• An import list defines a route-target extended community; only routes that have at
least one matching route target in their associated export list can be installed into the
VRF’s forwarding table.
• If the import and export lists are identical, use the both keyword to define both lists
simultaneously.
• You can add only one route target to a list at a time.
• Example
host1:vr1(config-vrf)#route-target export 100:1
host1:vr1(config-vrf)#route-target import 100:1
• Use the no version to remove a route target from the import list, the export list, or both
lists.
• See route-target.
Example: Fully Meshed
VPNs
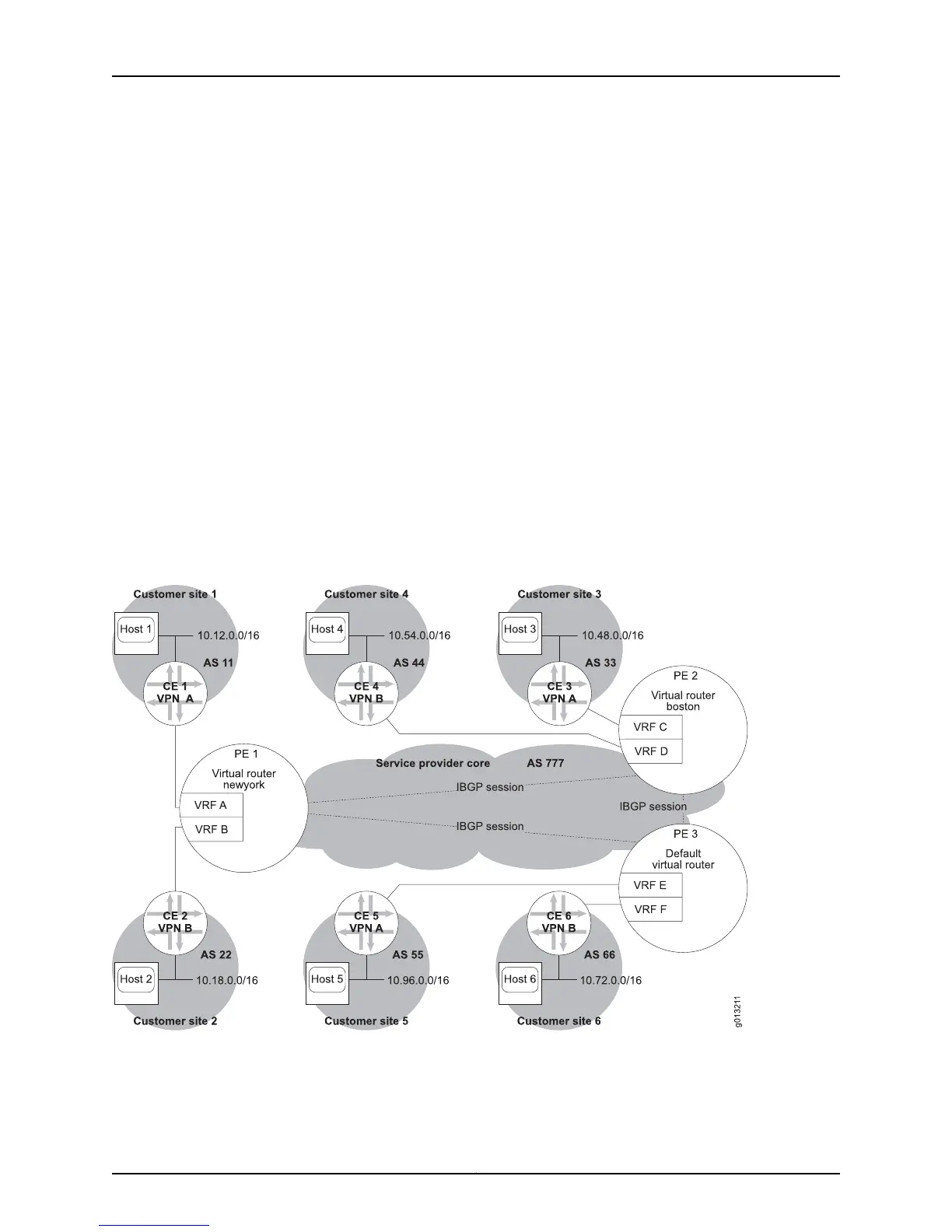
In a fully meshed VPN, each site in the VPN can reach every other site in the VPN. Figure
89 on page 426 illustrates a situation with two fully meshed VPNs, VPN A and VPN B. VPN
A includes Customer Sites 1, 3, and 5 through VRFs A, C, and E. VPN B includes Customer
Sites 2, 4, and 6 through VRFs B, D, and F.
Figure 89: Fully Meshed VPNs
BGP sessions exist between PE 1 and PE 2, PE 2 and PE 3, and PE 3 and PE 1. The MPLS
paths through the service provider core are omitted for clarity.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.426
JunosE 11.2.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...