LAN SERVICES E-SERVER : INTERNET APPLICATIONS
Ed. 042/8 Réf. 3EH 21000 BSAA
There are two types of IP address:
- public addresses: each public address is assigned and unique on the Internet;
- private addresses: these are assigned in a LAN and recognized within the LAN, but not recognized
by elements outside the LAN.
Using private addresses in a LAN allows total freedom of choice in allocating addresses. A host name
can have a fixed IP address, or it can be assigned one dynamically by a DHCP server each time it con-
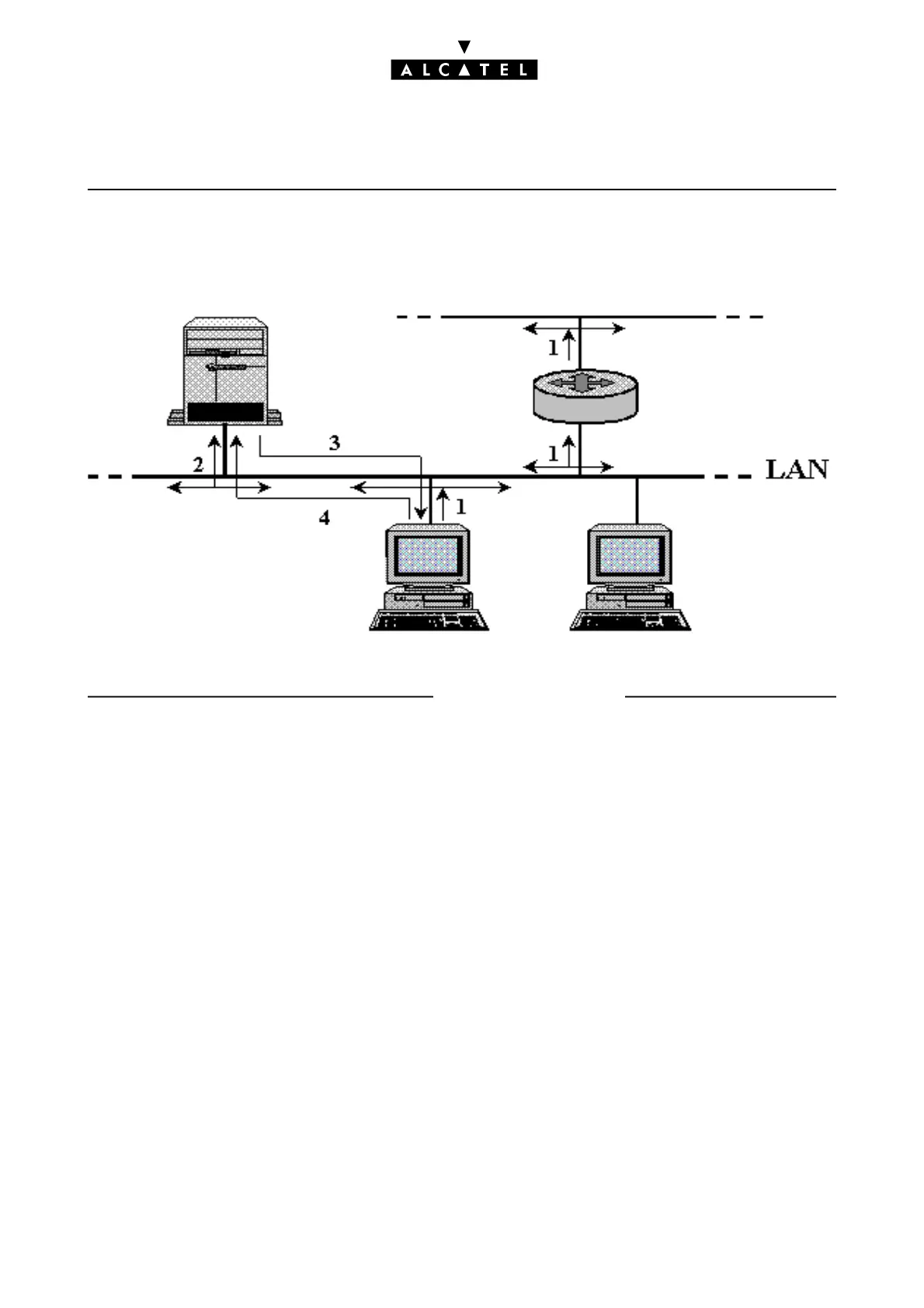
nects to the LAN. There are several stages in the LAN connection process (see diagram above):
1. the DHCP client connects up to the LAN, and requests an IP address allocation. The request is made
by sending out ("broadcasting") a DHCP request over the LAN;
2. the DHCP server on the LAN receives the request and allocates an available IP address from the
pre-defined range of addresses;
3. the allocated IP address is sent to the DHCP client;
4. the DHCP client accepts the IP address.
OmniPCX provides DHCP server functionality. The following parameters can be configured:
- the value range of IP addresses that the DHCP can allocate. These IP addresses are allocated for
all the network elements: client stations, telephones and mobile terminals;
OmniPCX
(integrated DHCP server)
Router
DHCP clients

 Loading...
Loading...