94
History group
The history group defines that the system periodically collects traffic statistics on interfaces and saves the
statistics in the history record table (ethernetHistoryTable). The statistics include bandwidth utilization,
number of error packets, and total number of packets.
The history statistics table record traffic statistics collected for each sampling interval. The sampling
interval is user-configurable.
Event group
The event group defines event indexes and controls the generation and notifications of the events
triggered by the alarms defined in the alarm group and the private alarm group. The events can be
handled in one of the following ways:
• Log—Logs event information (including event time and description) in the event log table so the
management device can get the logs through SNMP.
• Trap—Sends an SNMP notification when the event occurs.
• Log-Trap—Logs event information in the event log table and sends an SNMP notification when the
event occurs.
• None—No action.
Alarm group
The RMON alarm group monitors alarm variables, such as the count of incoming packets (etherStatsPkts)
on an interface. After you define an alarm entry, the system gets the value of the monitored alarm
variable at the specified interval. If the value of the monitored variable is greater than or equal to the
rising threshold, a rising event is triggered. If the value of the monitored variable is smaller than or equal
to the falling threshold, a falling event is triggered. The event is then handled as defined in the event
group.
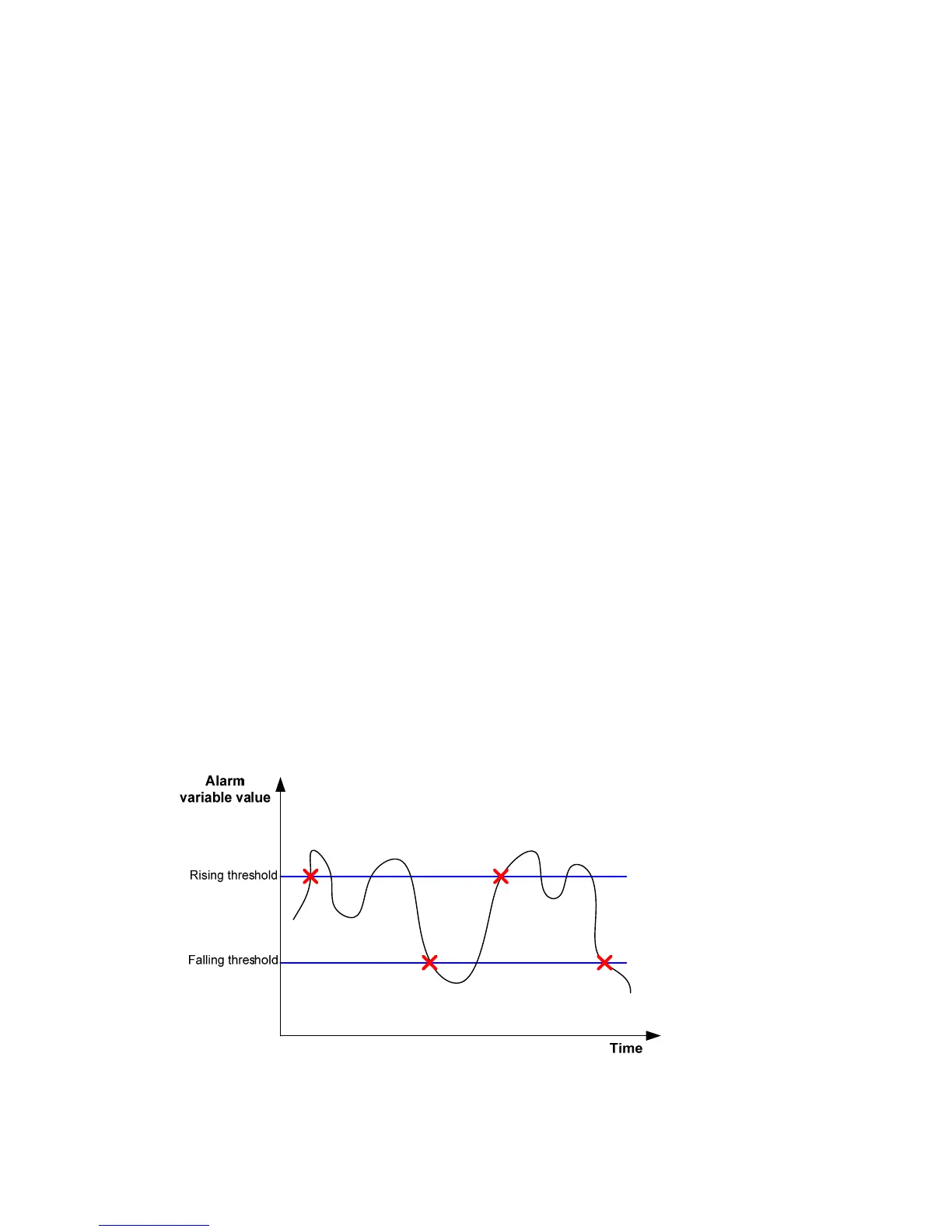
If an alarm entry crosses a threshold multiple times in succession, the RMON agent generates an alarm
event only for the first crossing. For example, if the value of a sampled alarm variable crosses the rising
threshold multiple times before it crosses the falling threshold, only the first crossing triggers a rising alarm
event, as shown in Figure 79.
Figure 79 Rising and falling alarm events

 Loading...
Loading...