R.4.6
SEL-421 Relay Reference Manual Date Code 20111215
Communications Interfaces
Communications Card
The SEL-421 uses the IPADDR and SUBNETM settings to determine its local
network and node address. The SUBNETM setting defines the subnet mask.
The subnet mask divides the local node IP address into two parts, a network
number and a node address on that network. A subnet mask is four bytes of
information and is expressed in the same format as an IP address.
The SEL-421 uses the DEFRTR address setting to determine how to
communicate with nodes on other local networks. The SEL-421
communicates with the default router to send data to nodes on other local
networks. If you change the DEFRTR setting from the default value of Null
(meaning that there is no default router), then the default router must be on the
same local network as the SEL-421 or the SEL-421 will reject the DEFRTR
setting. You must also coordinate the default router with your general network
implementation and administration plan. See Table 4.4 for examples of how
IPADDR and SUBNETM define the network and node and how these settings
affect the DEFRTR setting.
If the SEL-421 is purchased with IEC 61850 support, the ETCPKA setting,
along with the KAIDLE, KAINTV, and KACNT settings, can be used to
verify that the computer at the remote end of a TCP connection is still
available. If ETCPKA is enabled and the SEL-421 does not transmit any TCP
data within the interval specified by the KAIDLE setting, the SEL-421 sends a
keep-alive packet to the remote computer. If the SEL-421 does not receive a
response from the remote computer within the time specified by KAINTV, the
keep-alive packet is re-transmitted as many as KACNT times. After this count
is reached, the SEL-421 remote device is no longer available, so the SEL-421
can terminate the connection without waiting for the idle timer (TIDLE or
FTPIDLE) to expire.
The SEL-421 Ethernet card operates over either twisted-pair or fiber-optic
media. Each Ethernet card is equipped with two network ports. With an initial
ordering option, you can select the medium for each port (10/100 Mbps
twisted pair or 100 Mbps fiber optic). Speeds for the physical media are fixed
for fiber-optic connections. For twisted-pair connections, the Ethernet card
can auto-detect the network speed or you can set a fixed speed.
Network Port Fail-Over Operation
The SEL-421 Ethernet card has two network ports. Network port fail-over
mode enables the Ethernet card to operate as a single network adapter with a
primary and standby physical interface. You can connect the two network
ports to the same network or different networks depending on your specific
Ethernet network architecture. If you have a single network and want to use
only one network port, set NETPORT to the port you want to use and set
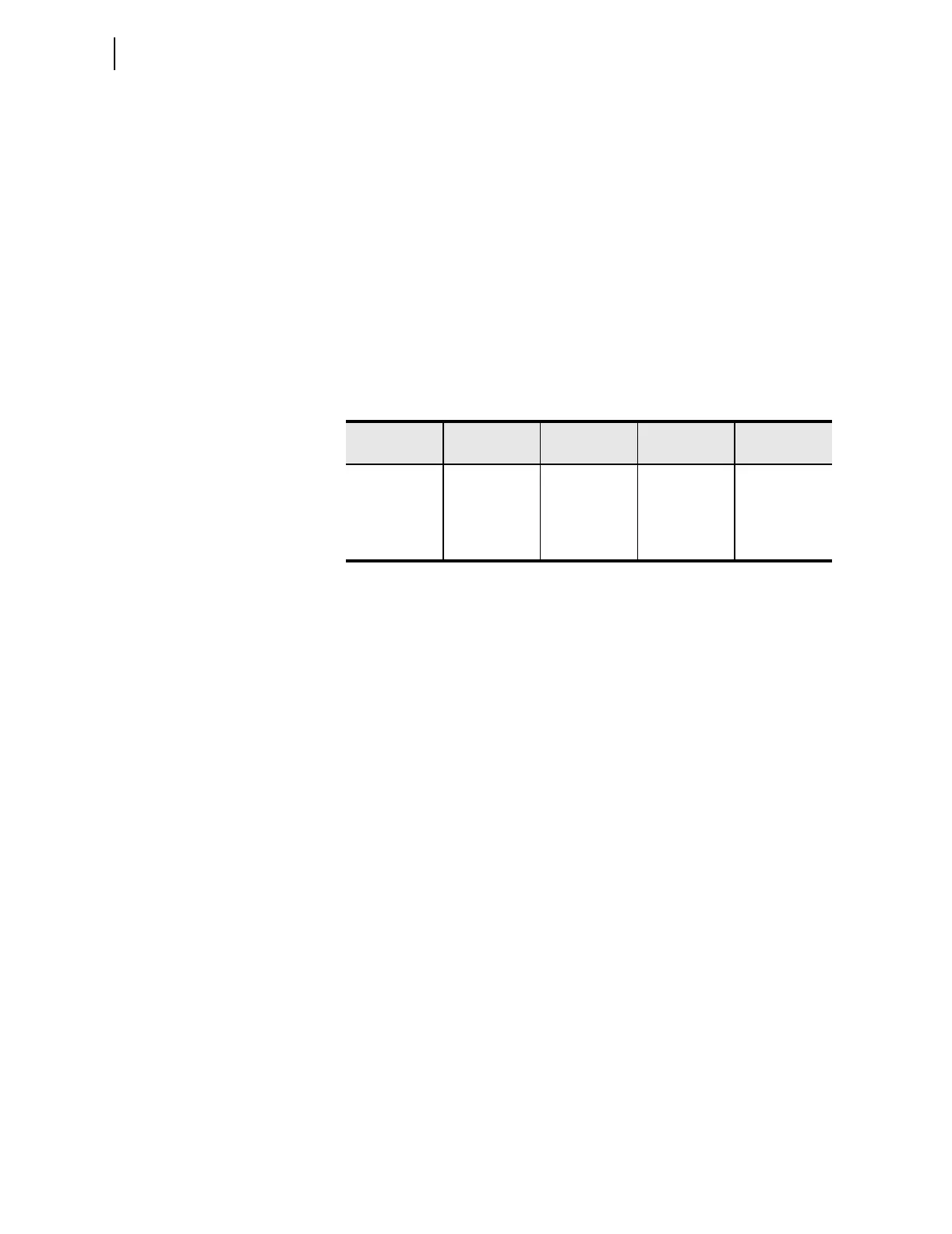
Table 4.4 DEFRTR Address Setting Examples
IPADDR SUBNETM
Network
Number
Node Address DEFRTR
192.92.92.92 255.255.255.0 192.92.92 92 192.92.92.a
a
a
Value in the range 0–255.
192.92.92.92 255.255.0.0 192.92 92.92 192.92.a
a
, b
a
192.92.92.92 255.0.0.0 192 92.92.92 192.a
a
, b
a
, c
a
192.92.92.92 0.0.0.0 n/a 192.92.92.92 a
a
, b
a
, c
a
, d
a

 Loading...
Loading...