General Troubleshooting 4-17
Check Shafts Menu
Deskew Shaft
Runs the media path drive train and engages the deskew clutch on the fly then disengages the
clutch. The test is repeated in both directions to determine clutch characteristics, steady state
drive requirements, bearing status, etc.
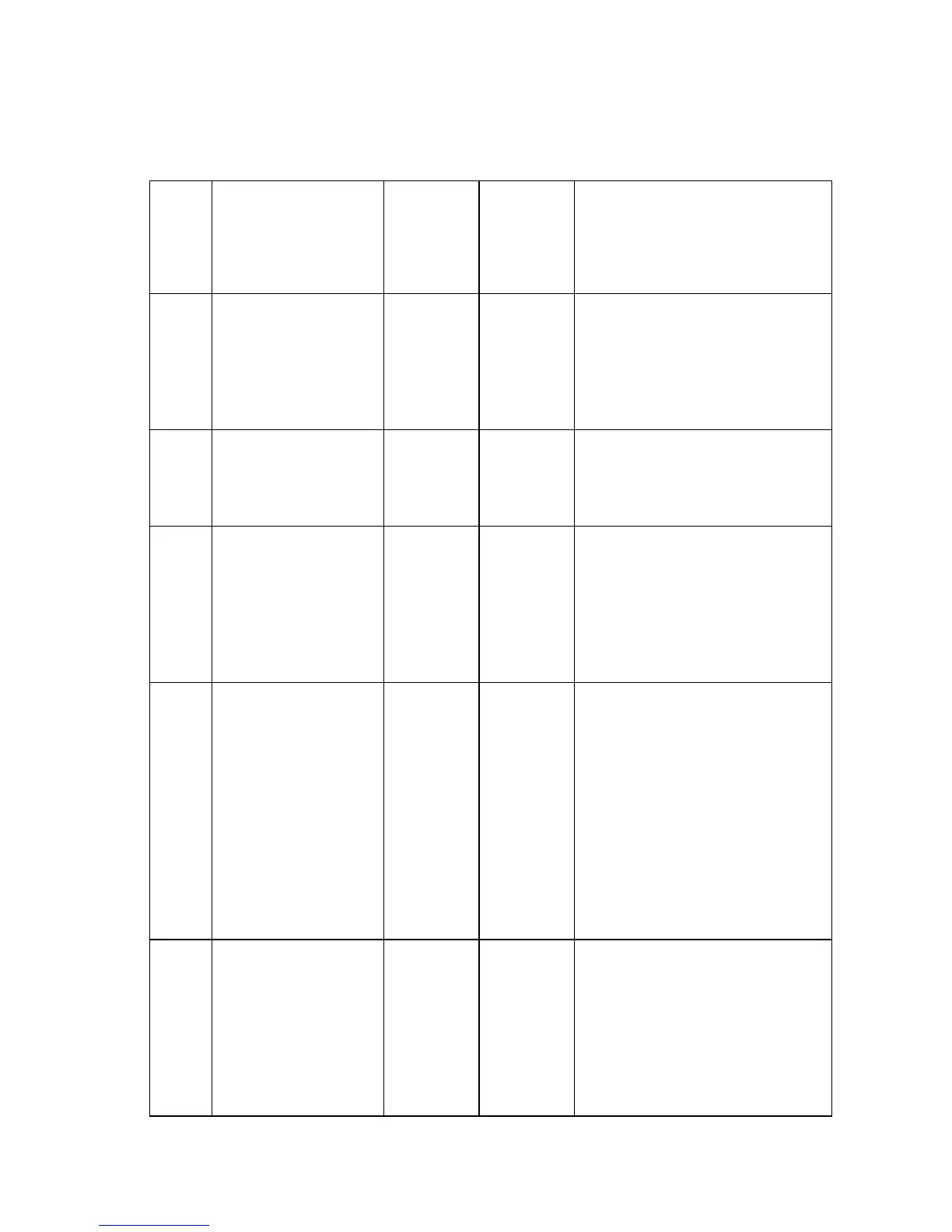
R# Definition
Typical
Value
(8400)
Typical
Value
(8500/
8550) Actions
0 Time to CCW On
peak fe (sec).
0.01 to
0.04
.01 to.04 Reports how long it takes the MP
motor servo system to react to
the sudden addition of the
deskew shaft load.
Larger values may show a
slipping/slow to engage clutch.
1 CCW On peak fe. 540 to
750
2.0 to 8.0 Reports peak effort needed to
accelerate the deskew shaft
load. A smaller value could
indicate a slipping clutch.
2 CCW On fe settling
time (sec).
0.017 to
0.21
0 to .2 Reports the time it takes the MP
motor servo system to "settle
down" after the sudden addition
of the deskew shaft load.
A longer time could indicate a
looseness in the deskew shaft
assembly or a slipping clutch.
3 CCW On average fe. 250 to
600
1.0 to 2.5 Reports the average effort
required to rotate the deskew
shaft in the CCW direction at a
constant velocity.
An unusual value could indicate
a difference in the composition
and/or number of the rollers, the
nip pressure, or out of range
mechanical dimensions due to
wear or contamination (such as
paper dust increasing the
effective diameter of a roller).
4 CCW On fe ripple. 115 to
360
0 to 2.0 Reports the variation of effort
required to rotate the deskew
shaft in the CCW direction at a
constant velocity.
A larger value could indicate
particles in the gears or non
uniform contamination of a roller
(causing a lump).

 Loading...
Loading...
















