File
3
LAN SERVICESE-SERVER : INTERNET APPLICATIONS
Ed. 04 5/8Réf. 3EH 21000 BSAA
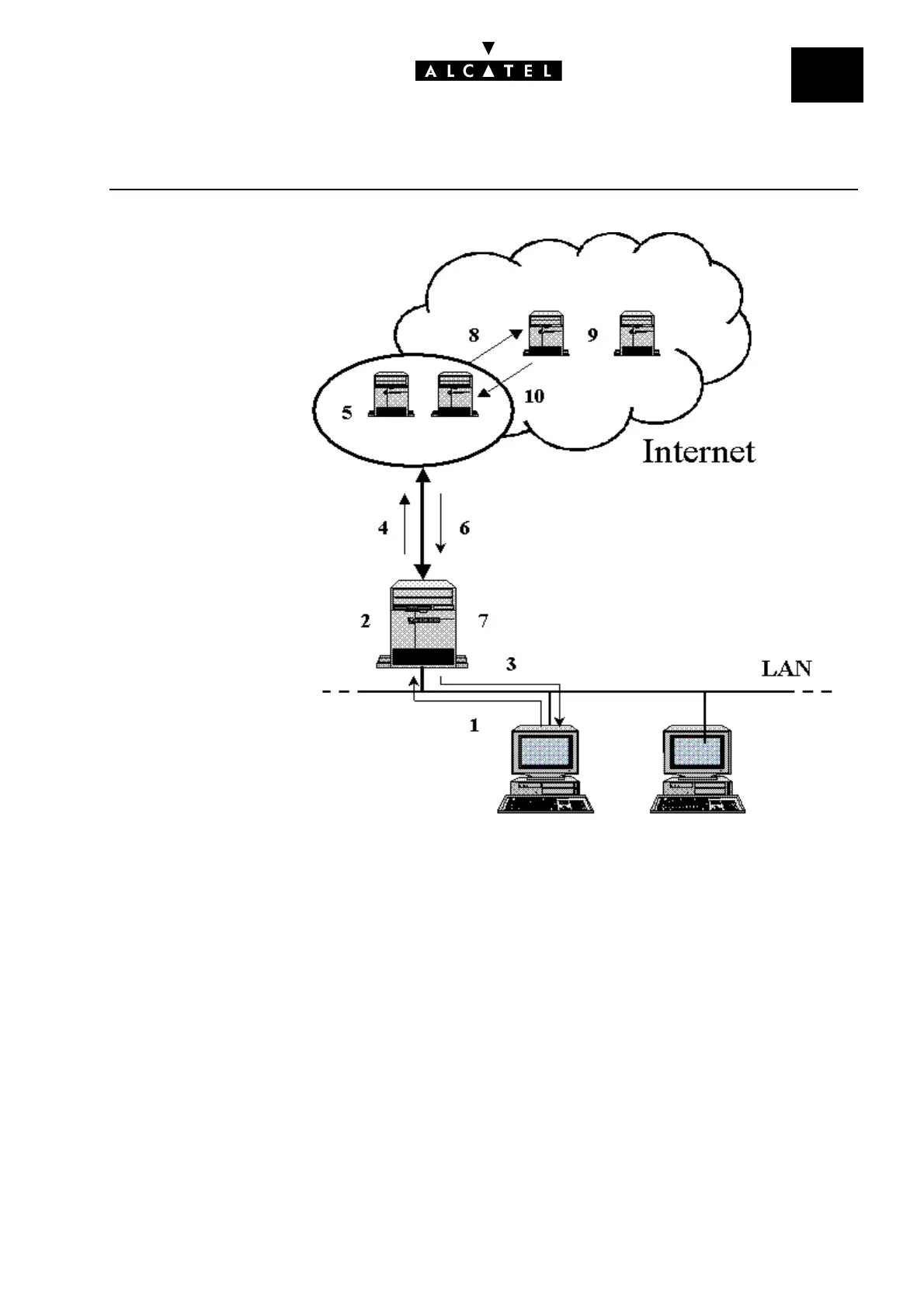
- The client station emits a DNS request (Step 1).
- The host name - DNS server IP address correspondence table is consulted (Step 2). If the host name
is found, the DNS server sends the corresponding IP address back to the client station (Step 3). If
not, the request is relayed to the ISP's DNS servers (Step 4).
- The ISP's DNS servers are consulted. If the request is resolved, the servers send the corresponding
IP address back to the DNS server on the LAN (Step 6). The LAN DNS server updates the DNS cache
to take account of the request (Step 7), and proceeds from Step 3.
- If the request can’t be resolved by the ISP's DNS servers, it is relayed to other DNSs on the Internet
(Step 8). At this stage, the request is continuously relayed until a DNS server manages to resolve
the host name (Step 9). The resolved IP address is then returned to the ISP's servers (Step 10), from
whence it follows the same route as before.
DNS Servers
DNS Servers
ISP
OmniPCX
(integrated DNS server)

 Loading...
Loading...