420
queue with the lowest priority is assured of at least 5 Mbps of bandwidth, avoiding the disadvantage of
SP queuing that packets in low-priority queues may fail to be served for a long time.
Another advantage of WRR queuing is that while the queues are scheduled in turn, the service time for
each queue is not fixed, that is, if a queue is empty, the next queue will be scheduled immediately. This
improves bandwidth resource use efficiency.
You can assign the output queues to WRR priority queue group 1 and WRR priority queue group 2.
Round robin queue scheduling is performed for group 1 first. If group 1 is empty, round robin queue
scheduling is performed for group 2.
NOTE:
You can implement SP+WRR queue scheduling on a port by assigning some queues on the port to the SP
scheduling group when configuring WRR. Packets in the SP schedulin
by SP. When the SP scheduling group is empty, the other queues are scheduled by WRR.
Line rate
Line rate is a traffic control method using token buckets. The line rate of a physical interface specifies the
maximum rate for forwarding packets (including critical packets). Line rate can limit all the packets
passing a physical interface.
Traffic evaluation and token bucket
A token bucket can be considered as a container holding a certain number of tokens. The system puts
tokens into the bucket at a set rate. When the token bucket is full, the extra tokens will cause the token
bucket to overflow.
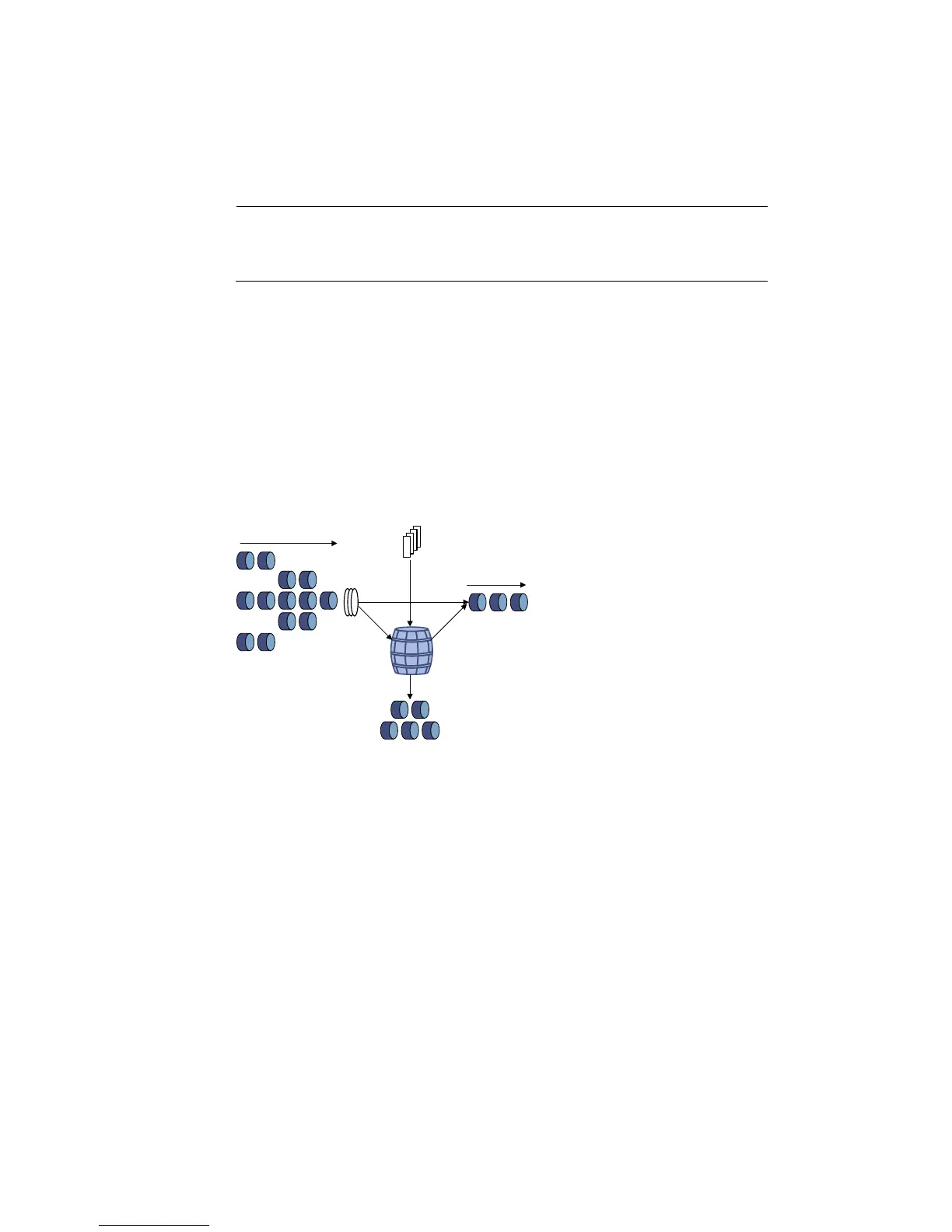
Figure 394 Evaluate traffic with the token bucket
Token
bucket
Packets dropped
Packet
classification
Packets to be sent
through this interface
Packets sent
Tokens are put into the
bucket at the set rate
The evaluation for the traffic specification is based on whether the number of tokens in the bucket can
meet the need of packet forwarding. If the number of tokens in the bucket is enough to forward the
packets (generally, one token is associated with a 1-bit forwarding authority), the traffic conforms to the
specification, and the traffic is called conforming traffic; otherwise, the traffic does not conform to the
specification, and the traffic is called excess traffic.
A token bucket has the following configurable parameters:
Mean rate—The rate at which tokens are put into the bucket (the permitted average rate of traffic).
It is usually set to the committed information rate (CIR).

 Loading...
Loading...











