R.4.9
Date Code 20111215 Reference Manual SEL-421 Relay
Communications Interfaces
Communications Card
ERR.TXT file contains any error messages generated by the Ethernet card and
host pertaining to these files.
The Ethernet card creates a subdirectory for each virtual device in the host.
The subdirectory name is DDnn_DeviceID, where nn is the virtual device
number and DeviceID is the device name derived from an identification string
stored in the host that is associated with the virtual device. The Ethernet card
uses the first identification string that it finds in the PORTID, DEVICEID, and
FIDID strings. The same substitution rules that govern substitutions for the
host subdirectory name govern creation of the substring. For example, if you
have an SEL-351 connected to an SEL-2030 on Port 3 with a PORTID setting
of “Feeder 1,” the subdirectory name will be “DD03_Feeder_1.”
Each virtual device subdirectory contains files that represent valid host data
regions associated with the virtual device. Data region files provide snapshots
of the corresponding host database regions. When an FTP client requests the
file, the Ethernet card sends a file containing values from the host database
region. If the voltage VA is 12.47 kV when you make an FTP request for the
METER.TXT file, then the file METER.TXT will contain VA = 12.47. If you
request the file at another time, when VA is 12.40, the file will contain
VA = 12.40. Two file formats are available, ASCII text and compressed ASCII
(CASCII). Names of the files correspond to the data region name (i.e.
METER.TXT, METER.CAS).
Access Control
FTP settings control some basic file access features. The host is responsible
for maintaining names and passwords for access control. The special FTP user
name “anonymous” does not require a password. It has the same access rights
as the user name in the FTPAUSR setting. For example, if FTPAUSR is set to
ACC, the FTP anonymous user has Access Level 1 rights. See the host-
specific sections for additional information about access rights. Table 4.7 lists
the settings that affect FTP server operation.
NOTE: SEL advises against enabling
anonymous FTP logins (FTPANMS = Y)
except under test conditions. The
Ethernet card does not require a
password for the special FTP user
name “anonymous.” If you enable
anonymous FTP logins, you are
allowing unrestricted access to the
Ethernet card and host files.
Telnet
Telnet is also part of the TCP/IP protocol suite. You can use Telnet to establish
terminal access to a remote device. A Telnet connection provides access to the
user interface of either the host or the Ethernet card. Host user interface access
is similar to an ASCII terminal connection to the front port of an SEL device.
You can use Telnet in the Ethernet card in one of three ways:
1. Connect from your PC to the Ethernet card user interface.
2. Connect from your PC to the host user interface.
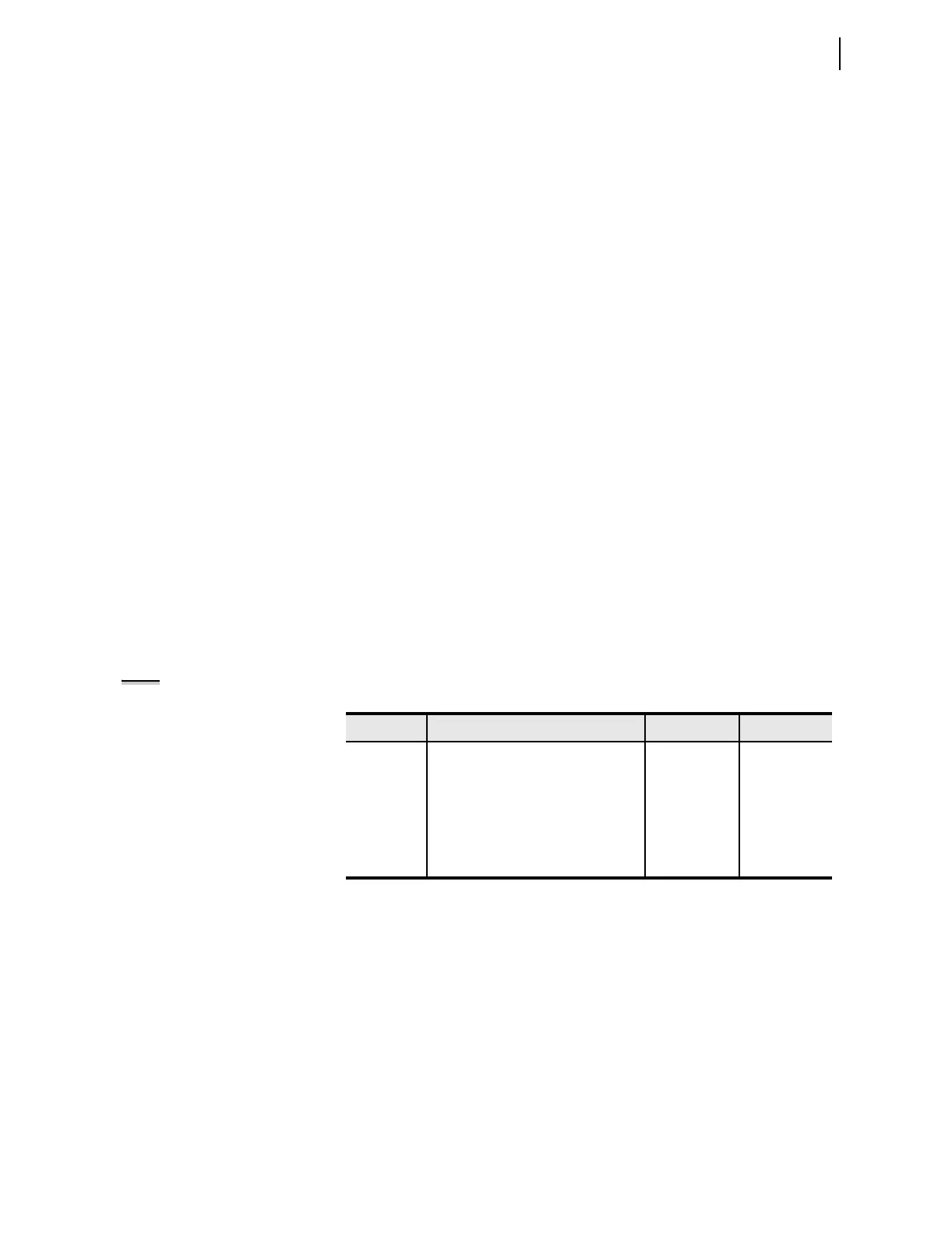
Table 4.7 Ethernet Card FTP Settings
Label Description Range Default
FTPSERV
a
a
If you change these settings and accept the new settings, the Ethernet card closes all active
network connections and briefly pauses network operation.
FTP session enable Y, N N
FTPCBAN FTP connect banner 254 characters FTP SERVER:
FTPIDLE
a
FTP connection timeout 5–255 minutes 5
FTPANMS
a
Anonymous login enable Y, N N
FTPAUSR Host user from which anonymous FTP
client inherits access rights
See host-
specific section
Empty String
 Loading...
Loading...