GR712RC-UM, Jun 2017, Version 2.9 73 www.cobham.com/gaisler
GR712RC
8 Multiprocessor Interrupt Controller
8.1 Overview
The interrupts generated by the GR712RC peripherals are forwarded to the IRQMP multi-processor
interrupt controller. The interrupt controller prioritizes, masks and propagates the interrupt with the
highest priority to the two processors.
8.2 Operation
8.2.1 Interrupt routing
The GR712RC device has an internal interrupt bus consisting of 31 interrupts, which are mapped on
the 15 SPARC interrupts by the IRQMP controller.
The lowest 15 interrupts (1 - 15) are mapped directly on the 15 SPARC interrupts. When any of these
lines are asserted high, the corresponding bit in the interrupt pending register is set. The pending bits
will stay set even if the PIRQ line is de-asserted, until cleared by software or by an interrupt acknowl-
edge from the processor. Interrupt 16-31 are generated as interrupt 12, and for those interrupts a
chained interrupt handler is typically used by the software.
8.2.2 Interrupt prioritization
Each interrupt can be assigned to one of two levels (0 or 1) as programmed in the interrupt level regis-
ter. Level 1 has higher priority than level 0. The interrupts are prioritised within each level, with inter-
rupt 15 having the highest priority and interrupt 1 the lowest. The highest interrupt from level 1 will
be forwarded to the processor. If no unmasked pending interrupt exists on level 1, then the highest
unmasked interrupt from level 0 will be forwarded.
Interrupts are prioritised at system level, while masking and forwarding of interrupts in done for each
processor separately. Each processor in an multiprocessor system has separate interrupt mask and
force registers. When an interrupt is signalled on the interrupt bus, the interrupt controller will priori-
tize interrupts, perform interrupt masking for each processor according to the mask in the correspond-
ing mask register and forward the interrupts to the processors.
When a processor acknowledges the interrupt, the corresponding pending bit will automatically be
cleared. Interrupt can also be forced by setting a bit in the interrupt force register. In this case, the pro-
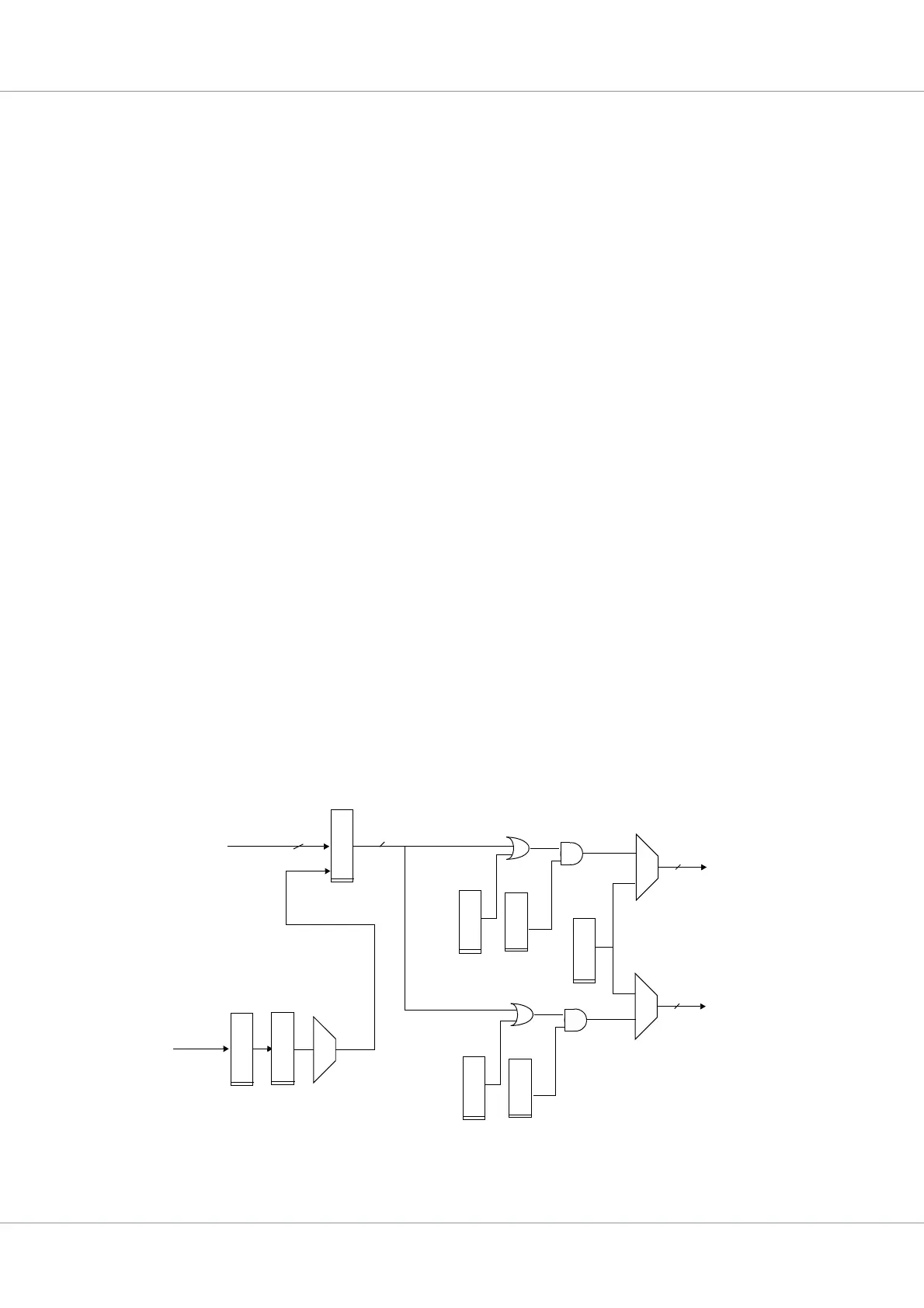
Figure 32. Interrupt controller block diagram
IRQ
Pending
15
4
CPU0 IRL[3:0]
Priority
select
IRQ
mask[0]
IRQ
Force[0]
Priority
encoder
4
CPU1 .IRL[3:0]
Priority
encoder
IRQ [15:1]
IRQ
mask[1]
IRQ
Force[1]
IRQ [31:16]
IRQ
Pending
IRQ
Mask
IRQ12
Priority
encoder

 Loading...
Loading...