R.5.15
Date Code 20111215 Reference Manual SEL-421 Relay
SEL Communications Protocols
SEL MIRRORED BITS Communications
SEL MIRRORED BITS Communications
Overview
With SEL-patented MIRRORED BITS communications protocol, protective
relays and other devices can directly exchange information quickly, securely,
and with minimal cost. Use M
IRRORED BITS communications for remote
control, remote sensing, or communications-assisted protection schemes such
as POTT and DCB.
SEL products support several variations of M
IRRORED BITS communications
protocols. Through port settings, you can set the SEL-421 for compatible
operation with SEL-300 series relays, the SEL-2505 or SEL-2506 Remote I/O
Modules, and the SEL-2100 Protection Logic Processors. These devices use
M
IRRORED BITS communications to exchange the states of eight logic bits.
You can also use settings to select extensions of the M
IRRORED BITS
communications protocols, available only in SEL-400 series relays, to
exchange analog values, synchronize clocks, and engage in virtual terminal
dialogs. Table 5.14 summarizes M
IRRORED BITS communications features.
Communications
Channels and Logical
Data Channels
The SEL-421 Relay supports two MIRRORED BITS communications channels,
designated A and B. Use the port setting PROTO to assign one of the
M
IRRORED BITS communications channels to a serial port; PROTO := MBA
for M
IRRORED BITS communications Channel A or PROTO := MBB for
M
IRRORED BITS communications Channel B.
Transmitted bits include TMB1A–TMB8A and TMB1B–TMB8B. The last
letter (A or B) designates with which channel the bits are associated. These
bits are controlled by SEL
OGIC
®
control equations. Received bits include
RMB1A–RMB8A and RMB1B–RMB8B. You can use received bits as
arguments in SEL
OGIC control equations. The channel status bits are ROKA,
RBADA, CBADA, LBOKA, ROKB, RBADB, CBADB, LBOKB, DOKA,
ANOKA, DOKB, and ANOKB. You can also use these bits as arguments in
SEL
OGIC control equations. Use the COM command for additional channel
status information.
Within each M
IRRORED BITS communications message for a given channel (A
or B), there are eight logical data channels (1–8). In operation compatible with
other SEL products, you can use the eight logical data channels for TMB1
through TMB8. If you use fewer than eight transmit bits, Data Channel 8 is
reserved to support data framing and time synchronization features. You can
assign the eight logical data channels as follows:
➤ Logic Bits. Setting MBNUM controls the number of channels
used for logic bits, TMB1–TMB8, inclusive.
➢ If you set MBNUM to 8, then you cannot use channels
for any of the following features.
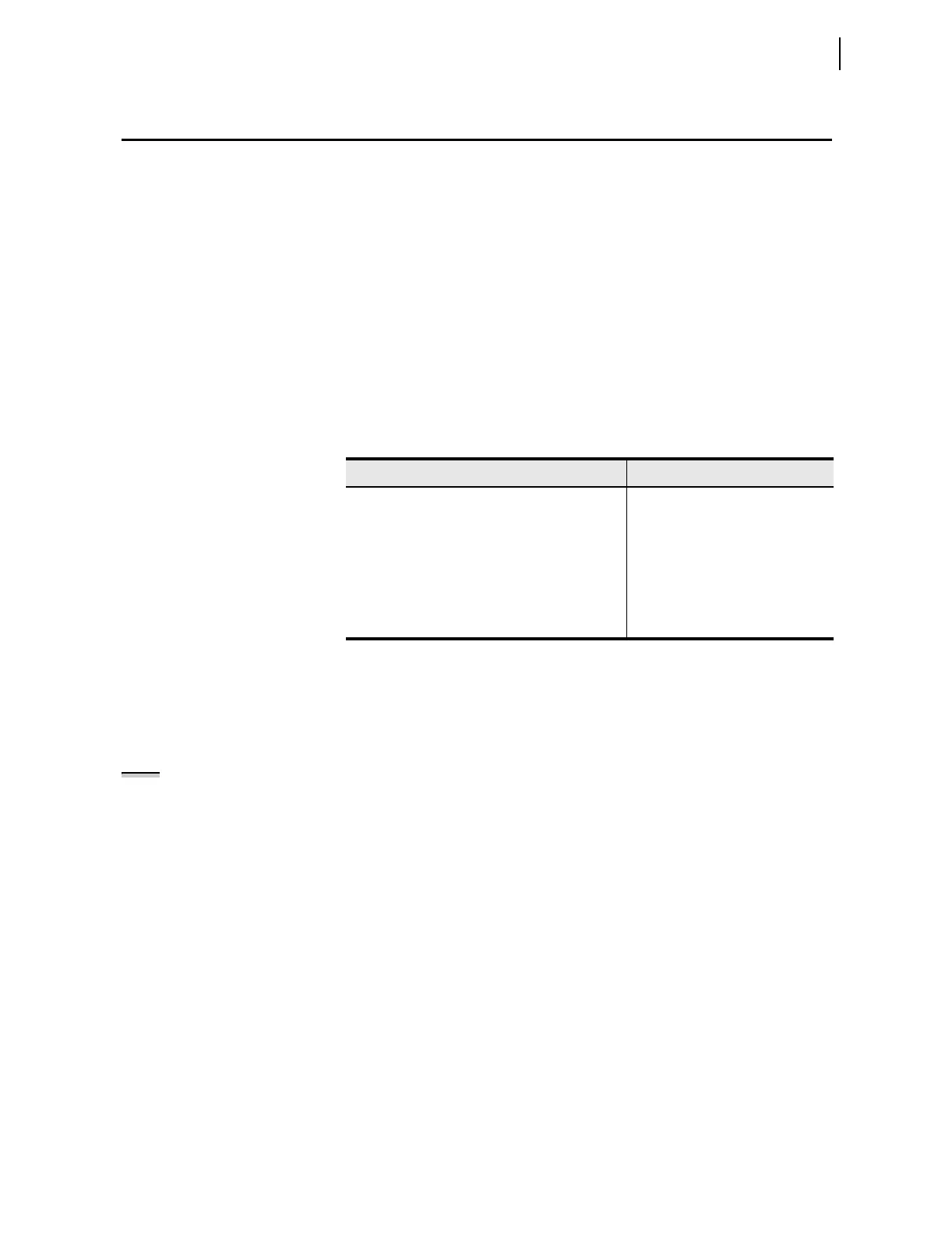
Tabl e 5 . 14 MIRRORED BITS Communications Features
Feature Compatibility
Transmit and receive logic bits SEL-300 series relays, SEL-2505,
SEL-2506, SEL-2100, SEL-400
series relays
Transmit and receive analog values SEL-400 series relays
Synchronize time SEL-400 series relays
Send and receive virtual serial port characters SEL-400 series relays
Support synchronous communications channel SEL-400 series relays
NOTE: Complete all of the port
settings for a port that you use for
M
IRRORED BITS communications before
you connect an external M
IRRORED BITS
communications device. If you
connect a M
IRRORED BITS
communications device to a port that
is not set for M
IRRORED BITS
communications operation, the port
will be continuously busy.
 Loading...
Loading...