host1(config-if)#mpls rsvp authentication
To clear the security association on a receiving peer for the specified sending peer:
•
Issue the clear mpls rsvp authentication command:
host1#clear mpls rsvp authentication 10.3.5.1
Related Topics Basic MPLS Configuration Tasks on page 276•
• Additional RSVP-TE Configuration Tasks on page 293
• clear rsvp authentication
• mpls rsvp authentication
• mpls rsvp authentication key
Configuring RSVP-TE Fast Rerouting with RSVP-TE Bypass Tunnels
The fast reroute extensions to RSVP-TE enable you to create a single LSP, known as a
bypass tunnel, to back up a set of LSPs by bypassing specific links in the LSP. In the event
of a failure in any link of the protected RSVP-TE LSP (the primary LSP), MPLS redirects
traffic to the associated bypass tunnel in tens of milliseconds.
You must statically configure the bypass tunnel for each link that you want to protect
on each router in the LSP. The bypass tunnel must intersect the protected LSP at two
locations. The start of the bypass tunnels is the point of local repair (PLR), which is the
head end of the protected link. The bypass tunnel terminates downstream of the PLR
on the node that represents the end of the bypassed link on the primary LSP.
Each bypass tunnel provides 1:N local protection; that is, each bypass tunnel can protect
one or more links depending on where you have configured it. The protected primary
LSPs are stacked over the bypass tunnel to redirect their traffic around the failure.
The bypass tunnel naturally protects all LSPs that share the bypassed link (the LSP
segment from the PLR to the downstream node) and that have requested protection.
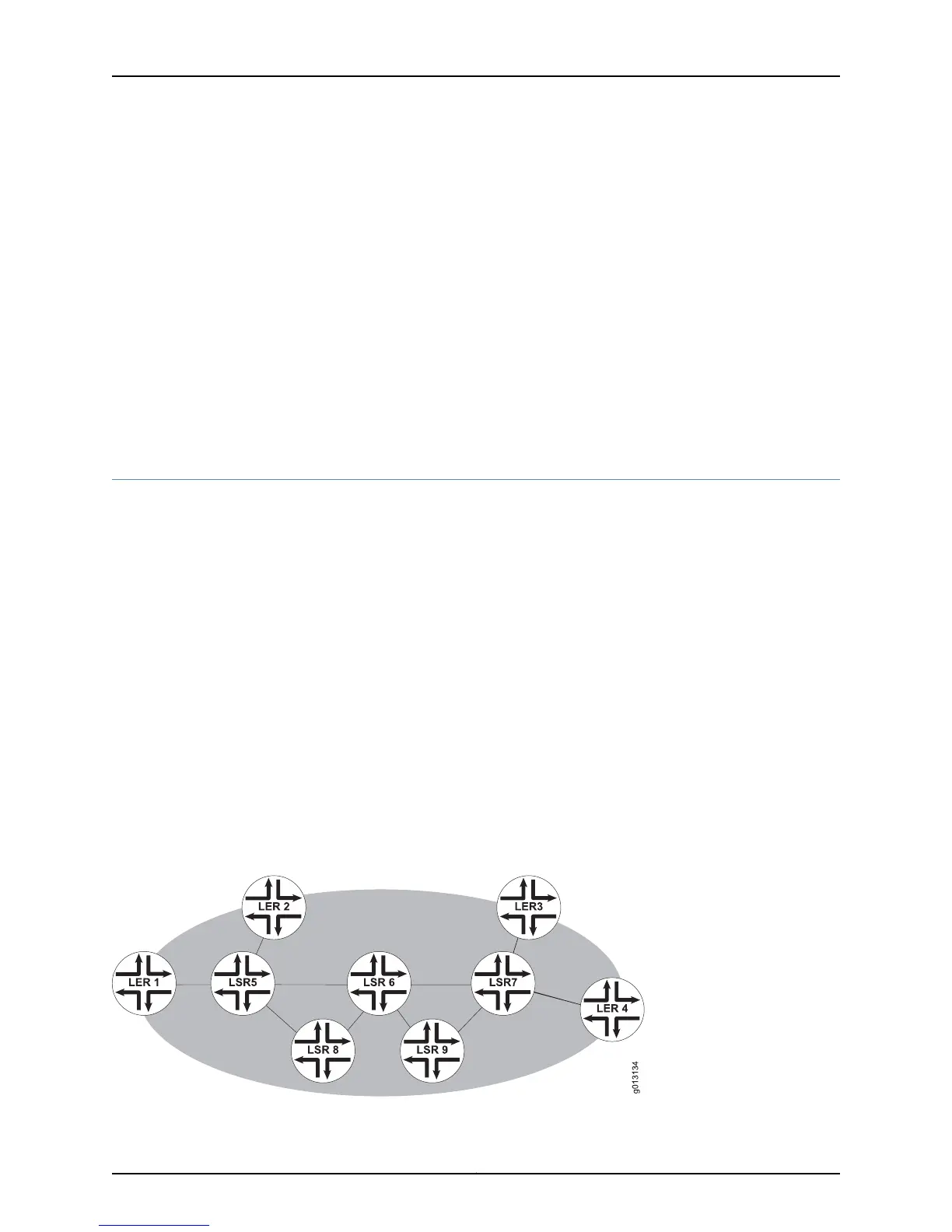
Consider the network shown in Figure 63 on page 295.
Figure 63: Bypass Tunnel
295Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 4: Configuring MPLS

 Loading...
Loading...