Type
Displays the client type:
• Dynamic—The IP-to-MAC binding is generated dynamically.
• Static—The IP-to-MAC binding is configured manually. Static bindings are not
supported.
Interface Name Displays the device interface to which the client is connected.
VLAN Displays the VLAN to which the device belongs.
Remaining Lease Time Displays the remaining lease time of the IP address.
DHCP snooping configuration example
Network requirements
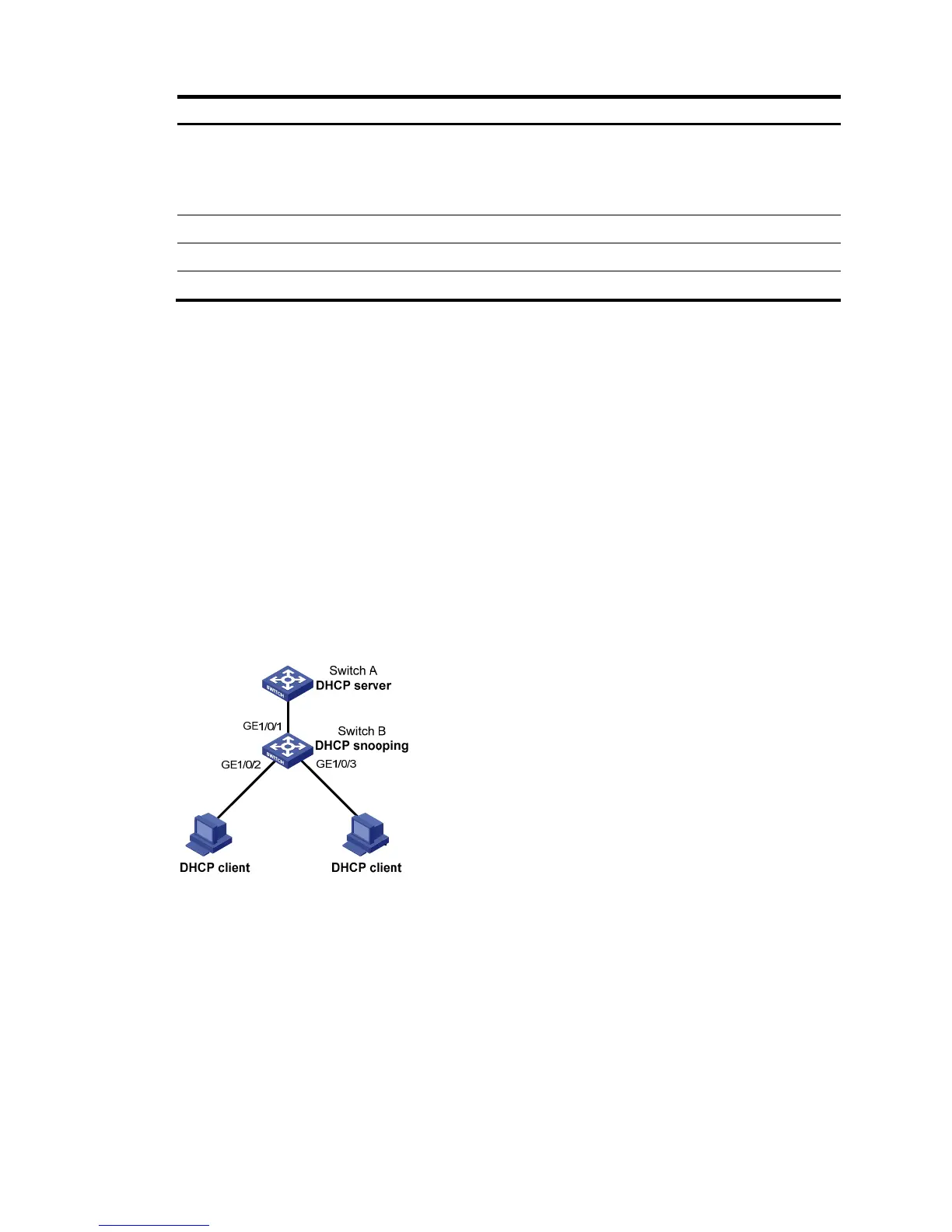
As shown in Figure 288, a DHCP snooping device (Switch B) is connected to a DHCP server through
GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, and to DHCP clients through GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and GigabitEthernet
1/0/3.
• Enable DHCP snooping on Switch B and configure DHCP snooping to support Option 82.
Configure the handling strategy for DHCP requests containing Option 82 as replace.
• Enable GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to forward DHCP server responses. Disable GigabitEthernet 1/0/2
and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 from forwarding DHCP server responses.
• Configure Switch B to record clients' IP-to-MAC address bindings in DHCP-REQUEST messages and
DHCP-ACK messages received from a trusted port.
Figure 288 Network diagram
Configuring Switch B
1. Enable DHCP snooping:
a. From the navigation tree, select Network > DHCP.
b. Click the DHCP Snooping tab.
c. As shown in Figure 289, selec
t the Enable option next to DHCP Snooping to enable DHCP
snooping.

 Loading...
Loading...