Appendix G Revision 4
CDM-760 Advanced High-Speed Trunking Modem MN-CDM760
G–2
G.2 Background
The CDM-760 system was originally based on DVB-S2 standards. New network specifications
such as DVB-S2-EB1 have been released by Comtech EF Data since the initial release of the CDM-
760. The DVB-S2 network specification in the CDM-760 offers 24 MODCODs that work over a
guaranteed Es/No range of 1.2dB to 16.5dB. By comparison, Comtech EF Data’s DVB-S2-EB1
Network Specification offers a suite of 40 MODCODs over this same Es/No range – nearly twice
the number of MODCOD selections for enhanced ACM performance
DVB standards also defined much of the system for both ACM and a related feature named
InBand Signaling. The CDM-760 supports duplex ACM operation between a pair of modems in a
point-to-point link (point-to-multipoint ACM operation is not currently supported). In ACM
mode, the symbol rate remains constant, and the modulation and coding (ModCod in DVB-S2
terms) changes to preserve the data integrity. Most links are designed with enough Es/No margin
to provide error free performance under faded conditions when there is higher attenuation in the
uplink or downlink path to/from the satellite.
Depending on the geographical region and link budget criteria, faded conditions can occur less
than 1% of the time. In such as case the operating Es/No of the link is higher than needed for more
than 99% of the year. ACM takes advantage of this link margin by increasing the ModCod during
unfaded conditions allowing the link to operate at a higher data rates during these periods. A
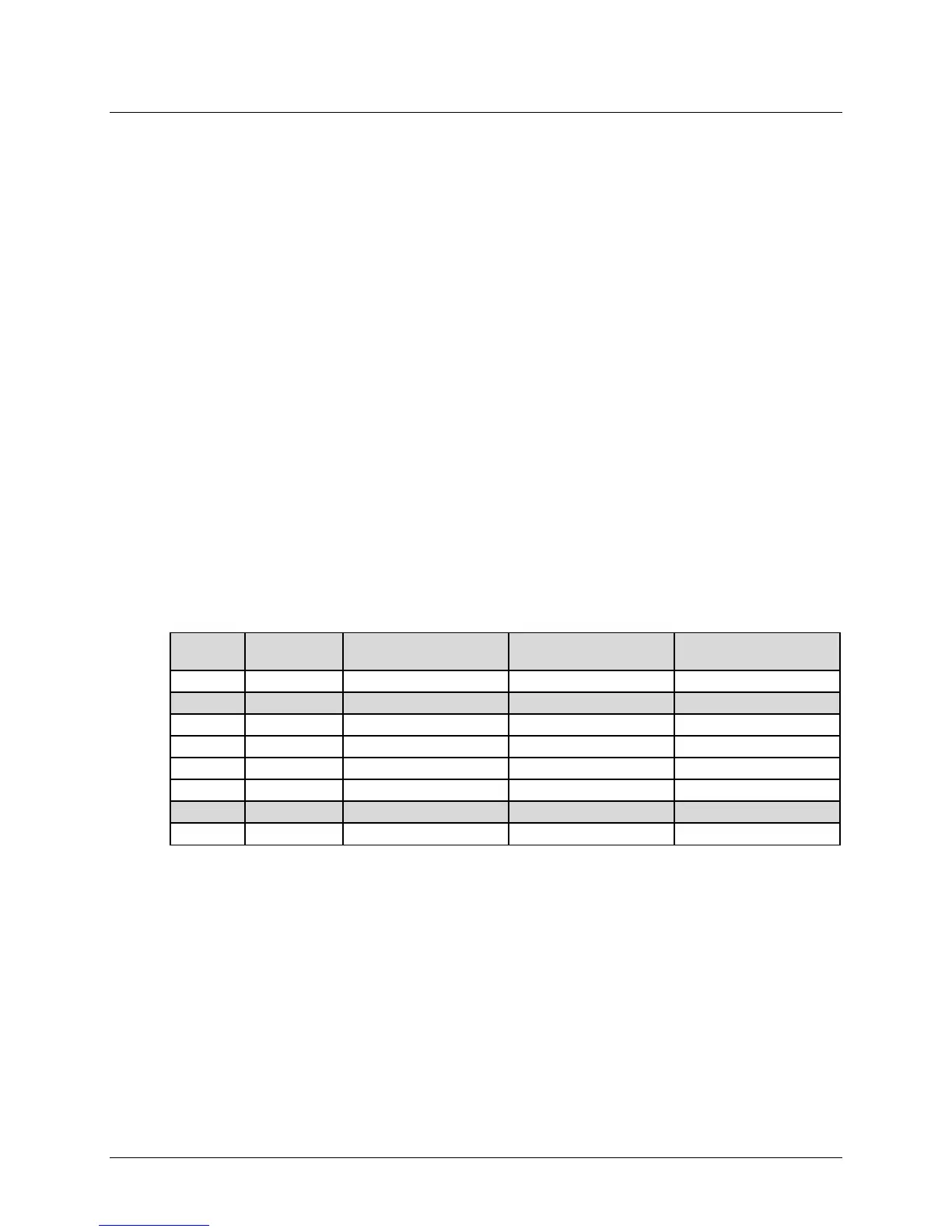
simplified example illustrates the point. Table G-1 shows the several ModCods, the Spectral
Efficiency (SE), and Es/No for the CDM-760 assuming Normal FEC Frame (64,800 bits).
Table G-1. ACM Example for Standard FECFrame (64,800 bits)
ModCod
Spectral Efficiency
Pilots ON
Data Rate (Mbps)
at 20 Msps
For example: If a link is designed to operate at an Es/No of 3.7dB during a 3.0dB fade, the 3.0dB
fade is commonly referred to as link margin. When fade conditions are not present, the link
margin is directly converted into a higher link Es/No: 3.7dB + 3.0dB margin = new Es/No of
6.7dB. This non-faded Es/No of 6.7dB allows for a much higher ModCod to be used, offering a
higher Spectral Efficiency. The corresponding Spectral Efficiencies in this example range from
1.1600 to 1.7244.
The Data Rate and Symbol Rate are related by the Spectral Efficiency as follows:
DR (Data Rate) = SR (Symbol Rate) x SE (Spectral Efficiency)

 Loading...
Loading...