Gocator Line Profile Sensors: User Manual
Gocator Web Interface • 244
the region of interest for a measurement is positioned in, as well as the coordinate reference used to
output measurement values.
For example, if you need to measure the average height in a certain location relative to the sensor's field
of view regardless of the objects passing under the sensor, the frame of reference should be set to
Sensor. This is typical in applications where a wide web of material is continuously scanned, such as
paper, rubber, fabrics, etc. If on the other hand you need to measure the average height in a certain
location of a scanned object, the frame of reference should be set to Part. This is typical in applications
where discrete objects pass under the sensor and specific locations on the objects need to be inspected.
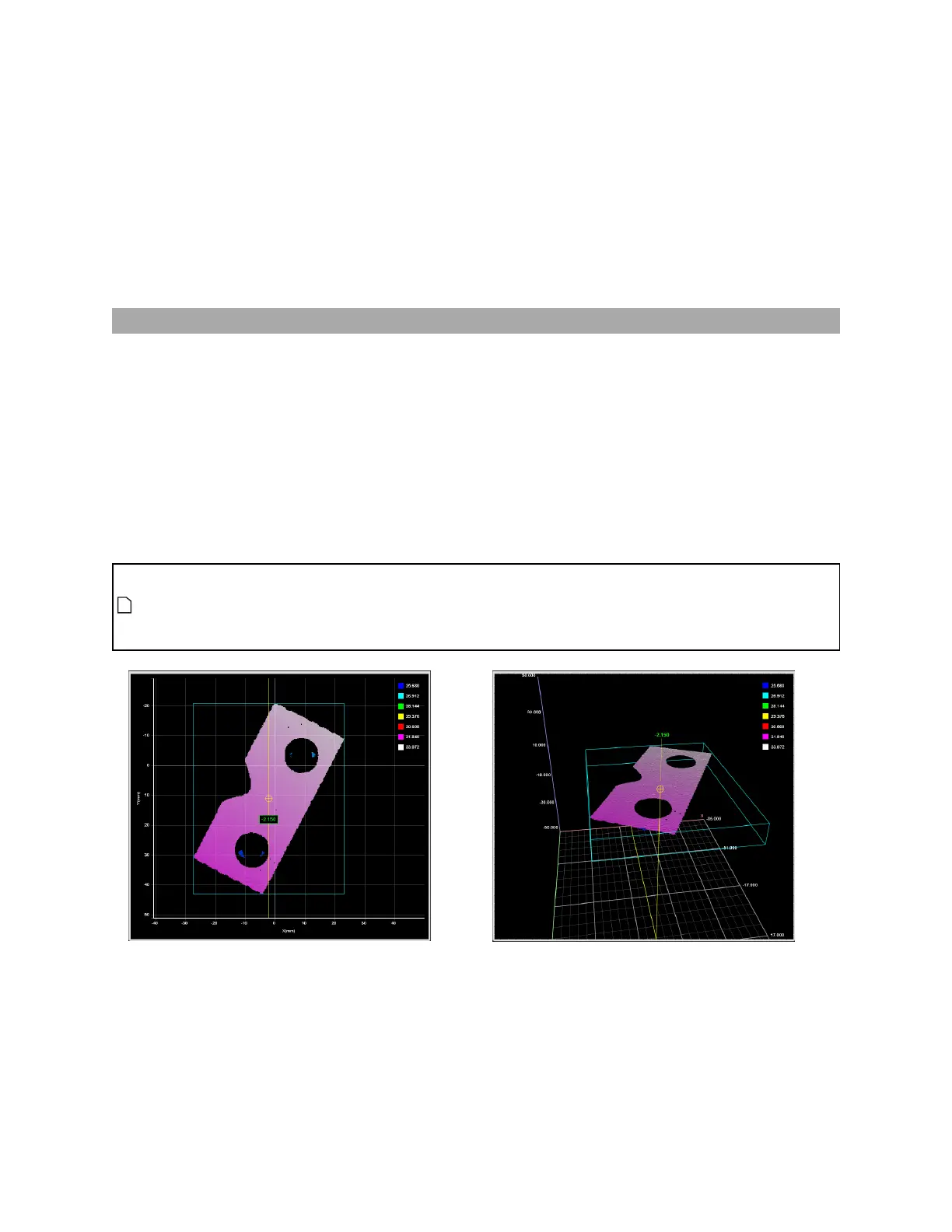
Bounding Box
The Bounding Box tool provides measurements related to the smallest box that contains the part (for
example, X position, Y position, width, length, etc.).
Gocator compares the measurement value with the values in Min and Max to yield a decision. For more
information on decisions, see Decisions on page 191.
See Adding and Configuring a Measurement Tool on page 182 for instructions on how to add
measurement tools.
A bounding box can be vertical or rotated. A vertical bounding box provides the absolute position from
which the Position centroids tools are referenced.
The vertical bounding box X and Y correspond to the part frame of reference origin. For this reason
all X and Y measurements (except Bounding Box Global X and Global Y) are referenced to this point
when Frame of Reference on the Part Detection panel is set to Part. See Part Detection on page
137 for more information.
2DView
3DView
 Loading...
Loading...

