73
5. OPERATION FOR TESTS
5.1.6 SMART CROSS TEST
Measure astigmatism accurately with the Jackson cross cylin-
der lens semi-automatically.
In general, the cross cylinder test forces the patient to compare
the targets having slightly different powers repeatedly. Conse-
quently the patient becomes tired from stress.
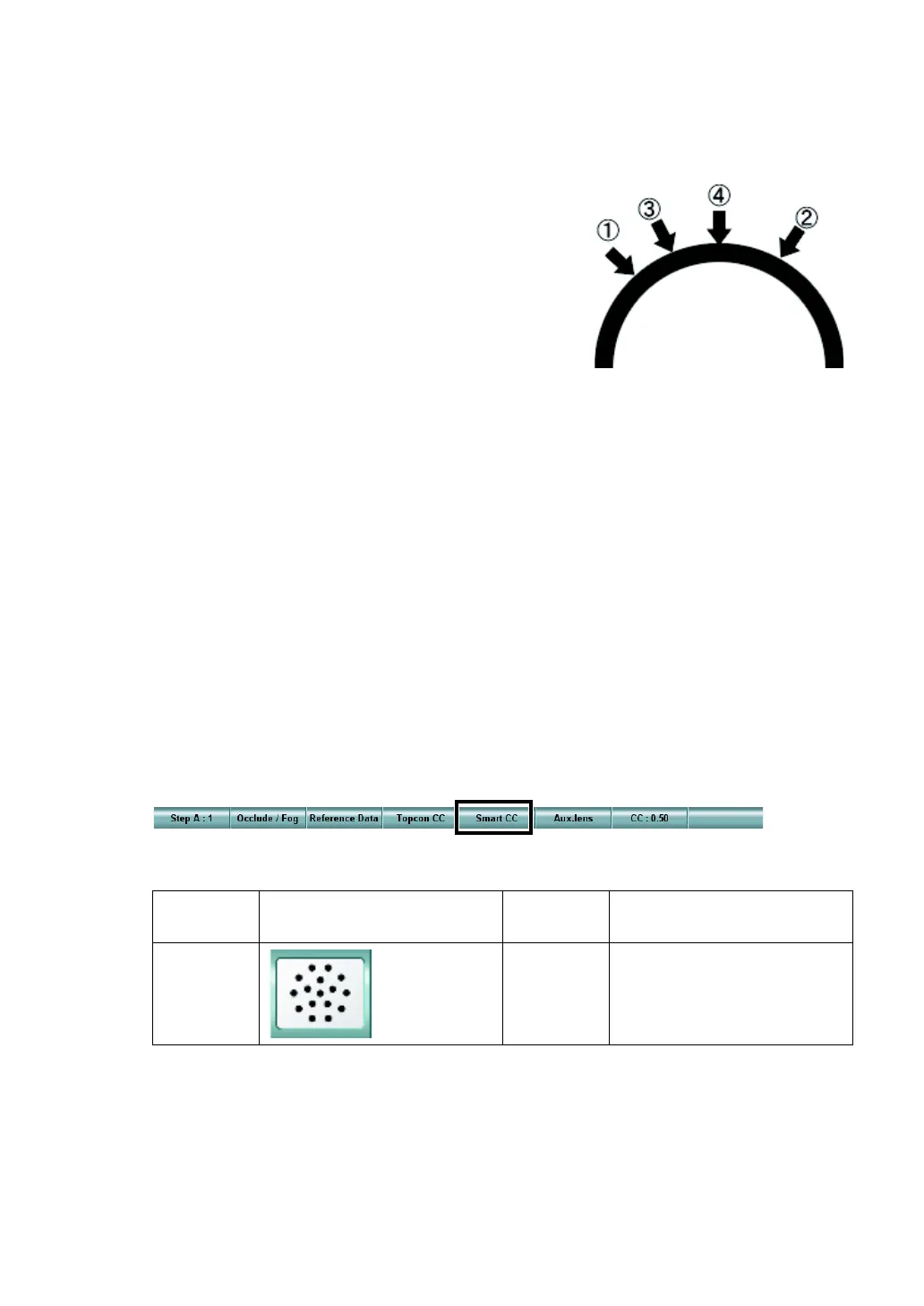
In the smart cross test, the cylinder power and axis, which are
input as the initial values, are regarded as the "Temporary-real
values". By referring to the temporary-real axis value, the sys-
tem calculates the axis whose view is most different on the front
and rear of the cross cylinder lens. First, the patient's compari-
son begins with this calculated axis. Then, the axis is moved to
the opposite side against the temporary real value and the sys-
tem asks the patient to compare the views of the chart. The
axis movement is automatically conducted. As the move width
is made smaller, the system searches for the "Real cylinder
axis". This test is performed to reduce the fatigue on the
patient.
At the final stage of the axis test, the type of the used cross cyl-
inder lens is automatically changed from "0.50D" to "0.25D"
to reduce uneasiness of the patient. The test finishes with a lower cross-cylinder power resulting
in a clearer end result and less fatigue for the patient.
1 Prepare for the test.
In some cases, measurement cannot be done. Before beginning the test, set the cylin-
der power and axis measured objectively.
2 Select the cross cylinder test chart.
Select the cross cylinder test chart icon on the chart page. Then, click the [Smart CC]
button from the function buttons.
Example of the test chart icons on chart page
Far-point
chart
Far-point test chart icon Near-point
chart
Near-point test chart icon
ACP-8(A) NC-3(E) -
Image of the cylinder axis
move during test
(Temporary-real value)
 Loading...
Loading...