204
9. APPENDICES
9.3 CORNEAL ALIGNING DEVICE
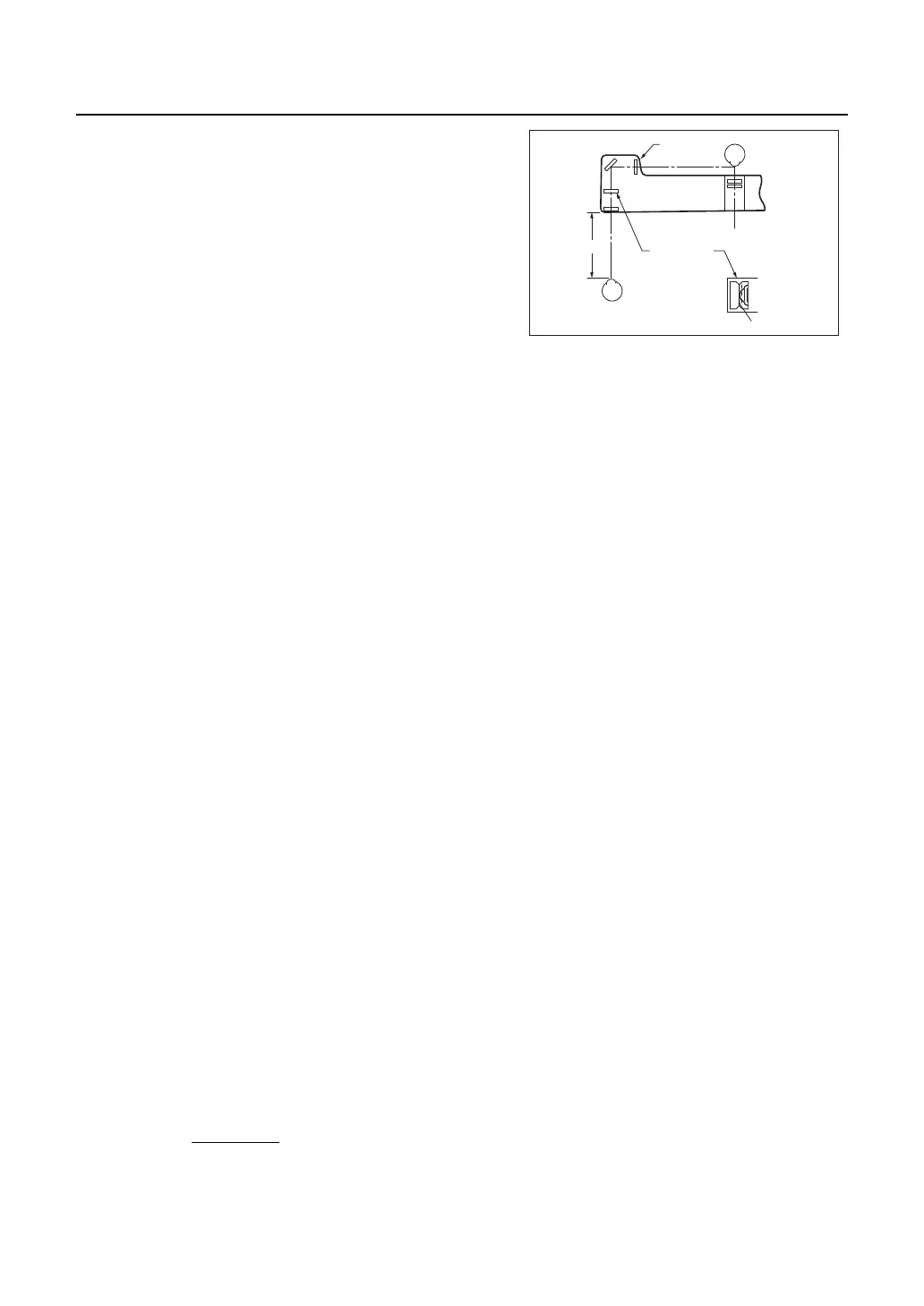
The forehead rest moves back and forth by turning
the forehead rest knob.
With the patient's forehead resting on the forehead
rest, the user look through the corneal aligning win-
dow with their eye positioned 25 cm from the cor-
neal aligning window.
Look at the patient's eye (corneal surface) so that
the long lines of the collimation and scale are
aligned.
If the eye (corneal surface) is on the long line, the
eyeglass refractive power will be measured at a distance of 12mm away from the surface of
cornea. The short lines are given at 2mm steps from the long line. The dotted line is 13.75mm
away from the corneal surface.
For example, if the corneal surface is 4mm away (on the second short line from the long line),
the eyeglass refractive power is measured at the position of "12+4=16mm".
If the eyeglass wearing distance defers from the measuring distance, a conversion should be
made referencing Tables 1 and 2.
Example 1:
When the measuring distance is 4mm from the long line (on the second short line) and the
prescription is the spherical power of +8.00D:
On Table 1, the intersection of "+8.00D" and "4mm" is the correction value "+0.26D".
Therefore, the lens refractive power at 12mm from the eye is "(+8.00) + (+0.26) = +8.26D".
After the conversion, the value needs to be rounded by either 0.25D or 0.12D.
In this case, the value is +8.25D.
Example 2:
When the measuring distance is 3mm from the long line (between the first and second short
lines) and the prescription is the spherical power of -10.50D:
When an intermediate value of the
conversion
values on the intersections of "-10.00D" and "-
11.00D" with "3mm" on Table 2 is calculated, it is 0.32. This value should be regarded as the cor-
rection value. Therefore, the lens refractive power at 12mm from the eye is calculated as follows.
(-10.50) + (+0.32) = -10.18D
Example 3:
When the measuring distance is 6mm from the long line (on the third short line) and the pre-
scription is the spherical power of -14.00D and the cylinder power of -6.00D:
On Table 2, the intersection of "-14.00D" and "6mm" is the conversion value "+1.08D".
Therefore, the lens refractive power at 12mm from the eye is "(-14.00) + (+1.08) = -12.92D".
For the cylinder power, perform the calculation "(-14.00) + (-6.00) = -20.00D".
The intersection of "-20.00D" and "6mm" is the conversion value "+2.14D".
Therefore, the lens refractive power at 12mm from the eye is "(-20.00) + (+2.14) = -17.86D".
Perform the calculation "(-17.86) – (-12.92) = -4.94D".
The spherical power "-12.92D" and the cylinder power "-4.94D" would be calculated.
If the difference between the measured refractive power or measuring distance and the eye-
glass wearing distance is odd, use the formula below:
Scale
Patient’s eyes
Approx. 25cm
Collimation
Operator’s eyes
Scale style
Position of 12mm
D’= ±
L×D
2
1000-L×D
D = Measured power (D)
D’= Corrected power (D)
L = Difference between the measuring distance and eyeglass
wearing distance (mm)
 Loading...
Loading...