Chapter 1 Outline
1-34
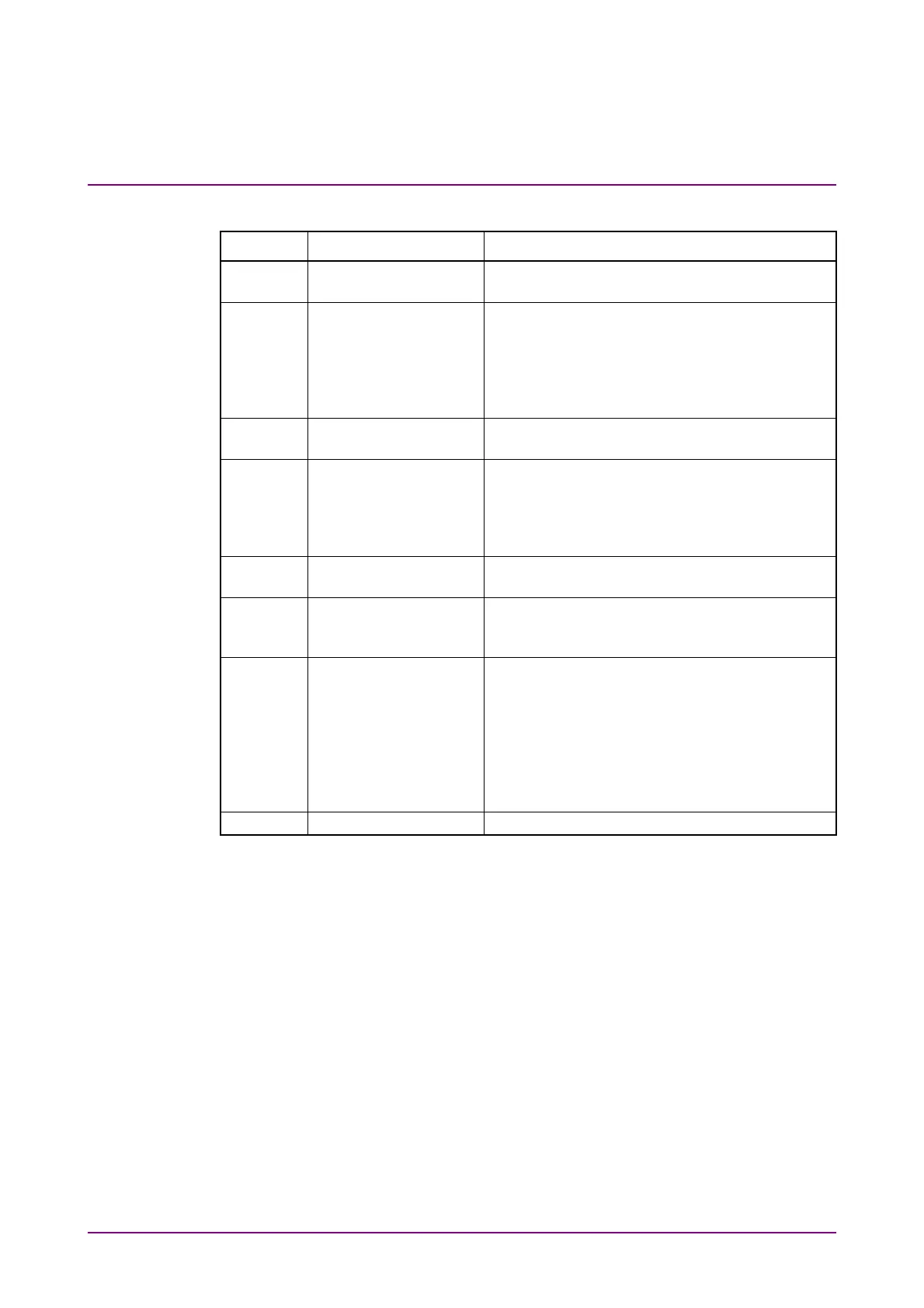
Table 1.5-1 Jitter Type
Abbrev. Name Description
TJ Total Jitter Jitter of combined RJ and DJ
Not a simple sum of RJ and DJ
RJ Random Jitter Jitter which occurs with external factors such
as thermal noise. It has a characteristic to
spread unlimitedly which approaches
Gaussian distribution. It is indicated with rms
(root mean square) because it spreads
unlimitedly.
DJ Deterministic Jitter Jitter with upper limit of amount relative to
the Random Jitter
BUJ Bounded Uncorrelated
Jitter
Jitter which occurs with external factors such
as cross talk effects from adjacent signal lines.
It has a random nature like the Random Jitter;
however, it is indicated with p-p (peak to peak)
because its spreading is limited.
DDJ Data Dependant
Jitter
Jitter which is DJ and the occurrence amount
depends on data.
DCD Duty Cycle Distortion Occurs with transmission/reception circuit
offset distortion difference of High pulse width
and Low pulse width.
ISI Inter Symbol
Interference
Occurs due to inadequate bandwidth and
reflections caused by impedance mismatching,
etc., in the transmission path. When
components with no correlation to data are
removed, it is defined either as
the difference between the fastest and slowest
rising edges, or as the difference between the
fastest and slowest falling edges.
PJ Period Jitter Jitter which is DJ and occurs periodically.
With the communications standards such as IEEE 802.3-2015*,
specifications for DDPWS (Data Dependent Pulse Width Shrinkage) have
been decided as well as the jitters above.
*: For the formal name, refer to Appendix E “Bibliography”.
 Loading...
Loading...