11-33
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Software Configuration Guide—Release 8.7
OL-8978-04
Chapter 11 Configuring VLANs
Configuring Token Ring VLANs on the Switch
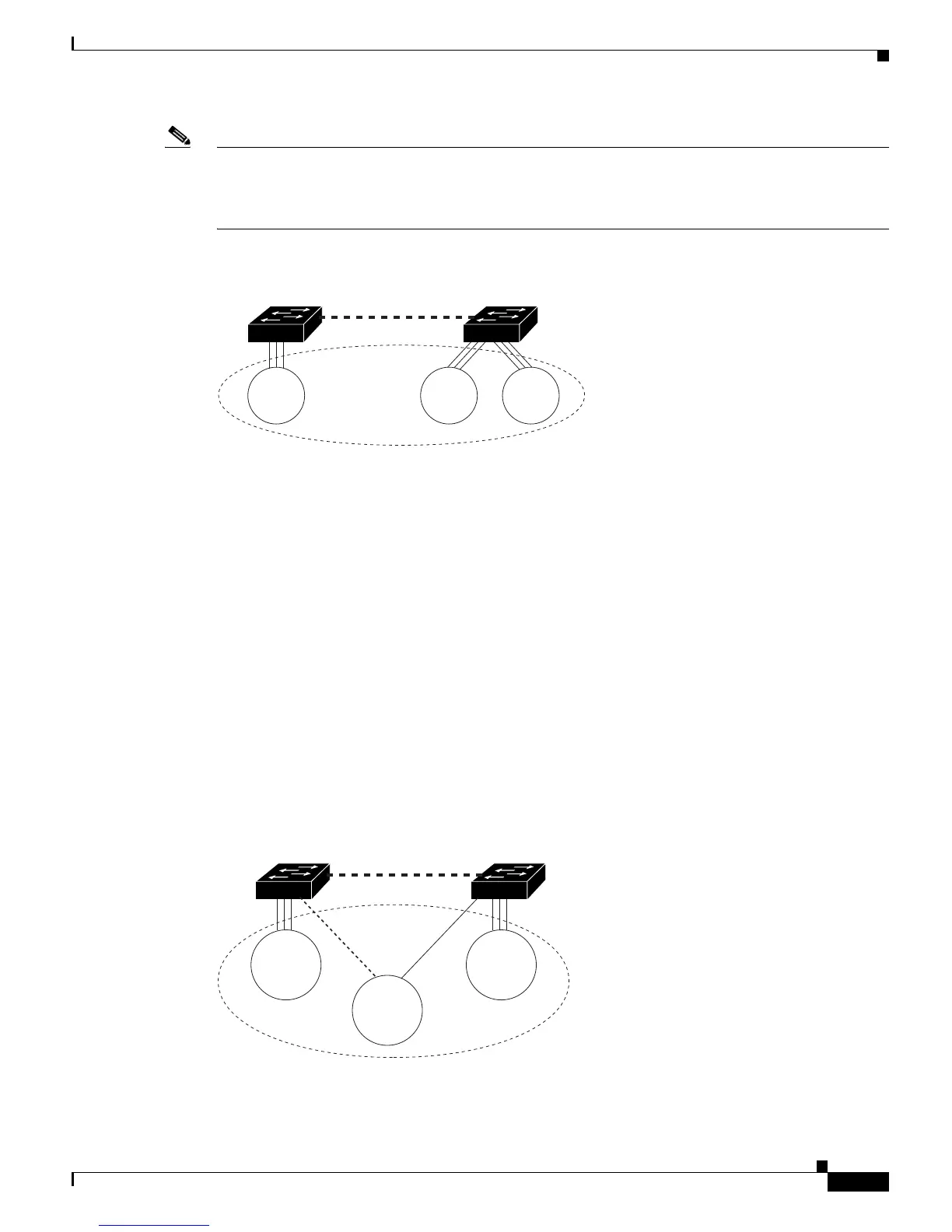
Note By default, the Token Ring ports are associated with the default TrCRF (VLAN 1003, trcrf-default),
which has the default TrBRF (VLAN 1005, trbrf-default) as its parent. In this configuration, a distributed
TrCRF is possible (see Figure 11-5), and the traffic is passed between the default TrCRFs that are located
on separate switches if the switches are connected through an ISL trunk.
Figure 11-5 Distributed TrCRF
Within a TrCRF, source-route switching forwards the frames that are based on either the MAC addresses
or the route descriptors. The entire VLAN can operate as a single ring, with frames that are switched
between the ports within a single TrCRF.
You can specify the maximum hop count for the All-Routes and Spanning Tree Explorer frames for each
TrCRF to limit the maximum number of hops that an explorer is allowed to traverse. If a port determines
that the explorer frame it is receiving has traversed more than the number of specified hops, it does not
forward the frame. The TrCRF determines the number of hops that an explorer has traversed based on
the number of bridge hops in the route information field.
A backup TrCRF enables you to configure an alternate route for the traffic between the undistributed
TrCRFs located on separate switches that are connected by a TrBRF if the ISL connection between the
switches fails. Only one backup TrCRF for a TrBRF is allowed, and only one port per switch can belong
to a backup TrCRF.
If the ISL connection between the switches fails, the port in the backup TrCRF on each affected switch
automatically becomes active, rerouting the traffic between the undistributed TrCRFs through the
backup TrCRF. When the ISL connection is reestablished, all but one port in the backup TrCRF is
disabled. Figure 11-6 shows the backup TrCRF.
Figure 11-6 Backup TrCRF
 Loading...
Loading...











