Front Panel Operation Revision 4
CDM-760 Advanced High-Speed Trunking Modem MN-CDM760
6–32
Frame going from WAN to LAN (Rx):
Packet is sent to LAN, Source MAC is learned to exist on WAN
Known to exist on LAN side
Packet is sent to LAN, Source MAC is learned to exist on WAN
Don’t care Known to exist on WAN side
Packet is NOT sent to LAN, Source MAC is learned to exist on
WAN
Broadcast or Multicast MAC
Packet is sent to LAN, Source MAC is learned to exist on WAN
The second process that is performed, with MAC Learning Enabled, is “aging”. This is why MAC
Leaning is also referred to as “learning and aging”. When a MAC Address is seen by the modem,
it is “learned” to exist as described previously. This learned address remains learned and
continues to exist in the modem’s Content Addressable Memory (CAM) table for 5 minutes. If
the MAC Address is not seen traversing through the product during this five minute period, the
table entry is “aged” out, and the MAC Address is no longer known to the modem and must be
re-learned. If, however, the MAC Address is seen within the CAM table’s five minute timer, the
MAC Address remains in the table and the Aging Clock resets once more to five minutes.
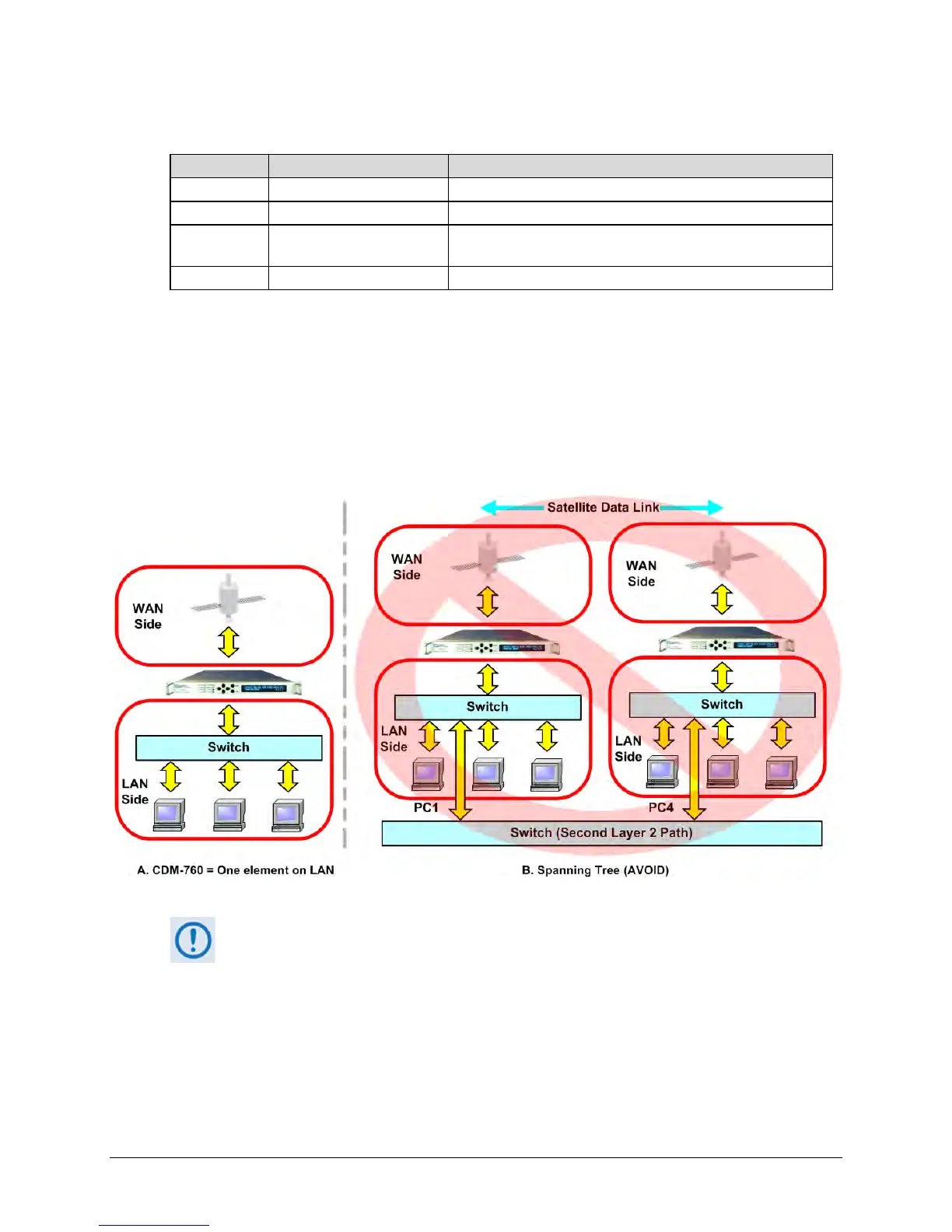
Figure 6-2. MAC Learning Operations
As Figure 6-2 shows, it is important to note that enabling MAC Learning allows you to
reduce the amount of traffic over the satellite link when the modem is one element
on the LAN (Detail ‘A’). However, should a second Layer 2 path exist to the far side
equipment – this condition is known as “Spanning Tree” (Detail ‘B’) – this will cause
data flow failure. In a “Spanning Tree” state, the MAC Address of a device – such as
PC1 in the figure – appears to exist on both the WAN and LAN sides of the modem.
This corrupts the modem’s CAM table and causes its failure.
 Loading...
Loading...