GR712RC-UM, Jun 2017, Version 2.9 184 www.cobham.com/gaisler
GR712RC
26 GRTC - Telecommand Decoder
26.1 Overview
The Telecommand Decoder (GRTC) is compliant with the Packet Telecommand protocol and specifi-
cation defined by [ECSS-E-ST-50-04C]. The decoder is compatible with the [PSS-04-107] and [PSS-
04-151] standards. The decoder is compatible with the CCSDS recommendations [CCSDS-231.0-B-
2], [CCSDS-232.0-B-2] and [CCSDS-232.1-B-2]. The Telecommand Decoder (GRTC) only imple-
ments the Coding Layer (CL).
In the Coding Layer (CL), the telecommand decoder receives bit streams on multiple channel inputs.
The streams are assumed to have been generated in accordance with the Physical Layer specifications.
In the Coding Layer, the decoder searches all input streams simultaneously until a start sequence is
detected. Only one of the channel inputs is selected for further reception. The selected stream is bit-
error corrected and the resulting corrected information is passed to the user. The corrected information
received in the CL is transfer by means of Direct Memory Access (DMA) to the on-board processor.
The Command Link Control Word (CLCW) and the Frame Analysis Report (FAR) can be read and
written as registers via the AMBA AHB bus. Parts of the two registers are generated by the Coding
Layer (CL). Note that most parts of the CLCW and FAR are not produced by the Telecommand
Decoder (GRTC) hardware portion. This is instead to be done in software. The CLCW register con-
tents need to be transferred from the Telecommand Decoder (GRTC) to the Telemetry Encoder
(GRTM) by means of software. The FAR register contents need also to be transferred from the Tele-
command Decoder to the Telemetry Encoder by means of software via the creation of a (Telemetry)
Space Packet. There is thus no automatic hardware connection between the Telecommand Decoder
and the Telemetry Encoder.
26.1.1 Concept
A telecommand decoder in this concept is mainly implemented by software in the on-board processor.
The supporting hardware in the Telecommand Decoder (GRTC) implements the Coding Layer, which
includes synchronisation pattern detection, channel selection, codeblock decoding, Direct Memory
Access (DMA) capability and buffering of corrected codeblocks.
The GRTC has been split into several clock domains to facilitate higher bit rates and partitioning. The
two resulting sub-cores have been named Telecommand Channel Layer (TCC) and the Telecommand
Interface (TCI). Note that TCI is called AHB2TCI. A complete ECSS/CCSDS packet telecommand
decoder can be realized at software level according to the latest available standards, staring from the
Transfer Layer.
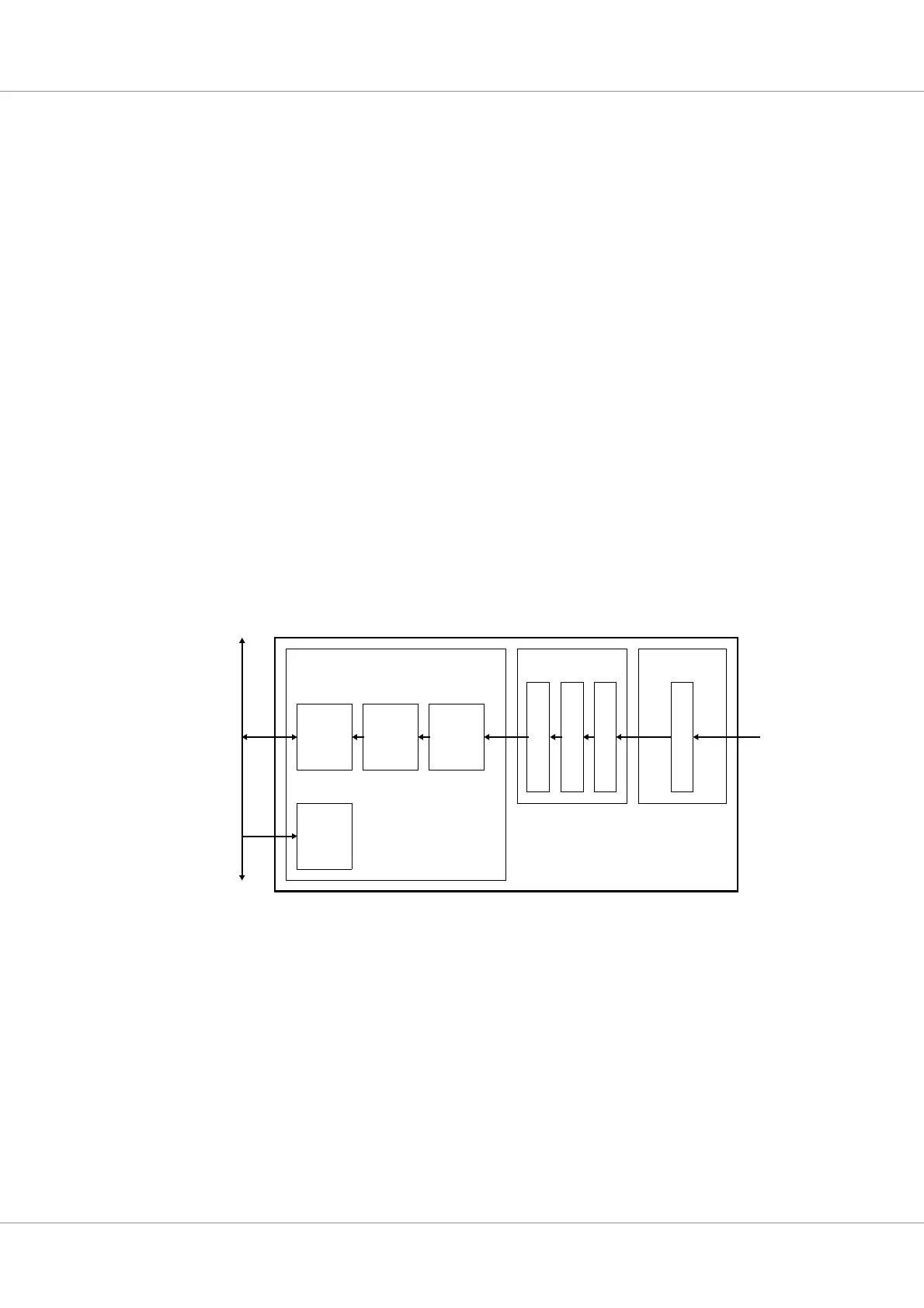
Figure 76. Block diagram
GRTC
Start sequence search
DMA
AMBA
AHB
Slave
Data Link Protocol Sub-Layer
NRZ-M
BCH Decoder
Coding Sub-Layer
FIFO
AMBA
AHB
Master
Telecommand input
AMBA AHB
Pseudo-Derandomizer
AMBA AHB
Physical Layer

 Loading...
Loading...