CAUTION: Changing the administrative distance of BGP internal routes is considered
dangerous and is not recommended. One problem that can arise is the accumulation
of routing table inconsistencies, which can break routing.
You can use the distance bgp command to configure these preferences. The following
commands leave the internal distance at 200, set the external distance to 150, and set
the local distance to 80:
host1(config)#router bgp 100
host1(config-router)#network 172.28.0.0
host1(config-router)#neighbor 156.128.5.5 remote-as 310
host1(config-router)#neighbor 142.132.1.1 remote-as 50
host1(config-router)#distance bgp 150 200 80
distance bgp
• Use to set the administrative distance for all BGP routes.
• You must specify the following:
• external-distance—Administrative distance for routes external to the AS in the range
1–255. The default is 20.
• internal-distance—Administrative distance for routes internal to the AS in the range
1–255. The default is 200.
• local-distance—Administrative distance for local routes in the range 1–255. The
default is 200.
• The default value is 20 for external routes, 200 for internal route, and 200 for local
routes.
• The new distance is applied to all routes that are subsequently placed in the IP routing
table. To apply the new distance to routes that are already present in the IP routing
table, you must use the clear ip routes * command to reinstall BGP routes in the IP
routing table.
• Use the no version to return the distances to their default values, 20, 200, and 200.
• See distance bgp.
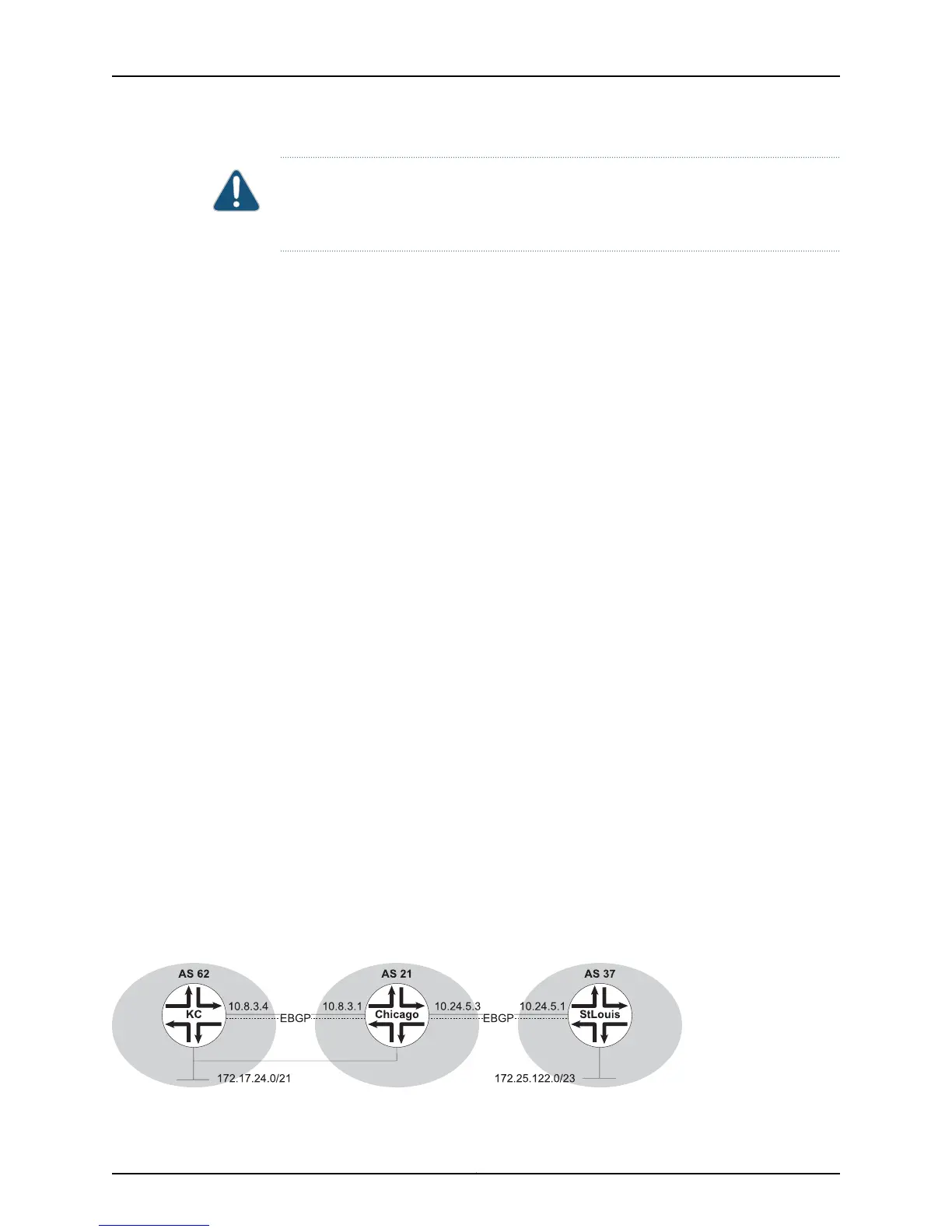
Example 1 Routes learned from other sources can be preferred to routes learned by means of BGP.
Consider the network structure shown in Figure 38 on page 135.
Figure 38: Administrative Distances
135Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 1: Configuring BGP Routing

 Loading...
Loading...