HemoSphere Advanced Monitor 12 Advanced Features
151
Aortic valve regurgitation may cause an over estimation of Stroke Volume / Cardiac
Output calculated depending on the amount of valvular disease and the volume lost
back into the left ventricle.
The Hypotension Probability parameter P(↓BP) which can be configured as a key parameter on all
monitoring screens, displays this probability as a percentage, ranging from 0-100%. In addition, the Acumen
Hypotension Probability Indicator software provides two additional non-configurable parameters only
displayed on the HPI Secondary Screen, dP/dt and Ea
dyn
, which together with SVV, provide decision
support based upon preload [SVV], contractility [dP/dt], and afterload [Ea
dyn
]. Refer to the Hypotension
Probability P(↓BP) on page 152, the HPI Secondary Screen on page 156, and the Clinical Application on page 158,
for additional information regarding SVV, dP/dt and Ea
dyn
.
To activate the Acumen HPI software, the platform requires entry of a password to access the Manage
Features screen, where an activation key must be entered. Please contact your local Edwards Representative
for more information on enabling this Advanced Feature.
Like other monitored parameters, the P(
↓BP) value updates every 20 seconds.When the P(↓BP) value
exceeds 85%, a high priority alarm is initiated. If the P(↓BP) value exceeds 85% for two consecutive readings
(total of 40 seconds), a P(↓BP) High Alert popup appears on the screen recommending a review of the
patient hemodynamics. Hemodynamic information associated with hypotension is available for the user on
the HPI Secondary Screen. That information includes several key parameters (MAP, CO, SVR, PR, and SV),
as well as more advanced indicators of preload, contractility, and afterload (SVV, dP/dt, Ea
dyn
). Additionally,
the patient hemodynamics may also be assessed by review of currently configured key parameters, as for
example, SVV, CO and SVR.
Once the HPI feature is activated, the user can choose to configure Hypotension Probability P(↓BP) as a
key parameter, display on the Information Bar, or choose not to display.
Refer to P(↓BP) as a Key Parameter and P(↓BP) in the Information Bar for information about configuring
the parameter. See P(↓BP) as a Key Parameter on page 153 and P(↓BP) on Information Bar on page 155.
The alarm and alert functions for P(↓BP) will differ with the chosen display option for P(↓BP) as described
in table 12-1.
Unlike other monitored parameters, the P(↓BP) alarm limits are not adjustable, as P(↓BP) is not a physiologic
parameter with a selectable target range (as with cardiac output, for example), but rather a quantitative
indication of physiological status. The alarm limits are displayed to the user in the software, but the controls
to change the alarm limits are disabled. The alarm limit for the P(↓BP) parameter (>85% for red alarm range,
>50% for yellow range) are fixed values set by the software and may not be modified. The P(↓BP) alarm
limits are provided in table 12-2 on page 152 and in table D-4 on page 206.
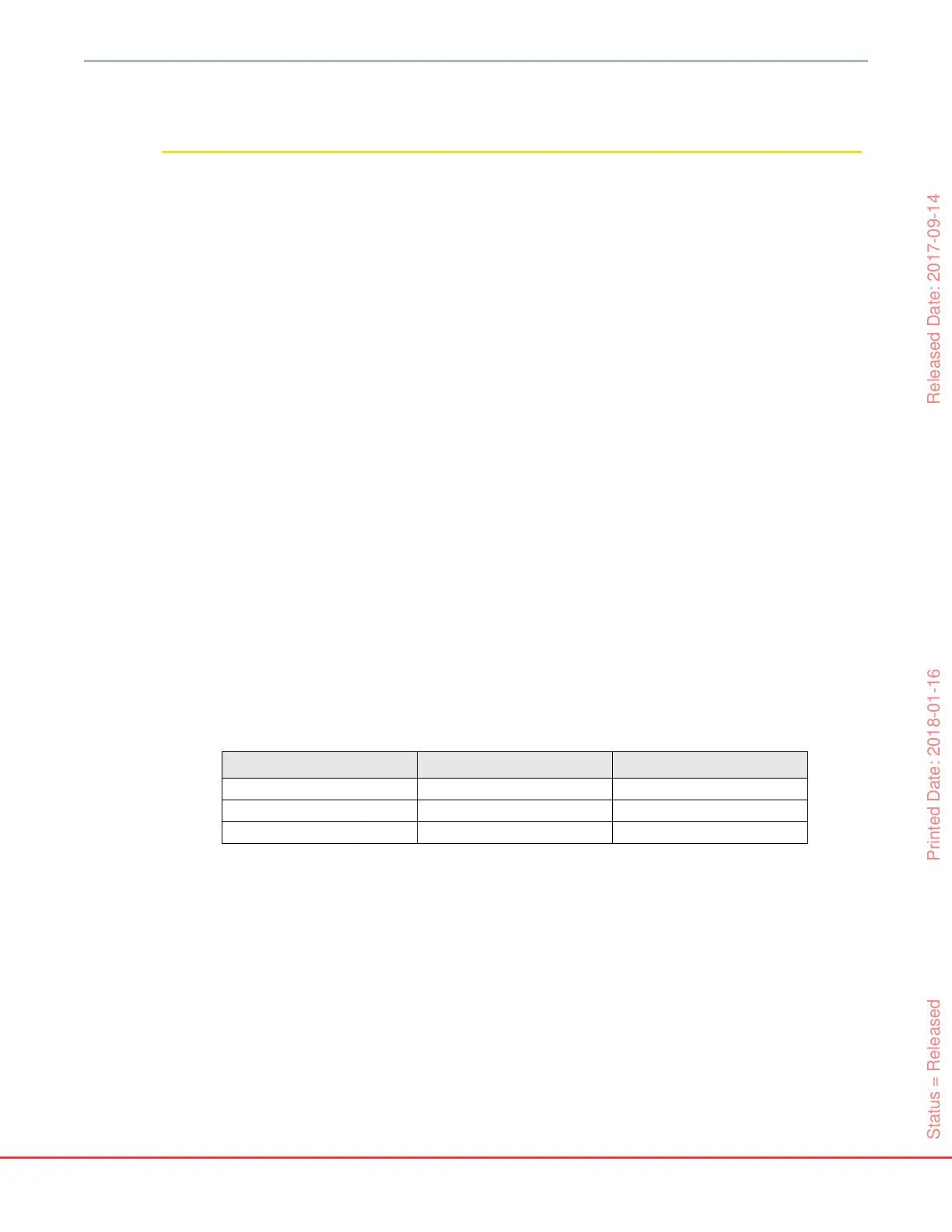
Table 12-1 P(↓BP) display configurations
Display option Audible and visual alarm Alert popup
Key Parameter
Yes Yes
Information Bar
No Yes
Not displayed
No No
Status = Released Printed Date: 2018-01-16 Released Date: 2017-09-14
 Loading...
Loading...