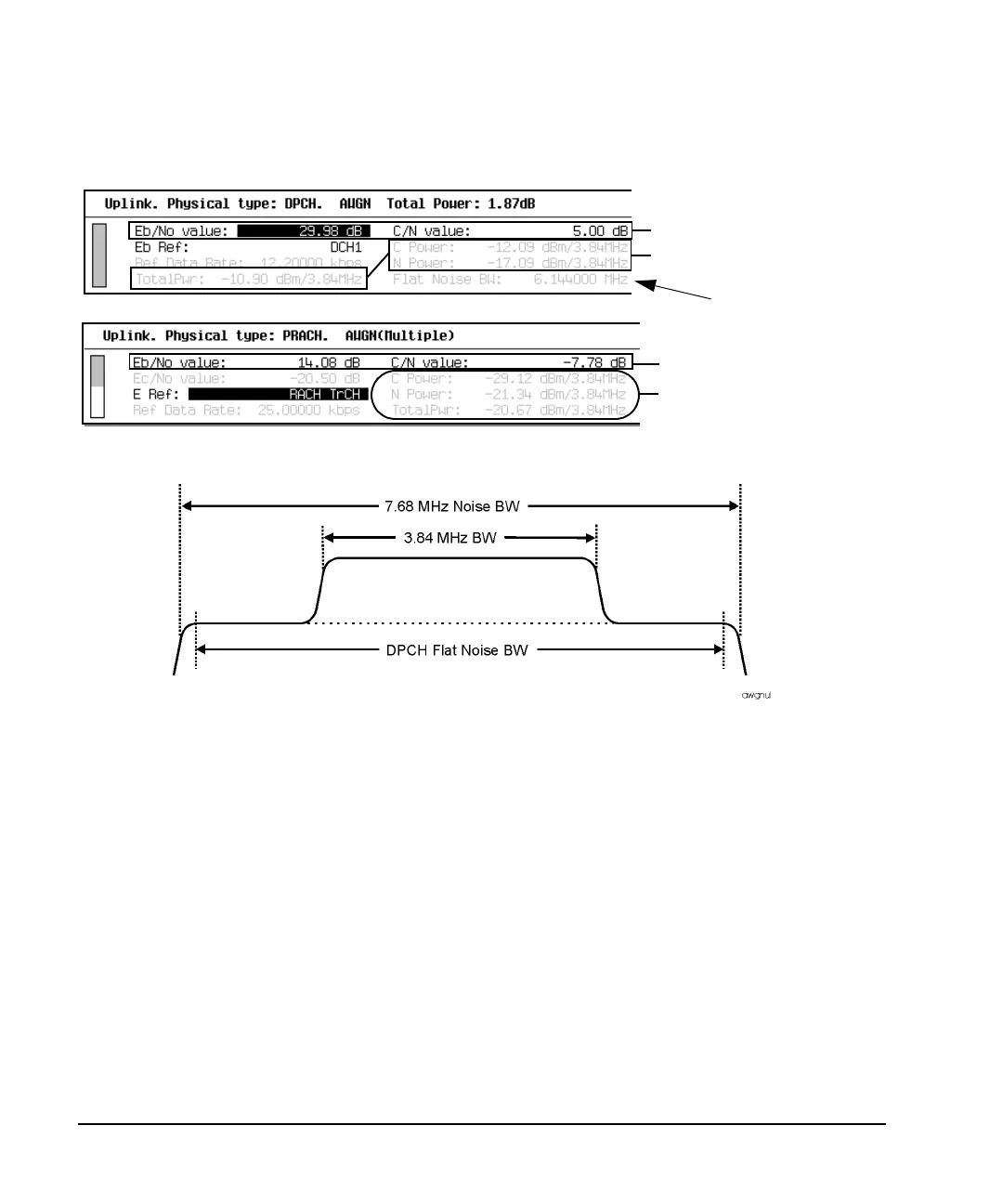
Figure 16-87 Noise Measurement Bandwidths
As shown in Figure 16-87, the noise signal is added to the W-CDMA signal across the entire W-CDMA
signal spectrum. The ESG gives you two ways to control the noise level. You can adjust the noise using
either E
b
/N
o
(energy per bit to noise power density ratio) or C/N (carrier power to noise power ratio). Any
adjustment to either noise parameter, E
b
/N
o
or C/N, will affect the other; they are not mutually exclusive.
E
b
/N
o
lets you set the noise ratio relative to the power of the data stream for the selected reference channel,
versus setting the noise relative to the carrier power (C/N). For example, if you have the RACH transport
channel selected as the data source (Eb Ref field, see Figure 16-88) with a 12.2 kbps data rate, the
bandwidth for the data is 12.2 kHz. The data within this bandwidth has a certain power level. This power
level is what is used in the ratio for E
b
/N
o
.
When you use E
b
/N
o
, you can select the reference to use as the data power source. For example, you can use
any of the transport channels for the DPDCH, the PRACH transport channel, the PRACH preamble, or the
DPCCH. Your choice does depend on whether you are using the PRACH or the DPCH mode. Figure 16-88
shows the PRACH data sources that can be used for E
b
/N
o
.
DPCH 3.84 MHz Values
PRACH 3.84 MHz Values
Flat Noise Bandwidth
AWGN 7.68 MHz Entries
AWGN 7.68 MHz Entries
 Loading...
Loading...

















