Because RFL™ and Hubbell® have a policy of continuous product improvement, we reserve the right to change designs and specifications without notice.
Chapter 4 - Command Control
SNMP Access Gateway User’s Manual - v1.0 -- 11/99 - Page 11
password settings, event (alarm) definition settings, alarm action settings, and other settings. See Chapter 5 - Use of
the SETUP Menu for further details of the use of the SETUP command.
4.2.5 - EVENTS
The EVENTS command is used to view the current status of the events (alarms), view the contents of the events log
file, clear contents of the events log file, view the current active alarm actions, acknowledge alarms, and view the
history log of alarm actions. See Chapter 12 - Use of the EVENTS Command for further details of the use of the
EVENTS command.
4.2.6 - DEFAULT
The DEFAULT command resets certain variables and settings to their default values. The network settings and
serial ports settings are not affected by the use of the DEFAULT command. The events log file is not cleared. The
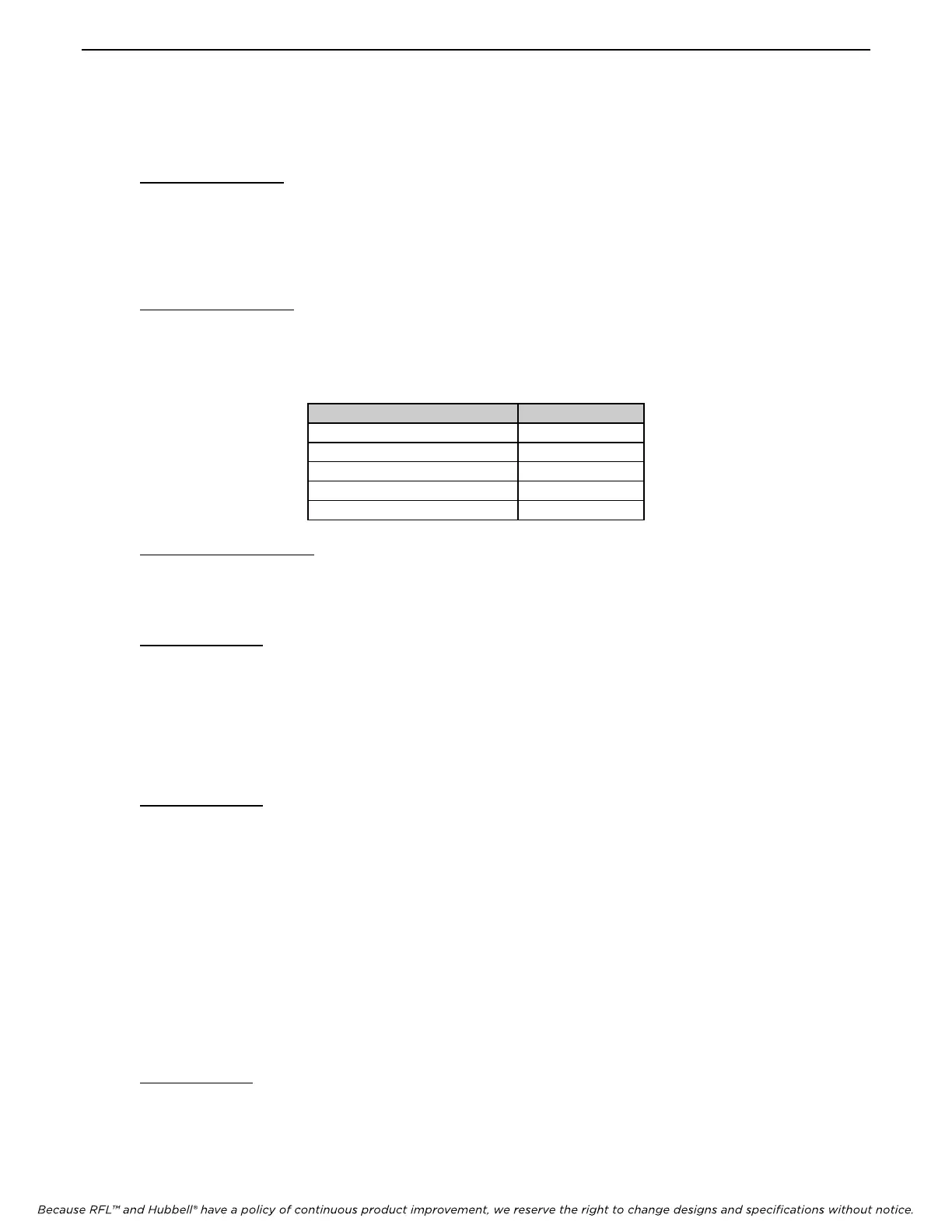
configuration variables and settings affected by the DEFAULT command are:
Setting Value Set To
Store data record events 1 (on)
Store alarm record events 1 (on)
Store command log 1 (on)
Store reset events 1 (on)
Store sensor events 1 (on)
4.2.7 - COLDSTART
The COLDSTART command is used to completely re-initialize the SNMP Access Gateway. All network and other
settings are re-initialized to their default values. The events log file is cleared.
4.2.8 - HELP
The HELP command provides a list of the command available with the SNMP Access Gateway. The display looks
something like this:
? SETUP EVENTS RELAYS EXIT
GET
GETNEXT GETX SET
4.2.9 - PING
The PING command executes an ICMP PING test to determine if an IP address is reachable and responding. The
PING command may be used to test the network connectivity of the SNMP Access Gateway. For example, if a
default router is used, the SNMP Access Gateway should be able to PING the default router, which demonstrates
network connectivity and proper network connections.
4.3 - Pseudo-SNMP Commands
The pseudo-SNMP commands are manual commands which can be entered via a dialup or telnet connection and
which may be used with the object IDs developed for SNMP for setting and retrieving the value of SNMP-
manageable objects. These objects may be part of the standard (MIB-II) MIB (as described in RFC 1213), or part of
the custom MIB of the SNMP Access Gateway. The pseudo-SNMP management section of this manual provides
further details and examples of use of the pseudo-SNMP commands.
4.3.1 - GET
The GET command is used with a specific object ID to obtain the value of that object.
 Loading...
Loading...