186 C
HAPTER
7: F
AST
IP
FastIP and the
Switch Database
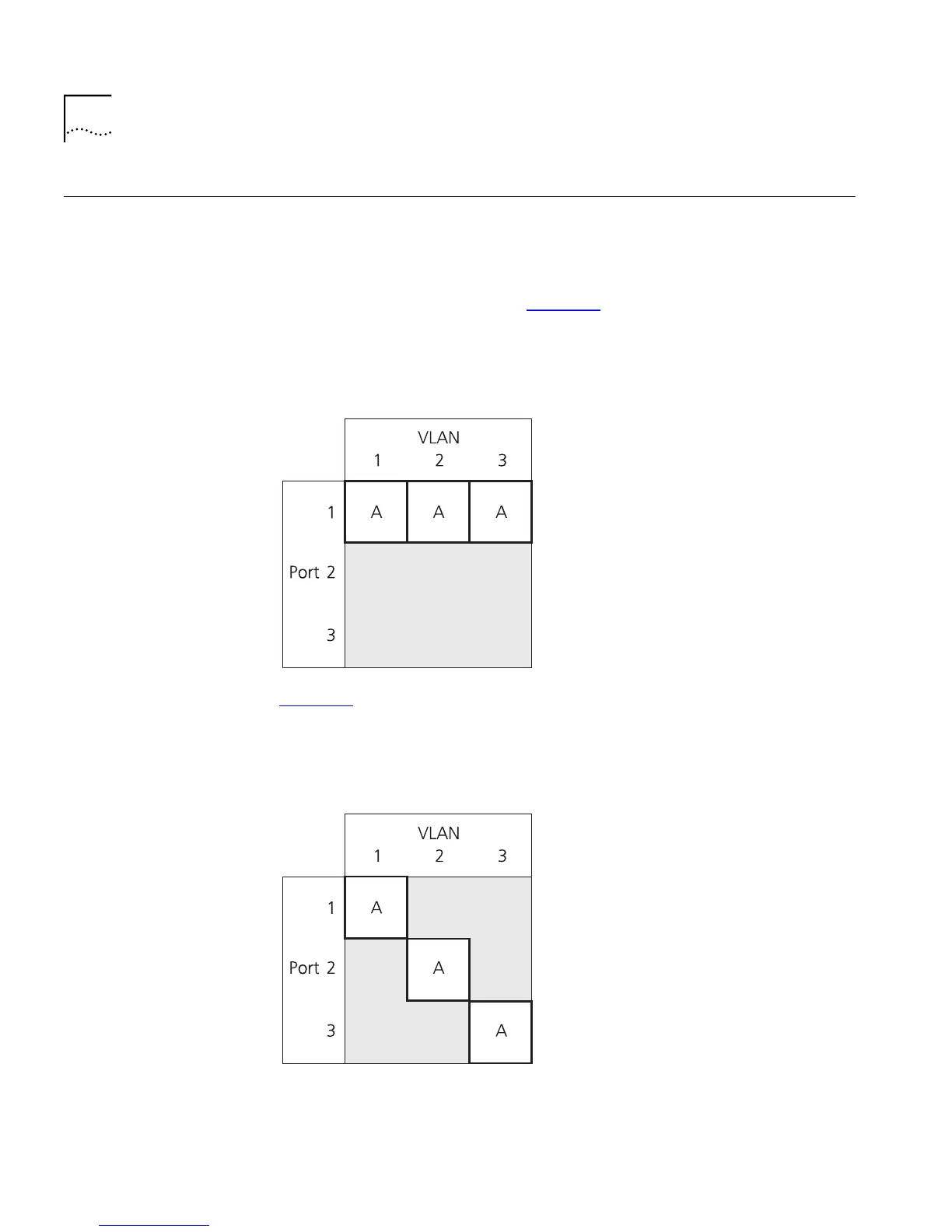
By default, the Switch Database of a Switch is divided by VLAN — each
VLAN has an independent area of the database. With this system, the
Switch Database can store an entry for a device in several VLANs at the
same time, and the entry for a particular VLAN can be stored against
different ports. As an example, Figure 42
illustrates the Switch Database
storing an entry for endstation A in VLANs 1, 2 and 3, and the entries are
all stored against port 1.
Figure 42
Entry stored in multiple VLANs
Figure 43 illustrates the Switch Database storing an entry for endstation
A in VLANs 1, 2 and 3 — here, the VLAN 1 entry is in port 1, the VLAN 2
entry is in port 2, and the VLAN 3 entry is in port 3.
Figure 43
Entry stored in multiple VLANs, each entry in a different port
 Loading...
Loading...











