COMMISSIONING
242 Service Manual Part No.: 4417340 Revision 1
954 SmartServo FlexLine
7.7.2.4 Hydrostatic deformation
Due to the liquid pressure on the tank shell, the tank shell will bulge.
Because of this tank shell deformation, the tank roof moves
downwards. Level gauges, which are installed on roof nozzles of fixed
roof tanks, are influenced by this movement. The SmartServo FlexLine
provides an innage compensation for this deformation. This
compensation is dependent on the innage level.
For the hydrostatic deformation compensation, the following
entities should be set:
Entity name Default Value Explanation
[Hydrostatic deformation level]
< 2.0 >
This entity contains the innage above which the
compensation becomes effective. Below this
innage no compensation is applied
[Hydrostatic deformation factor]
< 0 >
This entity contains the compensation factor in
[m]/[m].
First, the upper reference movement must be found. Then with linear
regression, a best fit line can be found as compensation. The outcome
of that calculation is used for the [Hydrostatic deformation factor] and
[Hydrostatic deformation minimum innage] values.
Calculation of upper reference movement
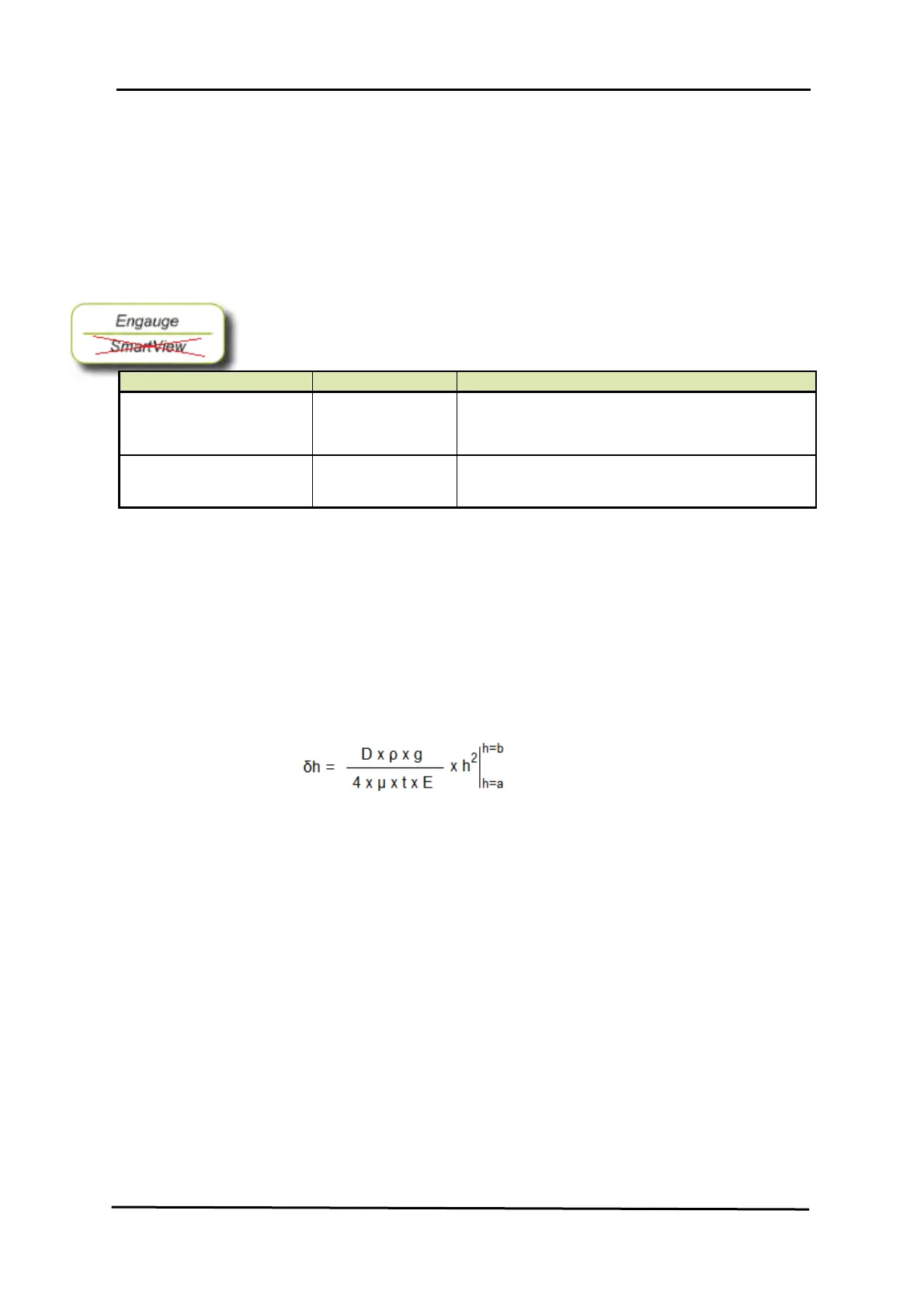
With the following formula (according to OIML R85) the tank shell
deformation can be calculated:
where
δh : tank shell deformation [m]
D : tank diameter [m]
ρ : product density [kg/m
3
]
g : local gravity constant [m/s
2
]
μ : Poisson’s constant (for steel μ=3.3)
E : modulus of elasticity (for steel E=206.1 x 10
9
)
t : tank shell (ring) thickness [m]
h : distance of the liquid surface with respect to a level
below the liquid surface
a and b are e.g. the distances of the liquid surface with respect to the
top and bottom of the shell segment under investigation.
If the tank shell thickness and internal diameter remains constant over
the total height, a=0 and b equals the innage level.
 Loading...
Loading...











