Configuring Route Reflectors
Router reflection is an alternative to confederations as a strategy to reduce IBGP meshing.
BGP specifies that a BGP speaker cannot advertise routes to an IBGP neighbor if the
speaker learned the route from a different IBGP neighbor. A route reflector is a BGP
speaker that advertises routes learned from each of its IBGP neighbors to its other IBGP
neighbors; routes are reflected among IBGP routers that are not meshed. The route
reflector’s neighbors are called route reflector clients. The clients are neighbors only to
the route reflector, not to each other. Each route reflector client depends on the route
reflector to advertise its routes within the AS; each client also depends on the route
reflector to pass routes to the client.
A route reflector and its clients are collectively referred to as a cluster. Clients peer only
with a route reflector and do not peer outside their cluster. Route reflectors peer with
clients and other route reflectors within the cluster; outside the cluster they peer with
other reflectors and other routers that are neither clients nor reflectors. Route reflectors
and nonclient routers must be fully meshed.
Clients and nonclients have no knowledge of route reflection; they operate as standard
BGP peers and require no configuration. You simply configure the route reflectors.
Route reflectors advertise routes learned from:
•
A nonclient peer only to clients
•
A client peer to all nonclient peers and to all client peers except for the originator of
the route
•
An EBGP peer to all nonclient peers and all client peers
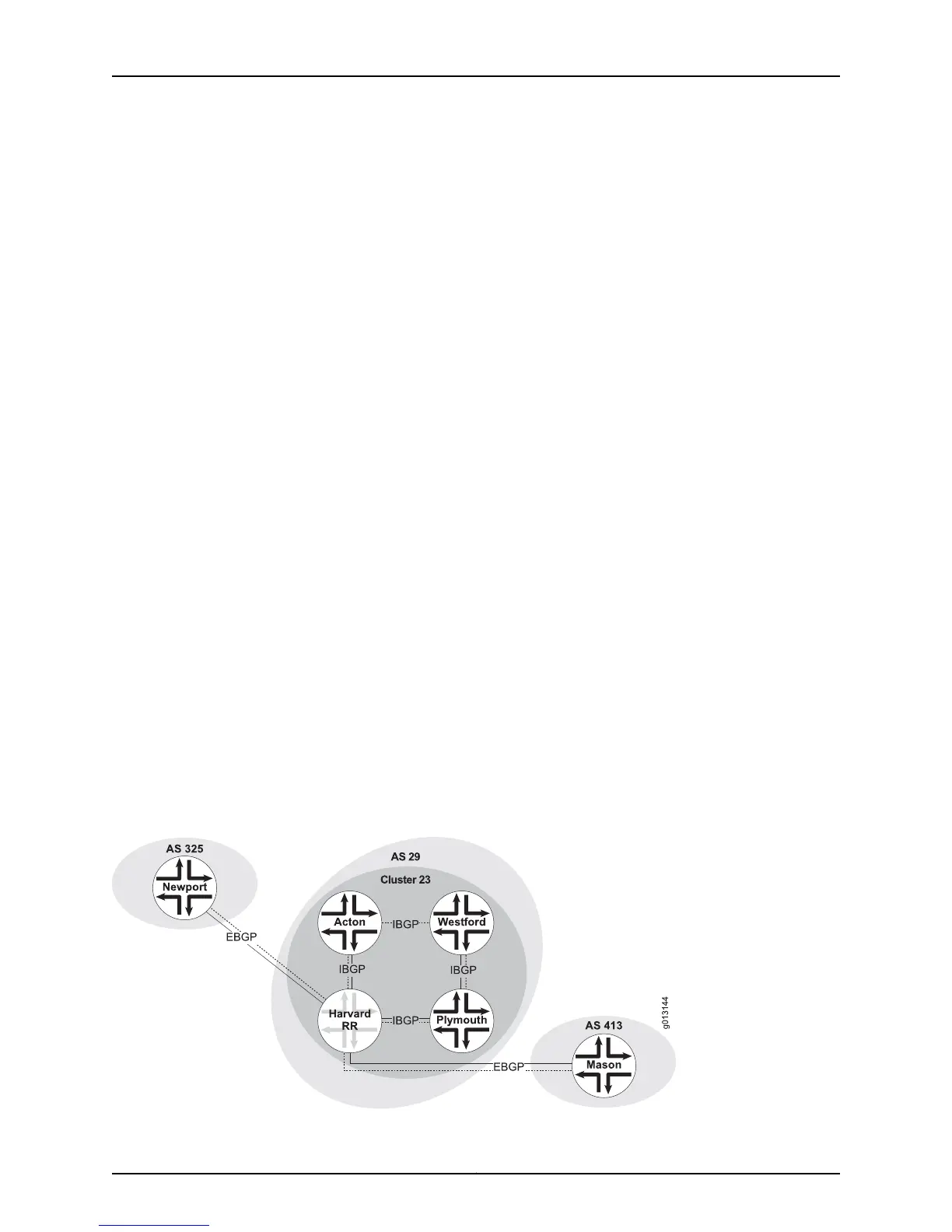
Figure 43 on page 145 illustrates a simple route reflection setup. Configured as a route
reflector, Router Harvard reflects routes among its clients within Cluster 23: Routers
Plymouth, Westford, and Acton. These route reflector clients see router Harvard and
each other simply as IBGP neighbors. Router Newport in AS 325 and router Mason in AS
413 see router Harvard simply as an EBGP neighbor in AS 29.
Figure 43: Simple Route Reflection
145Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 1: Configuring BGP Routing

 Loading...
Loading...