Appendix J Revision 4
CDM-760 Advanced High-Speed Trunking Modem MN-CDM760
J–8
J.4.2 Margin Requirements
Depending on the product, typical interfering signal cancellation is 28 to 35 dB. The residual
interfering signal appears as noise, causing a slight degradation in received Es/No. To
compensate for the residual noise, a small amount of additional link margin is required to
improve the Es/No and maintain the QEF performance. Margin requirements depend on the
product, modulation and power ratios; for the CDM-760, these additional margin requirements
are:
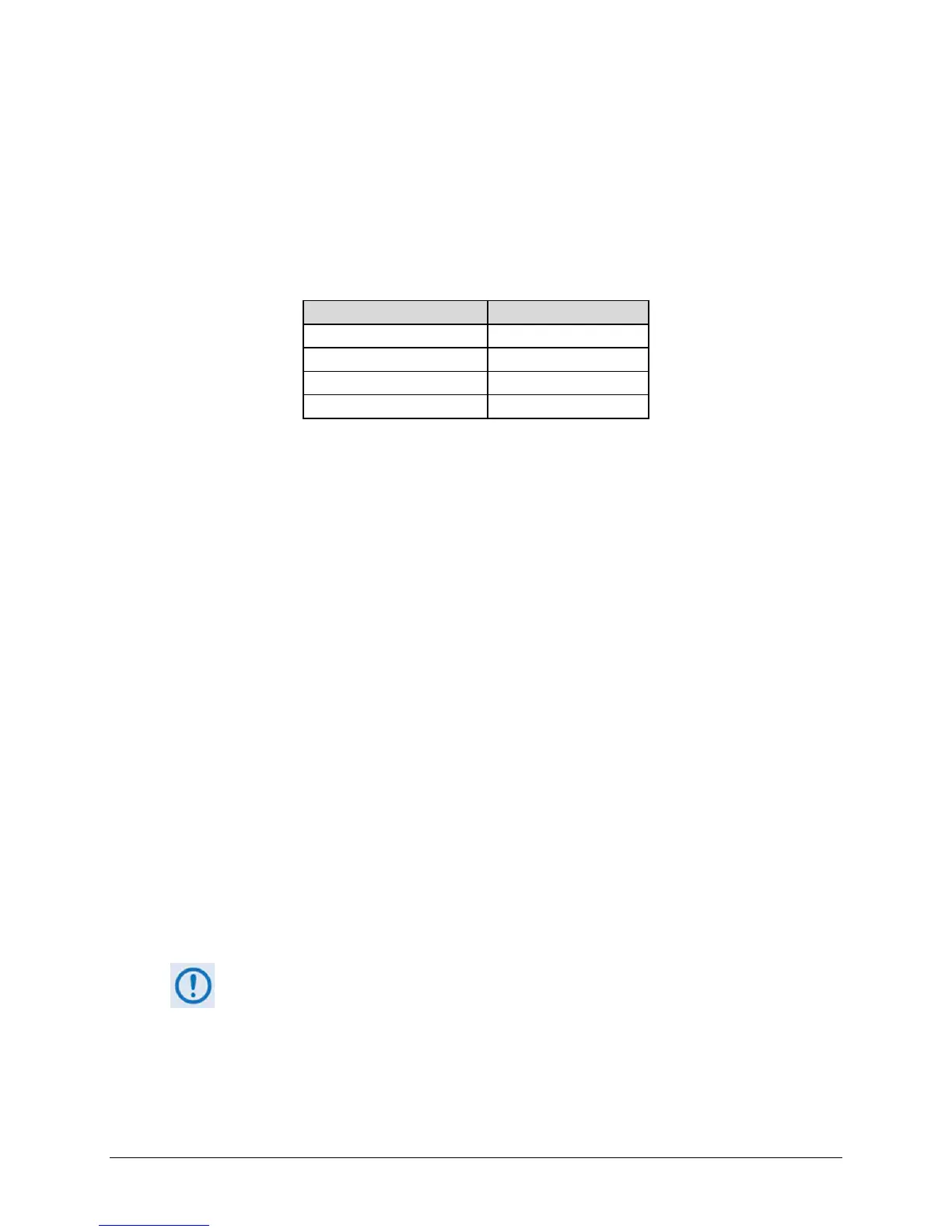
* Equal power and equal symbol rate for the interfering carrier and the desired carrier, i.e., 0 dB
CnC ratio. Measured at IF with AWGN, +7 dBc Adjacent Carriers, 1.3 spacing.
J.4.3 Carrier-in-Carrier Latency
DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier has no measurable impact on circuit latency.
J.4.4 Carrier-in-Carrier and Adaptive Coding and Modulation (ACM)
DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier is fully compatible with the Adaptive Coding and Modulation
(ACM) mode of operation in the CDM-760. CnC combined with ACM can provide 100 – 200%
increase in average throughput.
J.4.5 Carrier-in-Carrier Link Design
CnC link design involves finding the FEC and modulation combination that provides optimal
bandwidth utilization. Just like conventional link design, it is an iterative process that involves
trying different FEC and modulation combinations with CnC until an optimal combination is
found.
For optimal CnC performance, it is recommended that the two carriers have similar symbol rate
and power. This can be achieved by selecting appropriate ModCods, as shown in the appendix
sections that follow.
Normally, a CnC link results in saving bandwidth and power, so there are
satellite resources recovered that are deployable for additional links and more
throughput over the existing capacity. When sizing the link to transform existing
carriers into CnC links, also consider how the recovered capacity is best
deployed. In other words, evaluate the bandwidth and power (or power
equivalent bandwidth) tradeoffs with an eye to the future.

 Loading...
Loading...